Abstract
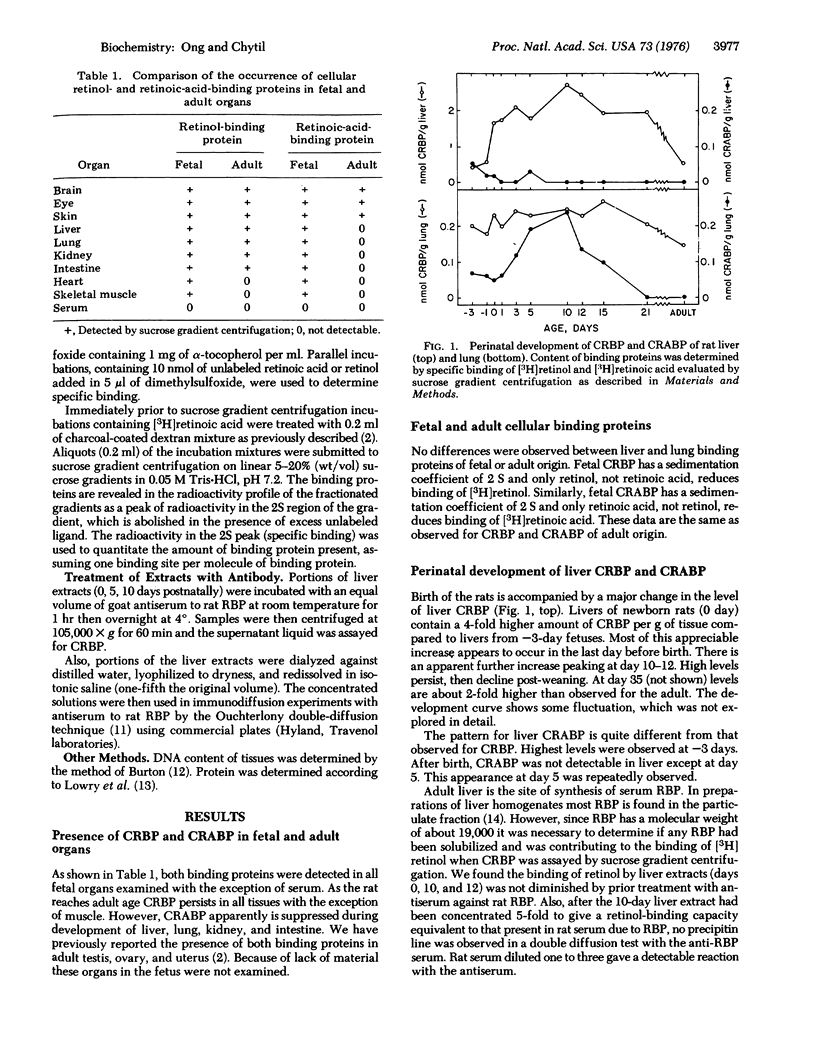
Cellular retinol-binding protein and cellular retinoic-acid-binding protein, canditates for mediating the action of vitamin A, were found to be present in tissues of the fetal rat. Cellular retinol-binding proteins were still present in most tissues of the adult, but the retinoic-acid-binding protein was not detected in some, including lung, liver, intestine, and kidney. During perinatal development of lung the level of cellular retinol-binding protein remained relatively constant while the level of the cellular retinoic-acid-binding protein peaked at 10 days postnatally, then declined. It was not detectable in lung tissue from 21-day-old rats. In liver, however, the retinoic-acid-binding protein was not detectable later than 5 days postnatally, while the level of the cellular retinol-binding proteinrose sharply near birth, declining only after 21 days to the lower adult levels. The variations observed in the levels of the two binding proteins suggest different and changing requirements for retinol and retinoic acid in organ development and maturation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashor M. M., Chytil F. Cellular retinol-binding protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 10;411(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90287-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashor M. M., Toft D. O., Chytil F. In vitro binding of retinol to rat-tissue components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3483–3487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chytil F., Glasser S. R., Splesberg T. C. Alterations in liver chromatin during perinatal development of the rat. Dev Biol. 1974 Apr;37(2):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90150-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chytil F., Ong D. E. Mediation of retinoic acid-induced growth and anti-tumour activity. Nature. 1976 Mar 4;260(5546):49–51. doi: 10.1038/260049a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard O., Federman M., Knox W. E. Cytomorphometry of developing rat liver and its application to enzymic differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1972 Feb;52(2):261–272. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto Y., Goodman D. S. Vitamin A transport in rat plasma. Isolation and characterization or retinol-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2533–2541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong D. E., Chytil F. Retinoic acid-binding protein in rat tissue. Partial purification and comparison to rat tissue retinol-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6113–6117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong D. E., Chytil F. Specificity of cellular retinol-binding protein for compounds with vitamin A activity. Nature. 1975 May 1;255(5503):74–75. doi: 10.1038/255074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong D. E., Page D. L., Chytil F. Retinoic acid binding protein: occurrence in human tumors. Science. 1975 Oct 3;190(4209):60–61. doi: 10.1126/science.1166300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong D. E., Tsai C. H., Chytil F. Cellular retinol-binding protein and retinoic acid-binding protein in rat testes: effect of retinol depletion. J Nutr. 1976 Feb;106(2):204–211. doi: 10.1093/jn/106.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. E., Muto Y., Goodman D. S. Tissue distribution and subcellular localization of retinol-binding protein in normal and vitamin A-deficient rats. J Lipid Res. 1975 Jul;16(4):318–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y. I., Smith J. E., Winick M., Goodman D. S. Vitam A deficiency and fetal growth and development in the rat. J Nutr. 1975 Oct;105(10):1299–1310. doi: 10.1093/jn/105.10.1299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



