Abstract
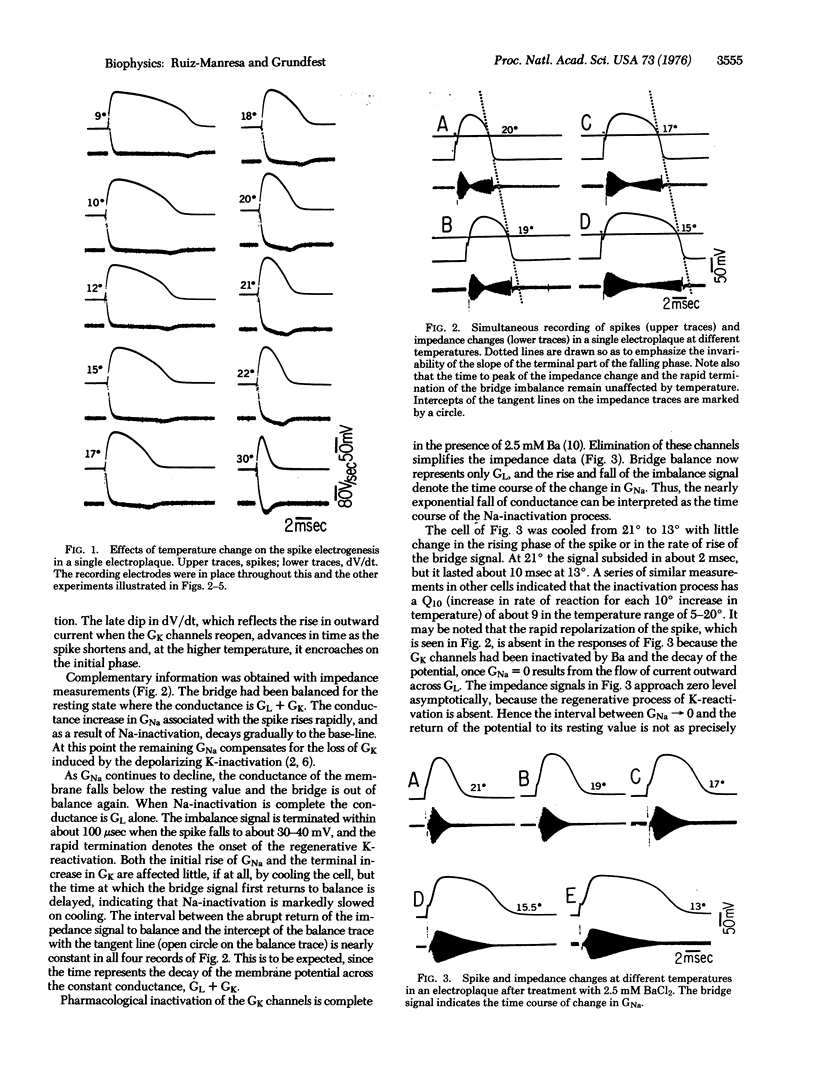
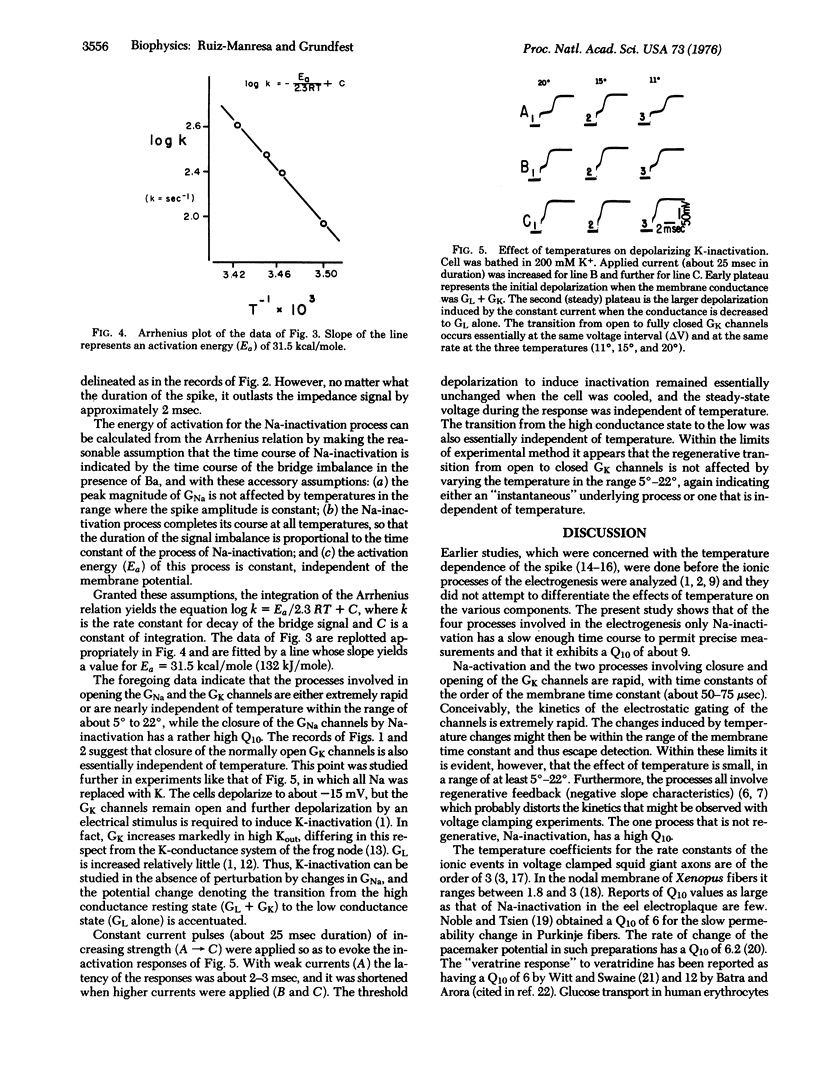
Spike electrogenesis of eel electroplaques involves four ionic processes which are controlled by the membrane potential. A threshold depolarization causes normally closed Na permselective channels to open (Na-activation) and normally open K channels to close (K-inactivation). The Na channels then close (Na-inactivation), and as the spike is terminated, the K channels reopen (K-reactivation). The temperature dependence of these four processes has been examined in the present work. Opening of the Na channels and closure and reopening of the K-channels are either effectively instantaneous or are relatively independent of temperature in the range of at least 5 degrees to 22 degrees. Closure of the Na-channels has a Q10 (increase in rate of reaction for each 10 degrees increase in temperature) of about 9, and activation energy (Ea) of this reaction is about 31.5 kcal/mole (132 kJ/mole).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CORABOEUF E., WEIDMANN S. Temperature effects on the electrical activity of Purkinje fibres. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1954;12(1):32–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., MOORE L. E. THE EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON THE SODIUM AND POTASSIUM PERMEABILITY CHANGES IN MYELINATED NERVE FIBRES OF XENOPUS LAEVIS. J Physiol. 1963 Nov;169:431–437. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDFEST H. Ionic mechanisms in electrogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1961 Sep 6;94:405–457. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1961.tb35554.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDFEST H. The mechanisms of discharge of the electric organs in relation to general and comparative electrophysiology. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1957;7:1–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman L. Quantitative description of the sodium conductance of the giant axon of Myxicola in terms of a generalized second-order variable. Biophys J. 1975 Feb;15(2 Pt 1):119–136. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(75)85796-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F. Ion movements during nerve activity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Aug 28;81:221–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb49311.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., MARTINS-FERREIRA H. Membrane potentials in the electroplates of the electric eel. J Physiol. 1953 Feb 27;119(2-3):315–351. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morlock M. L., Benamy D. A., Grundfest H. Analysis of spike electrogenesis of Eel electroplaques with phase plane and impedance measurements. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Jul;52(1):22–45. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Nakajima S., Grundfest H. Analysis of Spike Electrogenesis and Depolarizing K Inactivation in Electroplaques of Electrophorus electricus, L. J Gen Physiol. 1965 Nov 1;49(2):321–349. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble D., Tsien R. W. The kinetics and rectifier properties of the slow potassium current in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(1):185–214. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Manresa F., Ruarte A. C., Schwartz T. L., Grundfest H. Potassium inactivation and impedance changes during spike electrogenesis in eel electroplaques. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jan;55(1):33–47. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOFFENIELS E. Electrical activity of isolated single electroplax of electric eel as affected by temperature. Science. 1958 May 9;127(3306):1117–1118. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3306.1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulbricht W. Effect of temperature on the slowly changing sodium permeability of veratrinized nodes of Ranvier. Pflugers Arch. 1969;311(1):73–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00588063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WITT P. N., SWAINE C. R. Studies on Veratrum alkaloids. XXV. Veratrine response and antiveratrinic action in frog sartorius muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1957 May;120(1):63–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


