Abstract
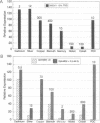
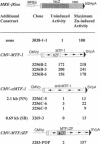
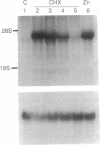
A construct, MRE-beta Geo, with five metal response elements fused to a selectable reporter gene was transfected into BHK cells and a stable clone that could be induced up to 100-fold by zinc, cadmium, bismuth, silver, cobalt, copper, mercury, or nickle was isolated. Some, and perhaps all, of these metals induce MRE-beta Geo by displacing zinc. Transfection of these cells with a construct encoding the transcriptional activator MTF-1 resulted in constitutive expression of MRE-beta Geo, whereas expression of an antisense MTF-1 construct in these cells prevented induction by all of the metals. A variant cell line with high constitutive expression in the absence of added metals was isolated; normal regulation was restored by cell fusion. These results suggest that regulation of metallothionein genes by metals is mediated by MTF-1 interacting with metal response elements and that zinc functions to release MTF-1 from an inhibitor.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam J., Smith A. Heme-hemopexin-mediated induction of metallothionein gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16379–16384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen R. D., Taplitz S. J., Oberbauer A. M., Calame K. L., Herschman H. R. Metal-dependent binding of a nuclear factor to the rat metallothionein-I promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6049–6055. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen R. D., Taplitz S. J., Wong S., Bristol G., Larkin B., Herschman H. R. Metal-dependent binding of a factor in vivo to the metal-responsive elements of the metallothionein 1 gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3574–3581. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau H. M., Chiu C. P., Webster C. Cytoplasmic activation of human nuclear genes in stable heterocaryons. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1171–1180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90300-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czupryn M., Brown W. E., Vallee B. L. Zinc rapidly induces a metal response element-binding factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10395–10399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. A practical approach for quantitating specific mRNAs by solution hybridization. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jun;131(2):385–393. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. Induction of metallothionein-I mRNA in cultured cells by heavy metals and iodoacetate: evidence for gratuitous inducers. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):484–491. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich G., Soriano P. Promoter traps in embryonic stem cells: a genetic screen to identify and mutate developmental genes in mice. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1513–1523. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst P., Hu S., Hackett R., Hamer D. Copper activates metallothionein gene transcription by altering the conformation of a specific DNA binding protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):705–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H. Metallothionein. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:913–951. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbert J., Zafarullah M., Culotta V. C., Gedamu L., Hamer D. Transcription factor MBF-I interacts with metal regulatory elements of higher eucaryotic metallothionein genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5315–5323. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi S., Suzuki K., Otsuka F. A nuclear factor that recognizes the metal-responsive elements of human metallothionein IIA gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18659–18664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kägi J. H., Kojima Y. Chemistry and biochemistry of metallothionein. Experientia Suppl. 1987;52:25–61. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-6784-9_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. E., Palmiter R. D. Glucocorticoid regulation of metallothionein-I mRNA synthesis in cultured mouse cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2621–2624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKendry R., John J., Flavell D., Müller M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. High-frequency mutagenesis of human cells and characterization of a mutant unresponsive to both alpha and gamma interferons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11455–11459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Salser S. J., Wold B. Constitutive and metal-inducible protein:DNA interactions at the mouse metallothionein I promoter examined by in vivo and in vitro footprinting. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):412–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Behringer R. R., Quaife C. J., Maxwell F., Maxwell I. H., Brinster R. L. Cell lineage ablation in transgenic mice by cell-specific expression of a toxin gene. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90497-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L. Differential regulation of metallothionein-thymidine kinase fusion genes in transgenic mice and their offspring. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):701–710. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radtke F., Heuchel R., Georgiev O., Hergersberg M., Gariglio M., Dembic Z., Schaffner W. Cloned transcription factor MTF-1 activates the mouse metallothionein I promoter. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1355–1362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle P. F., Stuart G. W., Palmiter R. D. Building a metal-responsive promoter with synthetic regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1480–1489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle P. F. Zinc dependent binding of a liver nuclear factor to metal response element MRE-a of the mouse metallothionein-I gene and variant sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. W., Searle P. F., Palmiter R. D. Identification of multiple metal regulatory elements in mouse metallothionein-I promoter by assaying synthetic sequences. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):828–831. doi: 10.1038/317828a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séguin C., Prévost J. Detection of a nuclear protein that interacts with a metal regulatory element of the mouse metallothionein 1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10547–10560. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamai K. T., Gralla E. B., Ellerby L. M., Valentine J. S., Thiele D. J. Yeast and mammalian metallothioneins functionally substitute for yeast copper-zinc superoxide dismutase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8013–8017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee B. L., Falchuk K. H. The biochemical basis of zinc physiology. Physiol Rev. 1993 Jan;73(1):79–118. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalkes M. P., Goering P. L. Metallothionein and other cadmium-binding proteins: recent developments. Chem Res Toxicol. 1990 Jul-Aug;3(4):281–288. doi: 10.1021/tx00016a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Schaffner W. A zinc-responsive factor interacts with a metal-regulated enhancer element (MRE) of the mouse metallothionein-I gene. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3763–3770. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]