Abstract
We have compared the behavior of a prokaryotic mRNA in a eukaryotic ribosome binding system and of a eukaryotic mRNA in a prokaryotic ribosome binding system. Using 32P- and 125I-labeled bacteriophage f1 mRNA, we have shown that rabbit reticulocyte 80S ribosomes can protect specific sequences from pancreatic RNase digestion, including those sequences protected by Escherichia coli ribosomes. We have also found that E. coli ribosomes fail to protect any region of 125I-labeled globin mRNA. Iodination of the mRNA appeared to have little or no effect on the specificity of binding or protection by the ribosomes of either system.
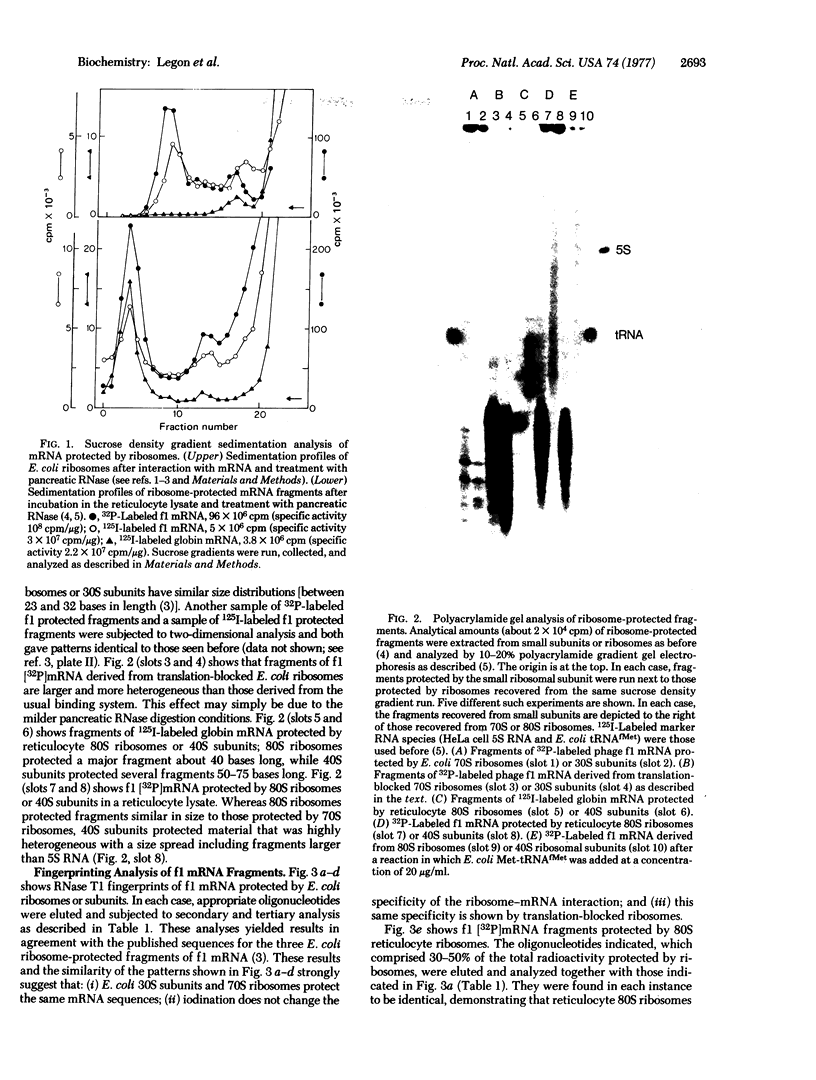
The eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems differ markedly in the ability of the small ribosomal subunits to protect mRNA from nuclease digestion. The regions of phage f1 mRNA protected by E. coli 30S subunits are virtually identical to those protected by the 70S ribosomes. By contrast, rabbit reticulocyte 40S subunits protect substantially larger fragments of mRNA from nuclease digestion than do the 80S ribosomes. These 40S-protected fragments are specific in the case of globin mRNA and overlap the shorter region protected by the 80S ribosomes. However, the 40S-protected fragments of phage f1 mRNA were found to be extremely heterogeneous, reflecting perhaps an important difference between the initial interactions made by these two mRNAs with the ribosomes.
Keywords: ribosome binding, protein synthesis, 125I-labeled mRNA
Full text
PDF


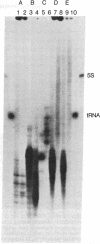
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. W., Atkins J. F., Dunn J. J. Bacteriophage T3 and T7 early RNAs are translated by eukaryotic 80S ribosomes: active phage T3 coded S-adenosylmethionine cleaving enzyme is synthesized. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2752–2756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Boime I., Loyd B., Leder P. Translation of bacteriophage Q messenger RNA in a murine Krebs 2 ascites tumor cell-free system. Science. 1972 Dec 22;178(4067):1293–1295. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4067.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan T. S., Model P., Zinder N. D. In vitro protein synthesis directed by separated transcripts of bacteriophage f1 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 15;99(3):369–382. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnbrough C., Legon S., Hunt T., Jackson R. J. Initiation of protein synthesis: evidence for messenger RNA-independent binding of methionyl-transfer RNA to the 40 S ribosomal subunit. J Mol Biol. 1973 May 25;76(3):379–403. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90511-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta R., Shih D. S., Saris C., Kaesberg P. Nucleotide sequence of a viral RNA fragment that binds to eukaryotic ribosomes. Nature. 1975 Aug 21;256(5519):624–628. doi: 10.1038/256624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edens L., Konings R. N., Schoenmakers J. G. Physical mapping of the central terminator for transcription on the bacteriophage M13 genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Oct;2(10):1811–1820. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.10.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin R. M. Purification and properties of the replicative intermediate of the RNA bacteriophage R17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1504–1511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett M. J., Rose J. K., Baltimore D. 5'-terminal structure of poliovirus polyribosomal RNA is pUp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):327–330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindley J., Staples D. H. Sequence of a ribosome binding site in bacteriophage Q-beta-RNA. Nature. 1969 Dec 6;224(5223):964–967. doi: 10.1038/224964a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo M., Eggerston G., Eisenstadt J., Lengyel P. Ribosome formation from subunits: dependence on formylmethionyl-transfer RNA in extracts from E. coli. Nature. 1968 Oct 26;220(5165):368–371. doi: 10.1038/220368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M., Shatkin A. J. Characterization of ribosome-protected fragments from reovirus messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4259–4266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legon S., Brayley A., Hunt T., Jackson R. J. The effect of cyclic AMP and related compounds on the control of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Feb 4;56(3):745–752. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90668-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legon S. Characterization of the ribosome-protected regions of 125I-labelled rabbit globin messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 5;106(1):37–53. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legon S., Robertson H. D. The binding of 125I-labelled rabbit globin messenger RNA to reticulocyte ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 5;106(1):23–36. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Secondary structure of bacteriophage f2 ribonucleic acid and the initiation of in vitro protein biosynthesis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 28;50(3):689–702. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazumder R. Effect of thiostrepton on recycling of Escherichia coli initiation factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1939–1942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Model P., Zinder N. D. In vitro synthesis of bacteriophage f1 proteins. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 25;83(2):231–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90389-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G., Lodish H. F. Translation of bacteriophage Q RNA by cytoplasmic extracts of mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):315–319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthukrishnan S., Both G. W., Furuichi Y., Shatkin A. J. 5'-Terminal 7-methylguanosine in eukaryotic mRNA is required for translation. Nature. 1975 May 1;255(5503):33–37. doi: 10.1038/255033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Noll H., Lingrel J. B. Initiation factor IF-3-dependent binding of Escherichia coli ribosomes and N-formylmethionine transfer-RNA to rabbit globin messenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1843–1847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Lee Y. F., Wimmer E. The 5' end of poliovirus mRNA is not capped with m7G(5')ppp(5')Np. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):375–380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Sugimoto K., Sugisaki H., Takanami M. Studies on bacteriophage fd DNA. II. Localization of RNA initiation sites on the cleavage map of the fd genome. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jun 15;95(1):33–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Brot N. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. IV. Effect of antibiotics on steps of bacterial protein synthesis: some new ribosomal inhibitors of translocation. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7715–7722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieczenik G., Model P., Robertson H. D. Sequence and symmetry in ribosome binding sites of bacteriophage f1 RNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 5;90(2):191–124. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rekosh D. M., Lodish H., Baltimore D. Protein synthesis in Escherichia coli extracts programmed by poliovirus RNA. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 14;54(2):327–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90433-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. D., Dickson E., Model P., Prensky W. Application of fingerprinting techniques to iodinated nucleic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3260–3264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Lodish H. F. Translation in vitro of vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA lacking 5'-terminal 7-methylguanosine. Nature. 1976 Jul 1;262(5563):32–37. doi: 10.1038/262032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Staehelin T., Gesteland R. F., Spahr P. F. Translation of bacteriophage R17 and Qbeta RNA in a mammalian cell-free system. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 15;75(3):575–578. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90462-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Schaller H. Mapping and characterization of promoters in bacteriophages fd, f1 and m13. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 25;92(2):261–277. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90226-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Determinant of cistron specificity in bacterial ribosomes. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):34–38. doi: 10.1038/254034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Identical 3'-terminal octanucleotide sequence in 18S ribosomal ribonucleic acid from different eukaryotes. A proposed role for this sequence in the recognition of terminator codons. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):609–615. doi: 10.1042/bj1410609a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A. Polypeptide chain initiation: nucleotide sequences of the three ribosomal binding sites in bacteriophage R17 RNA. Nature. 1969 Dec 6;224(5223):957–964. doi: 10.1038/224957a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Voorde A., Contreras R., Rogiers R., Fiers W. The initiation region of the SV40 VP1 gene. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):117–120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]