Abstract
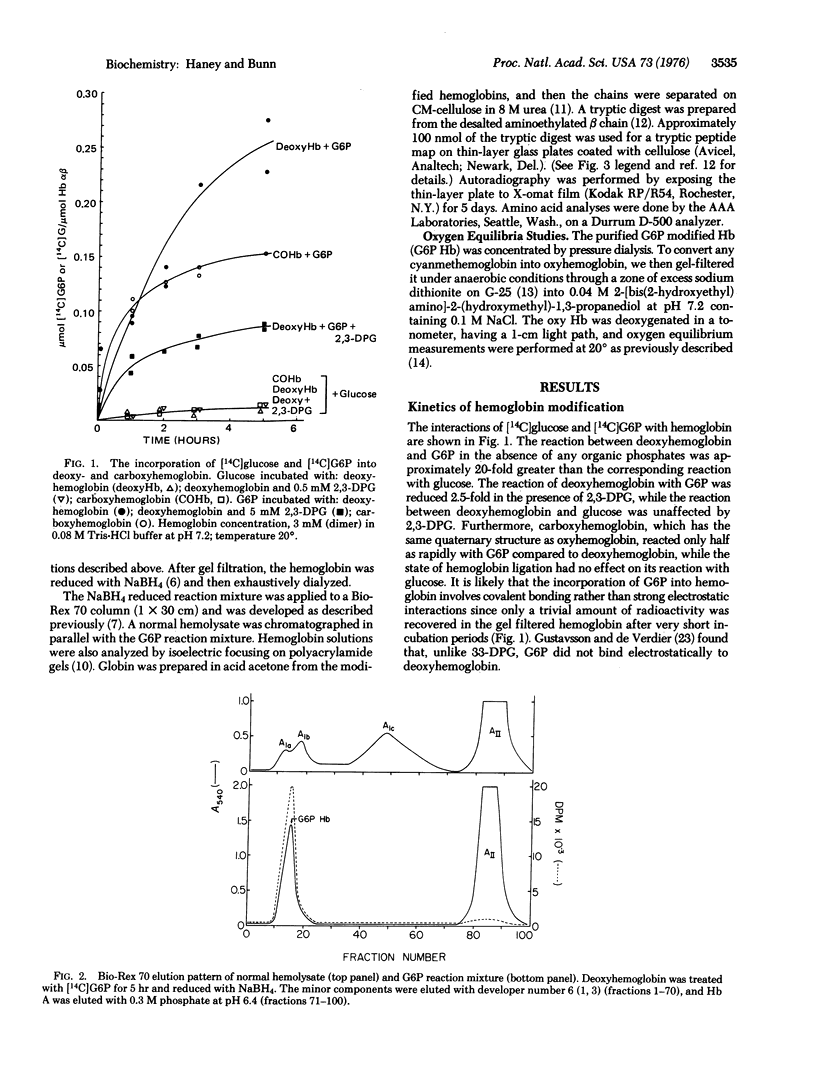
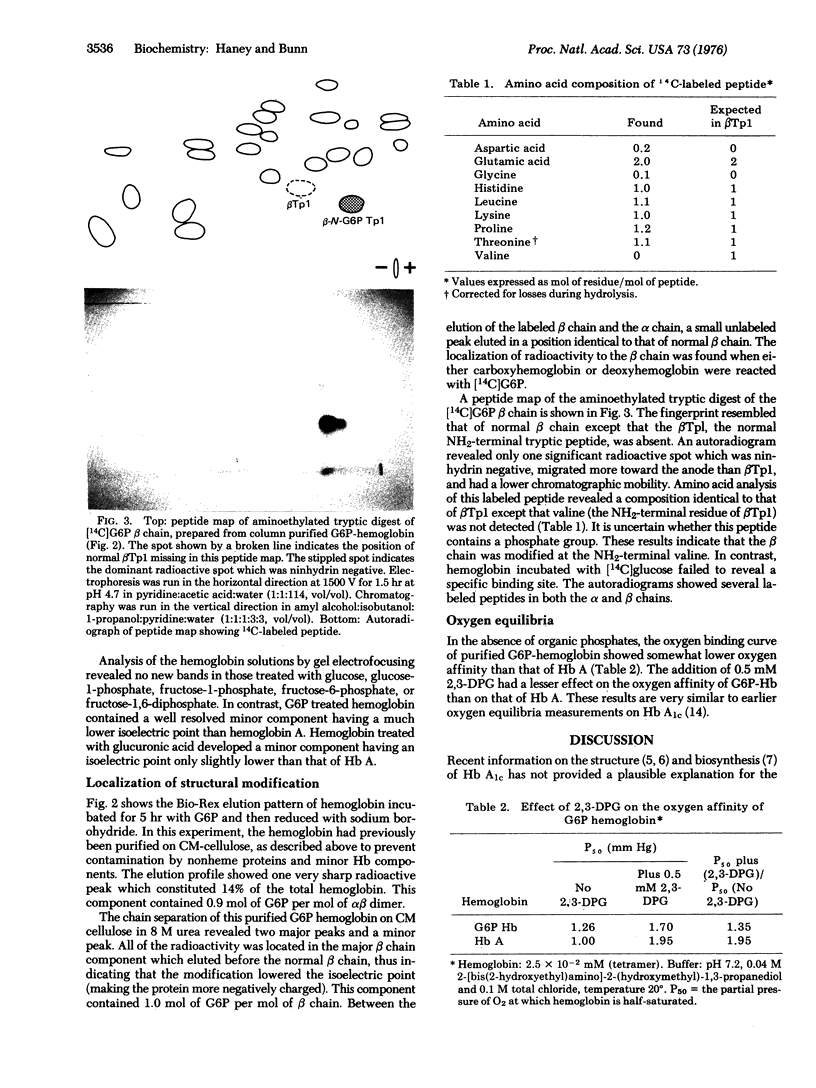
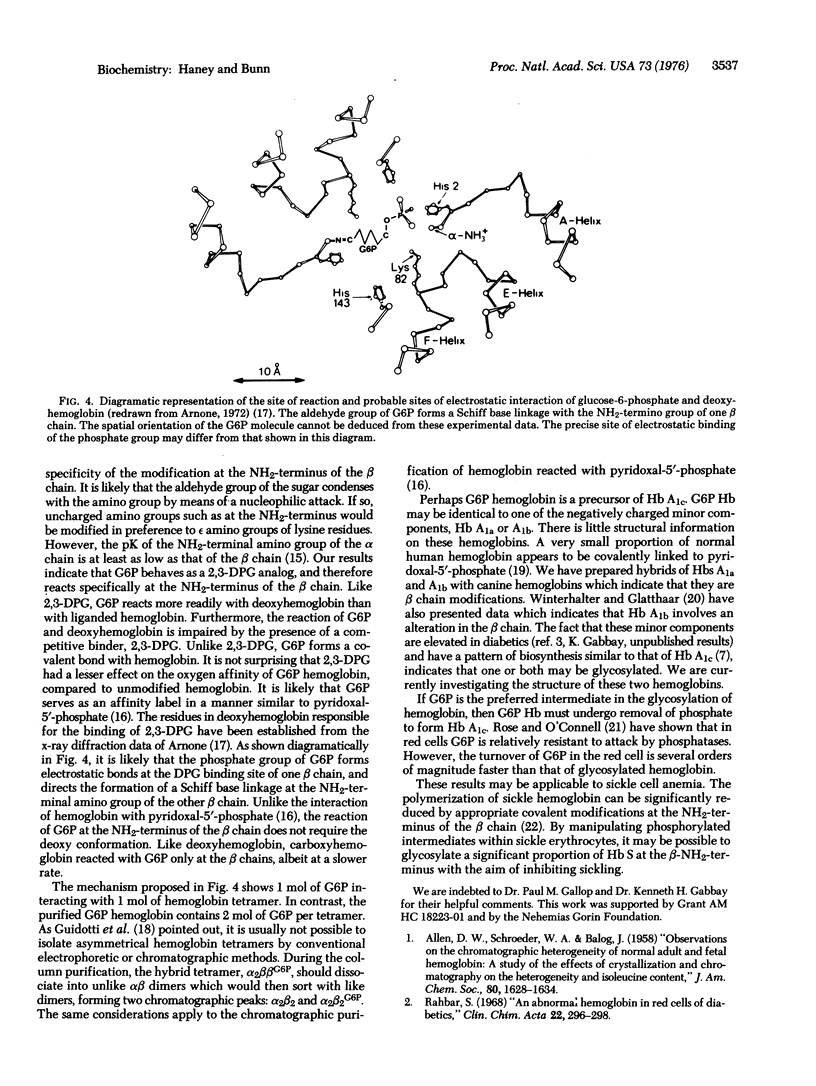
To determine the mechanism for the formation of hemoglobin A1c (Hb A1c) in vivo, we incubated human hemoglobin with glucose and metabolites of glucose. [14C]Glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) reacted readily with deoxyhemoglobin, and formed a covalent linkage. The reaction rate was considerably reduced in the presence of carbon monoxide or 2,3-diphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG). Purified G6P hemoglobin had a lowered oxygen affinity and decreased reactivity with 2,3-DPG compared to Hb A. G6P behaved as a 2,3-DPG analog and reacted specifically at the NH2-terminal amino group of the beta chain. In contrast, the interaction of hemoglobin with glucose was much slower, and was unaffected by carbon monoxide or 2,3-DPG. Neither glucose-1-phosphate, fructose-6-phosphate, nor fructose-1,6-diphosphate formed a reaction product with hemoglobin. G6P behaves as an affinity label with the phosphate group forming electrostatic bonds at the 2,3-DPG binding site and the aldehvde group reacting with the NH2-terminal amino group of the beta chain. Thus, G6P hemoglobin may be an intermediate in the conversion of Hb A to Hb A1c.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnone A. X-ray diffraction study of binding of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate to human deoxyhaemoglobin. Nature. 1972 May 19;237(5351):146–149. doi: 10.1038/237146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benesch R. E., Benesch R., Renthal R. D., Maeda N. Affinity labeling of the polyphosphate binding site of hemoglobin. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 12;11(19):3576–3582. doi: 10.1021/bi00769a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookchin R. M., Gallop P. M. Structure of hemoglobin AIc: nature of the N-terminal beta chain blocking group. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jul 11;32(1):86–93. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn H. F., Briehl R. W. The interaction of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate with various human hemoglobins. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jun;49(6):1088–1095. doi: 10.1172/JCI106324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn H. F., Haney D. N., Gabbay K. H., Gallop P. M. Further identification of the nature and linkage of the carbohydrate in hemoglobin A1c. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90289-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn H. F., Haney D. N., Kamin S., Gabbay K. H., Gallop P. M. The biosynthesis of human hemoglobin A1c. Slow glycosylation of hemoglobin in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jun;57(6):1652–1659. doi: 10.1172/JCI108436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. B., Naughton M. A., Weatherball D. J. Abnormal human haemoglobins. Separation and characterization of the alpha and beta chains by chromatography, and the determination of two new variants, hb Chesapeak and hb J (Bangkok). J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(1):91–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon H. B., McIntosh R. Reduction of methaemoglobin in haemoglobin samples using gel filtration for continuous removal of reaction products. Nature. 1967 Jan 28;213(5074):399–400. doi: 10.1038/213399a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drysdale J. W., Righetti P., Bunn H. F. The separation of human and animal hemoglobins by isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 19;229(1):42–50. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90315-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUIDOTTI G., KONIGSBERG W., CRAIG L. C. ON THE DISSOCIATION OF NORMAL ADULT HUMAN HEMOGLOBIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Oct;50:774–782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.4.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. H., Bogardt R. A., Jr, Gurd F. R. Determination of the pK values for the alpha-amino groups of human hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4398–4404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustavsson T., de Verdier C. H. Binding of some phosphorylated intermediates to oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin A. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1973;30(1):25–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUISMAN T. H., MEYERING C. A. Studies on the heterogeneity of hemoglobin. I. The heterogeneity of different human hemoglobin types in carboxymethylcellulose and in amberlite IRC-50 chromatography qualitative aspects. Clin Chim Acta. 1960 Jan;5:103–123. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(60)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist W. R., Schroeder W. A. A new N-terminal blocking group involving a Schiff base in hemoglobin AIc. Biochemistry. 1966 Aug;5(8):2489–2503. doi: 10.1021/bi00872a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen M., Oski F. A., Nathan D. G., Bunn H. F. Hemoglobin Syracuse (alpha2beta2-143(H21)His leads to Pro), a new high-affinity variant detected by special electrophoretic methods. Observations on the auto-oxidation of normal and variant hemoglobins. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):469–477. doi: 10.1172/JCI107953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigen A. M., Njikam N., Lee C. K., Manning J. M. Studies on the mechanism of action of cyanate in sickle cell disease. Oxygen affinity and gelling properties of hemoglobin S carbamylated on specific chains. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 25;249(20):6611–6616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSE I. A., O'CONNELL E. L. THE ROLE OF GLUCOSE 6-PHOSPHATE IN THE REGULATION OF GLUCOSE METABOLISM IN HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:12–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava S. K., Van Loon C., Beutler E. Characterization of a previously unidentified hemoglobin fraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Oct 31;278(3):617–621. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trivelli L. A., Ranney H. M., Lai H. T. Hemoglobin components in patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1971 Feb 18;284(7):353–357. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197102182840703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterhalter K. H., Glatthaar B. Intermediates of hemoglobin and their relation to biosynthesis. Ser Haematol. 1971;4(3):84–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



