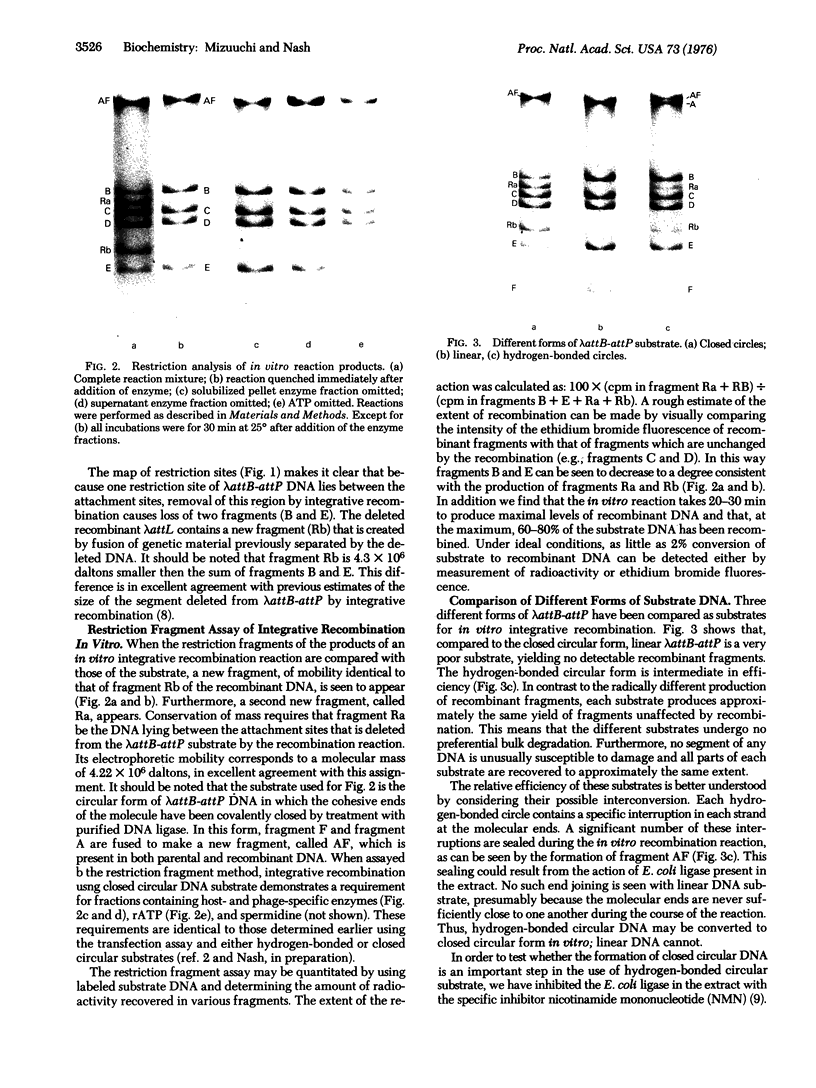
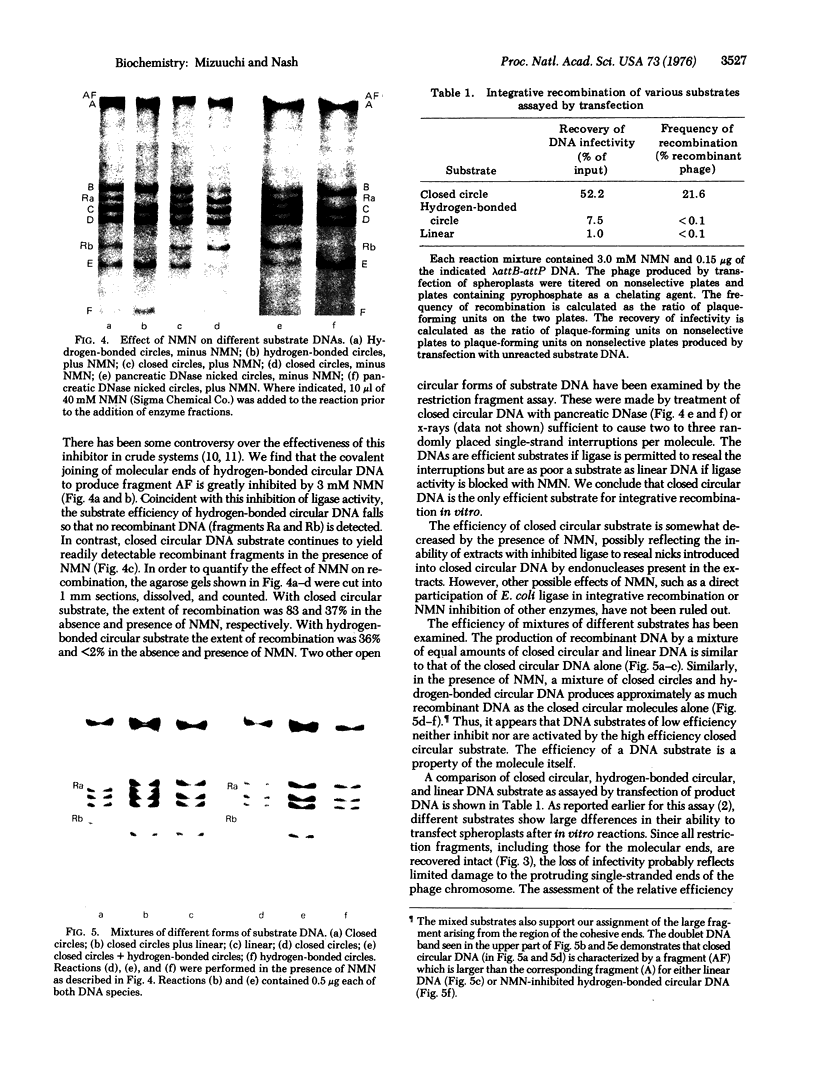
Abstract
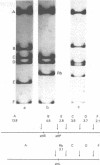
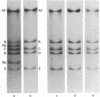
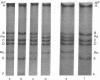
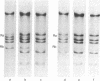
A novel assay has been developed for in vitro genetic recombination of DNA. Substrate and product DNAs are cleaved with a restriction endonuclease and the resulting fragments are separated by electrophoresis in agarose gels. The substrate DNA has been chosen so that the recombination to be studied deletes a segment of DNA. The remaining DNA gives rise to a unique restriciton fragment, as does the DNA segment that has been removed. The method provides a convenient and physical, rather than genetic, assessment of the conversion of parental to recombinant DNA. This method has been applied to an in vitro system that carries out integrative recombination of bacteriophage lambda. We find that, different molecular forms of DNA tested, closed circular DNA is the only efficient substrate. Linear DNA and three kinds of circular DNA containing interruptions are at best very poor substrates. The implications of this surprising result are discussed. In addition, we show that the in vitro recombination system completes the breaking and rejoining steps of recombination. No stable DNA intermediates involving chiasmata or broken end structures are found.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker A., Gold M. Isolation of the bacteriophage lambda A-gene protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):581–585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drahovský D., Morris N. R. Mechanism of action of rat liver DNA methylase. I. Interaction with double-stranded methyl-acceptor DNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 14;57(3):475–489. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L., Tiemeier D., Leder P., Weisberg R., Sternberg N. Safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambdagt-lambdaC for use in cloning of recombinant DNA molecules. Nature. 1976 Feb 19;259(5544):596–598. doi: 10.1038/259596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloman W. K., Wiegand R., Hoessli C., Radding C. M. Uptake of homologous single-stranded fragments by superhelical DNA: a possible mechanism for initiation of genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2394–2398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson B., Upholt W. B., Devinny J., Vinograd J. The use of an ethidium analogue in the dye-buoyant density procedure for the isolation of closed circular DNA: the variation of the superhelix density of mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):813–820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Zimmerman S. B., Oshinsky C. K., Gellert M. Enzymatic joining of DNA strands, II. An enzyme-adenylate intermediate in the dpn-dependent DNA ligase reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):2004–2011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. K., Fried M. Construction of infectious polyoma hybrid genomes in vitro. Nature. 1976 Feb 19;259(5544):598–601. doi: 10.1038/259598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Murray K. Manipulation of restriction targets in phage lambda to form receptor chromosomes for DNA fragments. Nature. 1974 Oct 11;251(5475):476–481. doi: 10.1038/251476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Integrative recombination in bacteriophage lambda: analysis of recombinant DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 5;91(4):501–514. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90276-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Integrative recombination of bacteriophage lambda DNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1072–1076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. LambdaattB-attP, a lambda derivative containing both sites involved in integrative recombination. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakakibara Y., Tomizawa J. I. Termination point of replication of colicin E1 plasmid DNA in cell extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4935–4939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Williams J., Sharp P. A., Grodzicker T. Physical mapping of temperature-sensitive mutations of adenoviruses. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 25;97(3):369–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M. J. Model for wandering restriction enzymes. Nature. 1974 Nov 1;252(5478):76–78. doi: 10.1038/252076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syvanen M. In vitro genetic recombination of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2496–2499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., Davis R. W. Studies on the cleavage of bacteriophage lambda DNA with EcoRI Restriction endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 25;91(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Interactions between twisted DNAs and enzymes: the effects of superhelical turns. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 25;87(4):797–816. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90085-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]