Abstract
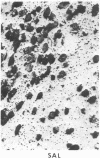
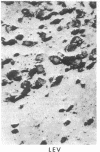
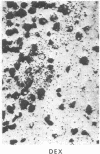
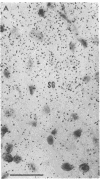
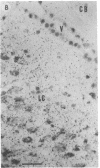
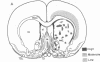
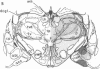
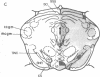
Opiate receptor sites in rat brain can be labeled in vivo by [3H]diprenorphine, a potent opiate antagoinst. Using techniques to minimize diffusion in fresh, frozen, unfixed brain, we have localized [3H]diprenorphine by autoradiography to visualize the distribution of opiate receptors. Silver grains indicative of the binding of labeled [3H]diprenorphine are discretely localized in numerous areas of the brain with very high densities in the locus coeruleus, the substantia gelatinosa of the spinal cord, and in clusters within the caudate-putamen, amygdala, and parts of the periventricular gray matter.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. H., Greenwald G. S. Autoradiographic analysis of estradiol uptake in the brain and pituitary of the female rat. Endocrinology. 1969 Dec;85(6):1160–1165. doi: 10.1210/endo-85-6-1160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach J. L., McEwen B. S. Rat brain binds adrenal steroid hormone: radioautography of hippocampus with corticosterone. Science. 1972 Mar 10;175(4026):1133–1136. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4026.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiller J. M., Pearson J., Simon E. J. Distribution of stereospecific binding of the potent narcotic analgesic etorphine in the human brain: predominance in the limbic system. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1973 Nov;6(3):1052–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquet Y. F., Lajtha A. Morphine action at central nervous system sites in rat: analgesia or hyperalgesia depending on site and dose. Science. 1973 Nov 2;182(4111):490–492. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4111.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitahata L. M., Kosaka Y., Taub A., Bonikos K., Hoffert M. Lamina-specific suppression of dorsal-horn unit activity by morphine sulfate. Anesthesiology. 1974 Jul;41(1):39–48. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197407000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korf J., Bunney B. S., Aghajanian G. K. Noradrenergic neurons: morphine inhibition of spontaneous activity. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Feb;25(2):165–169. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Regional distribution of opiate receptor binding in monkey and human brain. Nature. 1973 Oct 26;245(5426):447–450. doi: 10.1038/245447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., Yamamura H. I. Light autoradiographic localisation of cholinergic muscarinic receptors in rat brain by specific binding of a potent antagonist. Nature. 1975 Feb 13;253(5492):560–561. doi: 10.1038/253560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamotte C., Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor binding in primate spinal cord: distribution and changes after dorsal root section. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 13;112(2):407–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90296-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON A. A. Role of gelatinous substance of spinal cord in conduction of pain. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1952 Oct;68(4):515–529. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1952.02320220092011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palkovits M., Jacobowitz D. M. Topographic atlas of catecholamine and acetylcholinesterase-containing neurons in the rat brain. II. Hindbrain (mesencephalon, rhombencephalon). J Comp Neurol. 1974 Sep 1;157(1):29–42. doi: 10.1002/cne.901570104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert A., Yaksh T. Sites of morphine induced analgesia in the primate brain: relation to pain pathways. Brain Res. 1974 Nov 8;80(1):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90731-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Kuhar M. J., Snyder S. H. Autoradiograhic localization of the opiate receptor in rat brain. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1849–1853. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90289-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Identification of opiate receptor binding in intact animals. Life Sci. 1975 May 15;16(10):1623–1634. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor: demonstration in nervous tissue. Science. 1973 Mar 9;179(4077):1011–1014. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4077.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth L. J., Diab I. M., Watanabe M., Dinerstein R. J. A correlative radioautographic, fluorescent, and histochemical technique for cytopharmacology. Mol Pharmacol. 1974 Nov;10(6):986–998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Snyder S. H. Morphine-like peptides in mammalian brain: isolation, structure elucidation, and interactions with the opiate receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2515–2519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpf W. E., Roth L. J. High resolution autoradiography with dry mounted, freeze-dried frozen sections. Comparative study of six methods using two diffusible compounds 3H-estradiol and 3H-mesobilirubinogen. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Mar;14(3):274–287. doi: 10.1177/14.3.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terenius L., Wahlström A. Search for an endogenous ligand for the opiate receptor. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 May;94(1):74–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb05863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungerstedt U. Stereotaxic mapping of the monoamine pathways in the rat brain. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1971;367:1–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-201x.1971.tb10998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]