Abstract
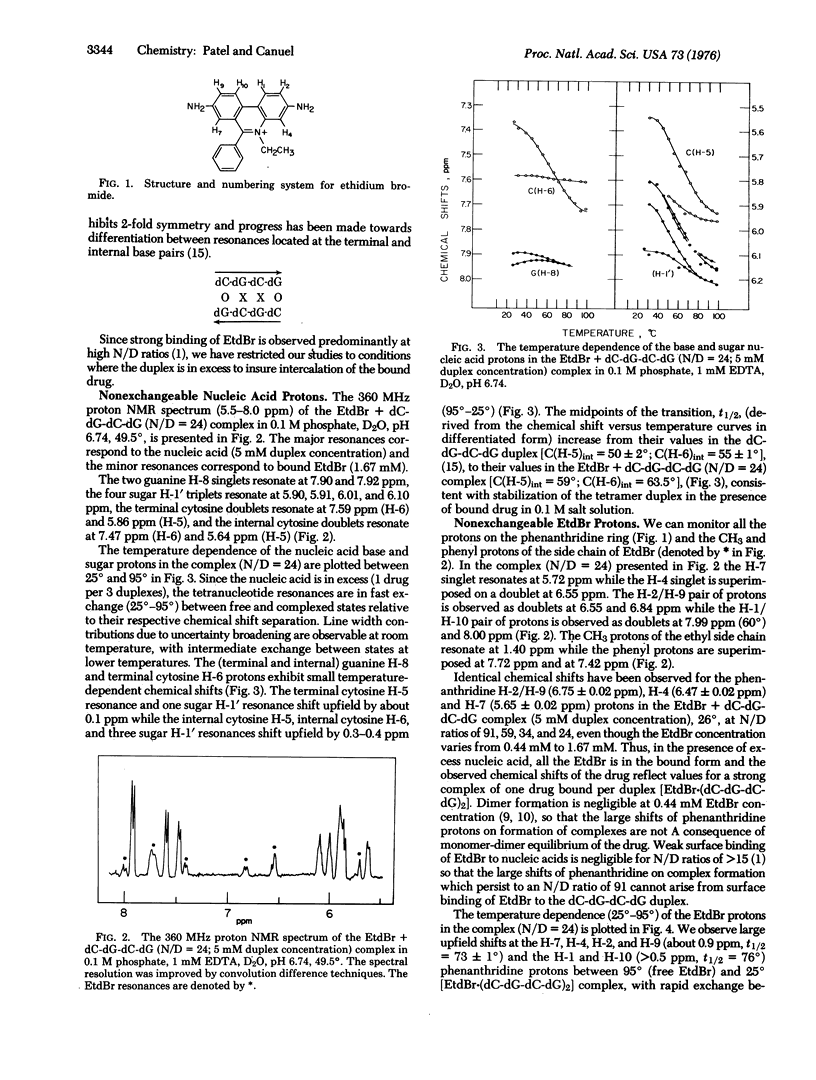
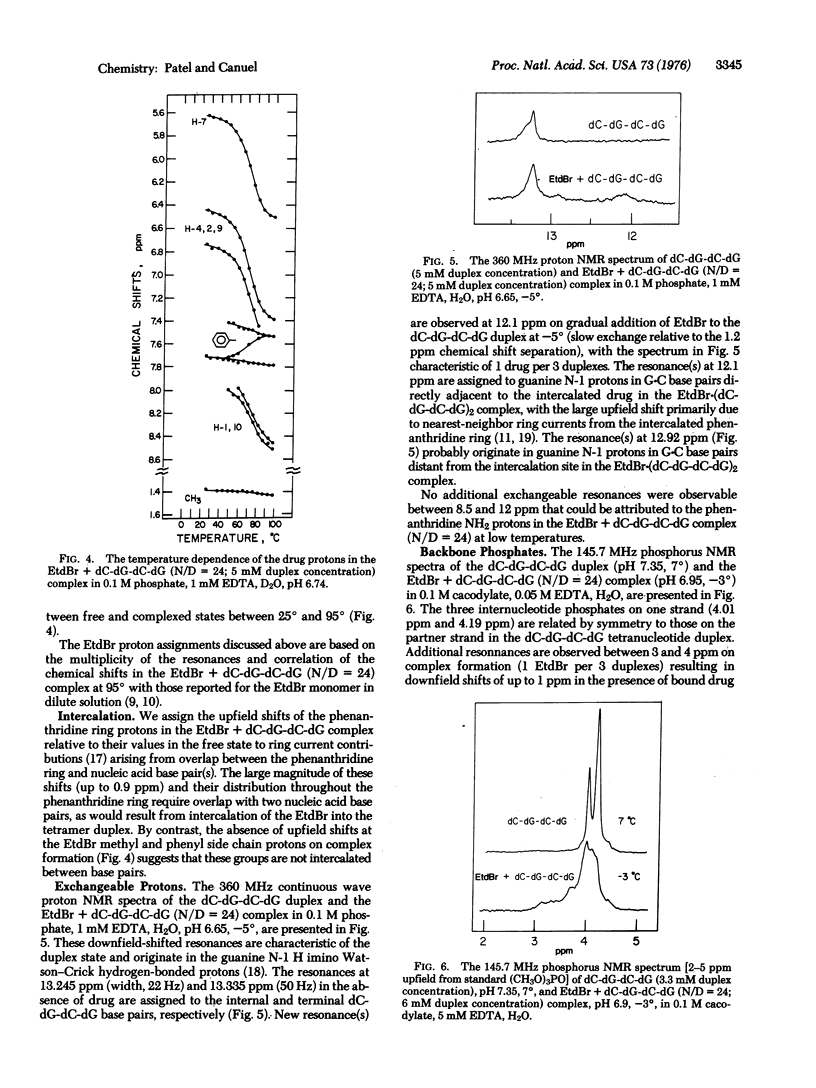
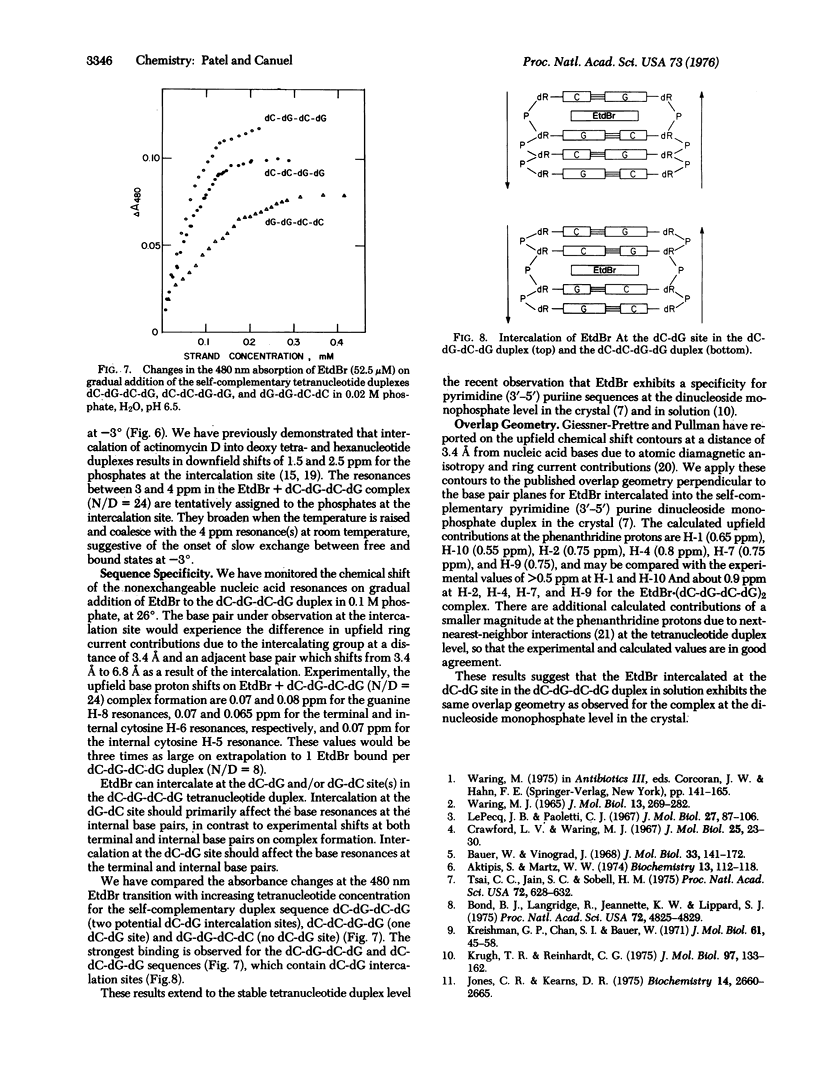
The binding of ethidium bromide (EtdBr) to the dC-dG-dC-dG self-complementary duplex has been monitored at the resolvable drug and nucleic acid protons and backbone phosphates at high nucleotide/drug (N/D) ratios by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy in aqueous solution. We observe averaged resonances (25 degrees-95 degrees) for the nucleic acid and drug nonexchangeable protons in the presence of excess tetranucleotide (N/D = 24), indicative of rapid exchange relative to the chemical shifts in the free and complexed states. Complex formation results in upfield shifts for the base protons at the terminal and internal base pairs and an increase in the transition midpoint for the duplex-to-strand conversion. We observe upfield chemical shift changes of 1.2 ppm at the Watson-Crick guanine N-1 proton(s) on complex formation (N/D = 24), with slow exchange between (dC-dG-dC-dG)2 and EtdBr-(dC-dG-dC-dG)2 relative to this chemical shift difference at-5 degrees. The EtdBr phenanthridine ring protons shift upfield by about 0.9 ppm (H-2, H-4, H-7, H-9) and greater than 0.5 ppm (H-1, H-10) on complex formation, with the chemical shifts versus temperature plots (25 degrees-95 degrees) monitoring the dissociation of the EtdBr-(dC-dG-dC-dG)2 structure. These upfield shifts at the exchangeable and nonexchangeable base protons and phenanthridine ring (but not side chain) protons demonstrate intercalation of the phenanthridine ring of EtdBr into the dC-dG-dC-dG duplex in solution. The intercalation model may be supported by the observation of downfield shifts (up to 1ppm) at the internucleotide phosphate(s) of the tetranucleotide duplex on addition of EtdBr at low temperatures. We observe stronger binding of EtdBr to the self-complementary dC-dG-dC-dG (2 dC-dG intercalation sites) and dC-dC-dG-dG (1 dC-dG site) duplexes compared to the dG-dG-dC-dC (no dC-dG sites) as monitored by UV absorbance changes at 480 nm. These studies extend to the tetranucleotide duplex level earlier observations that EtdBr exhibits a selectivity for formation of complexes to dinucleoside monophosphates with a pyrimidine (3'-5') purine sequence in the crystal and in solution. The experimental proton NMR upfield shifts at the phenanthridine protons on formation of the EtdBr-(dC-dG-dC-dG)2 complex compare favorably with calculated values (atomic diamagnetic anisotropy and ring current contributions) based on the overlap geometry for EtdBr intercalated into the pyrimidine (3'-5') purine dinucleoside monophosphate duplex in the crystal.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aktipis S., Martz W. W. Circular dichroism and temperature--optical density studies on the conformation of polynucleotide--ethidium bromide complexes. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 1;13(1):112–118. doi: 10.1021/bi00698a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arter D. B., Walker G. C., Uhlenbeck O. C., Schmidt P. G. PMR or the self-complementary oligoribonucleotide CpCpGpG. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1089–1094. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80395-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer W., Vinograd J. The interaction of closed circular DNA with intercalative dyes. I. The superhelix density of SV40 DNA in the presence and absence of dye. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):141–171. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond P. J., Langridge R., Jennette K. W., Lippard S. J. X-ray fiber diffraction evidence for neighbor exclusion binding of a platinum metallointercalation reagent to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4825–4829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresloff J. L., Crothers D. M. DNA-ethidium reaction kinetics: demonstration of direct ligand transfer between DNA binding sites. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jun 15;95(1):103–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90339-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Waring M. J. Supercoiling of polyoma virus DNA measured by its interaction with ethidium bromide. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90276-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giessner-Prettre C., Pullman B. Intermolecular nuclear shielding values for protons of purines and flavins. J Theor Biol. 1970 Apr;27(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(70)90130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giessner-Prettre C., Pullman B. On the atomic or "local" contributions to proton chemical shifts due to the anisotropy of the diamagnetic susceptibility of the nucleic acid base. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 17;70(2):578–581. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. R., Kearns D. R. Identification of a unique ethidium bromide binding site on yeast tRNAPhe by high resolution (300 MHz) nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 17;14(12):2660–2665. doi: 10.1021/bi00683a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearns D. R., Patel D. J., Shulman R. G. High resolution nuclear magnetic resonance studies of hydrogen bonded protons of tRNA in water. Nature. 1971 Jan 29;229(5283):338–339. doi: 10.1038/229338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreishman G. P., Chan S. I., Bauer W. Proton magnetic resonance study of the interaction of ethidium bromide with several uracil residues, uridylyl (3' leads to 5') uridine and polyuridylic acid. J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 14;61(1):45–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroon P. A., Kreishman G. P., Nelson J. H., Chan S. I. The effects of chain length on the secondary structure of oligoadenylates. Biopolymers. 1974 Dec;13(12):2571–2592. doi: 10.1002/bip.1974.360131214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krugh T. R., Reinhardt C. G. Evidence for sequence preferences in the intercalative binding of ethidium bromide to dinucleoside monophosphates. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 15;97(2):133–162. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LePecq J. B., Paoletti C. A fluorescent complex between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. Physical-chemical characterization. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):87–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90353-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J. Peptide antibiotic-dinucleotide interactions. Nuclear magnetic resonance investigations of complex formation between actinomycin D and d-pGpC in aqueous solution. Biochemistry. 1974 May 21;13(11):2388–2395. doi: 10.1021/bi00708a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J. Proton and phosphorus NMR studies of d-CpG(pCpG)n duplexes in solution. Helix-coil transition and complex formation with actinomycin-D. Biopolymers. 1976 Mar;15(3):533–558. doi: 10.1002/bip.1976.360150310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. C., Jain S. C., Sobell H. M. X-ray crystallographic visualization of drug-nucleic acid intercalative binding: structure of an ethidium-dinucleoside monophosphate crystalline complex, Ethidium: 5-iodouridylyl (3'-5') adenosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):628–632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. J. Complex formation between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1965 Aug;13(1):269–282. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


