Abstract
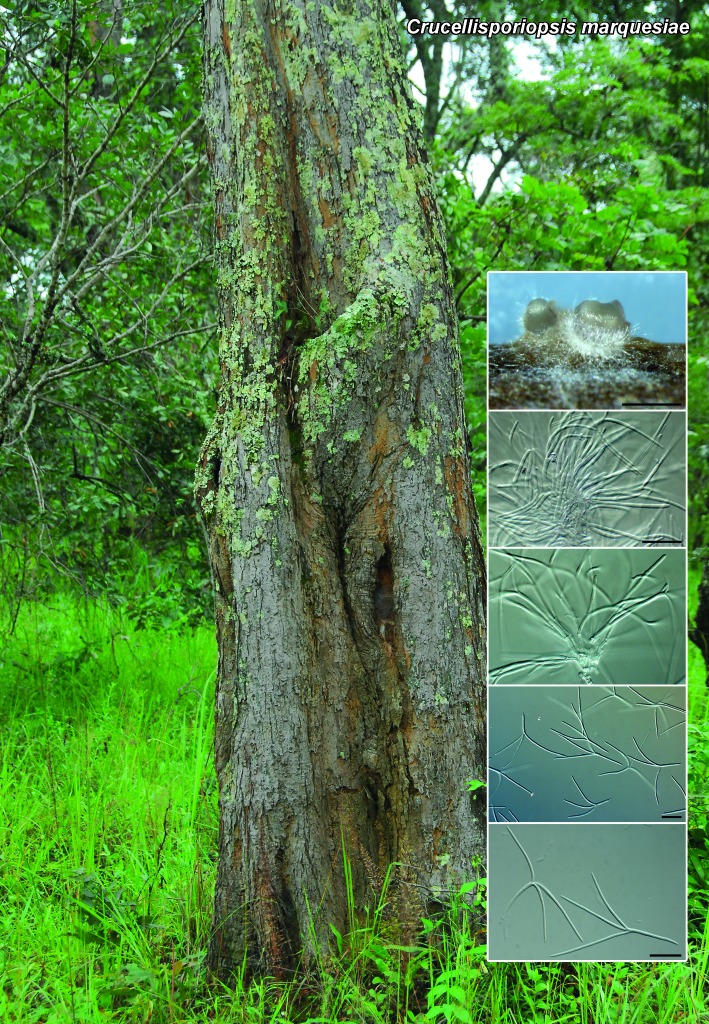
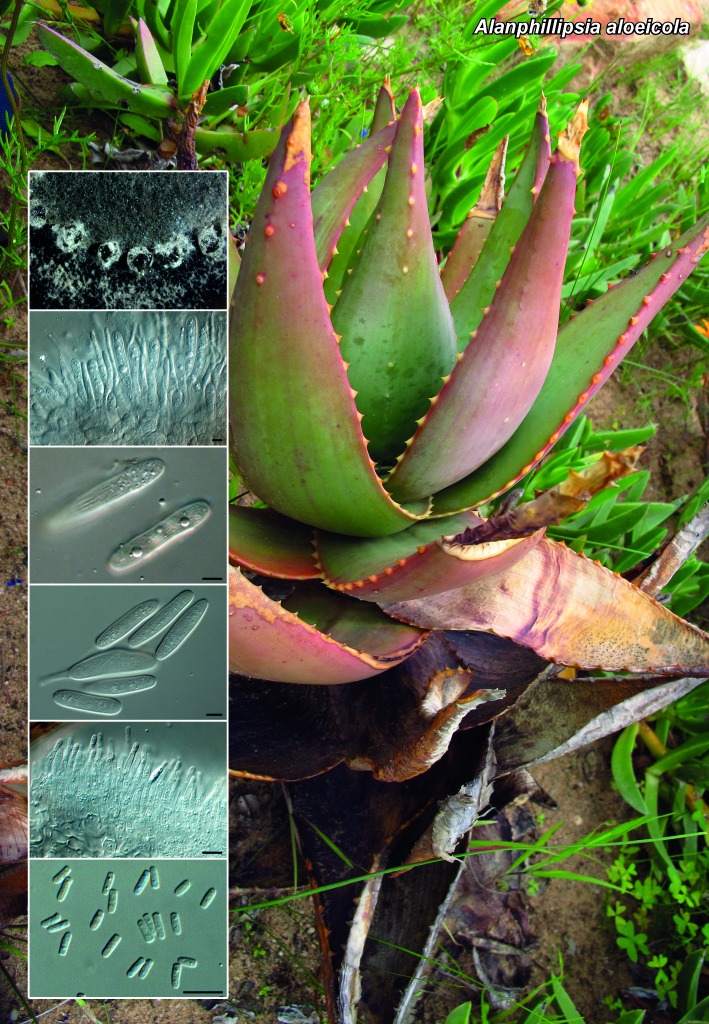
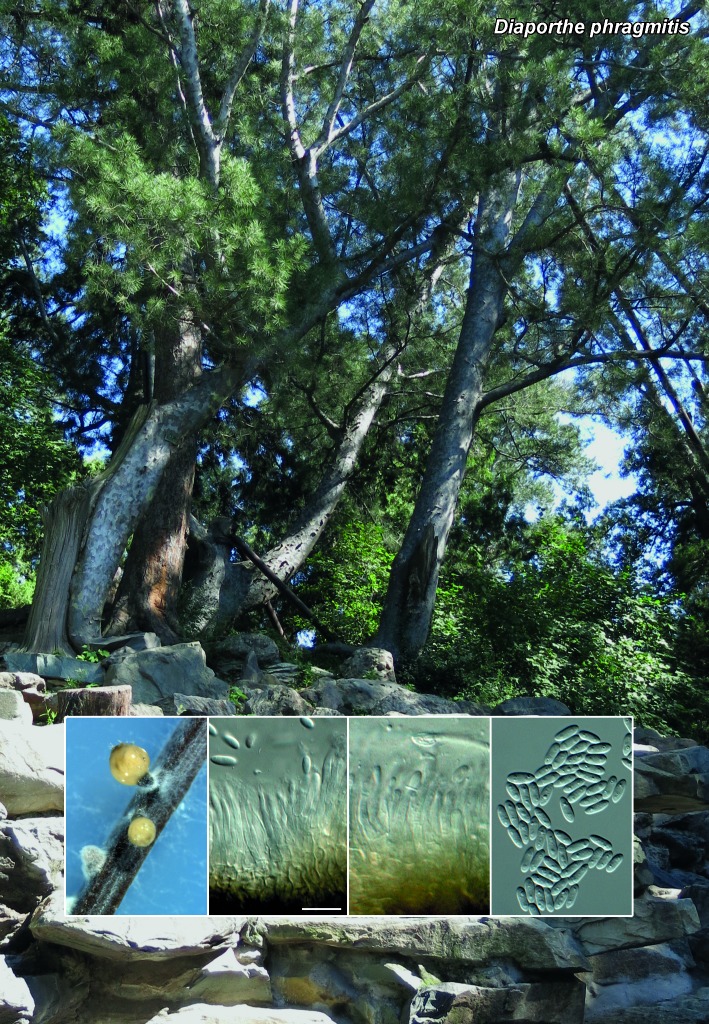
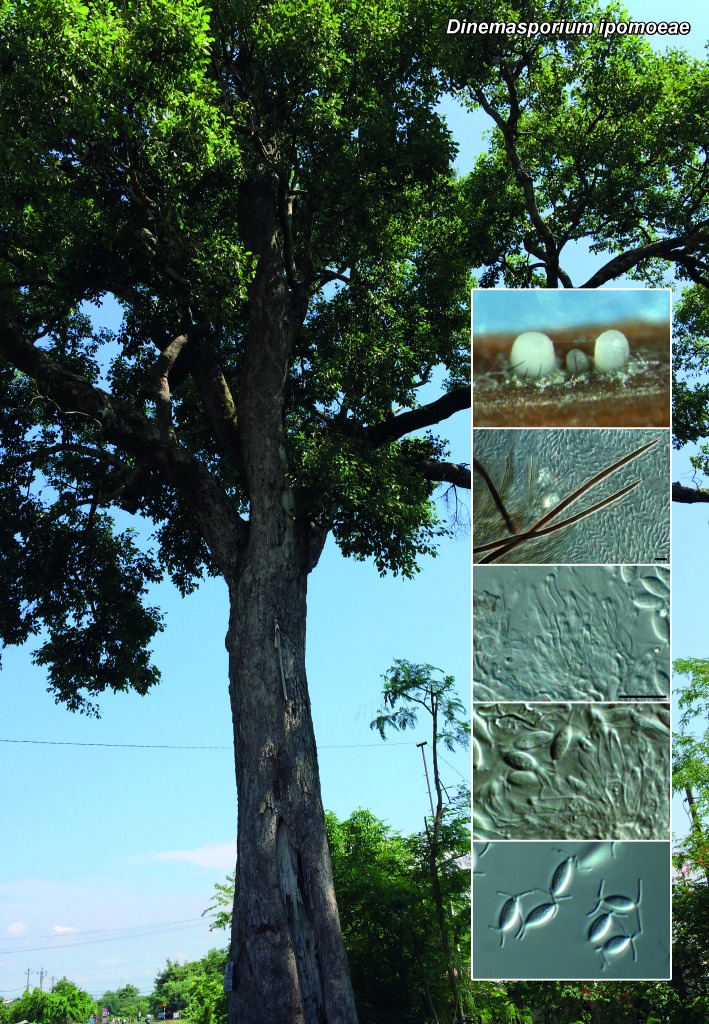
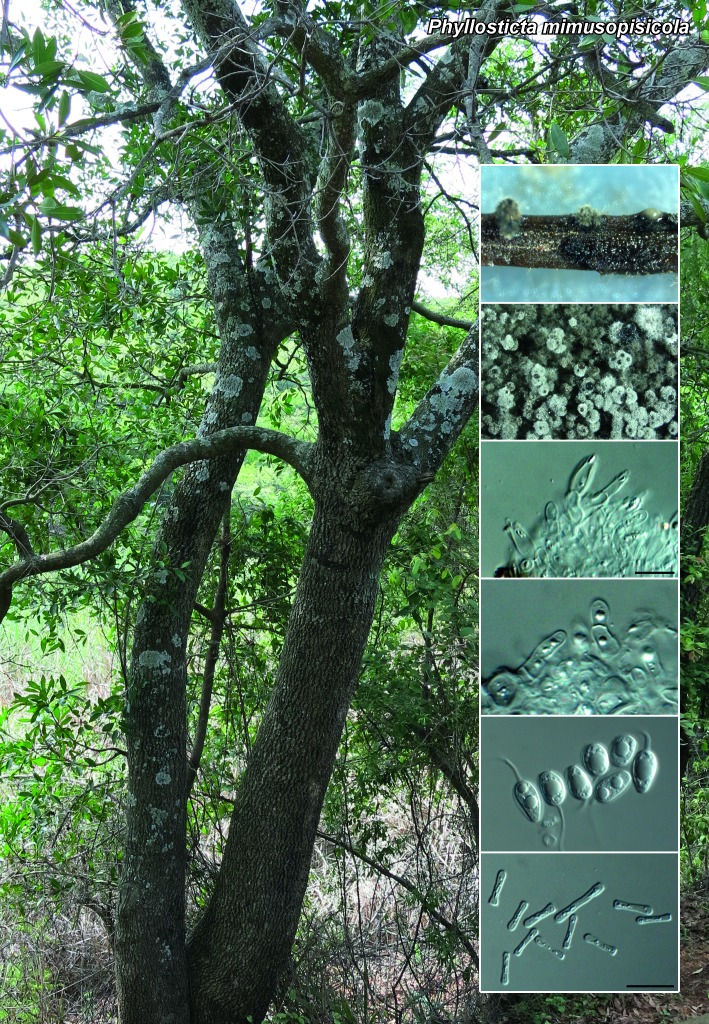
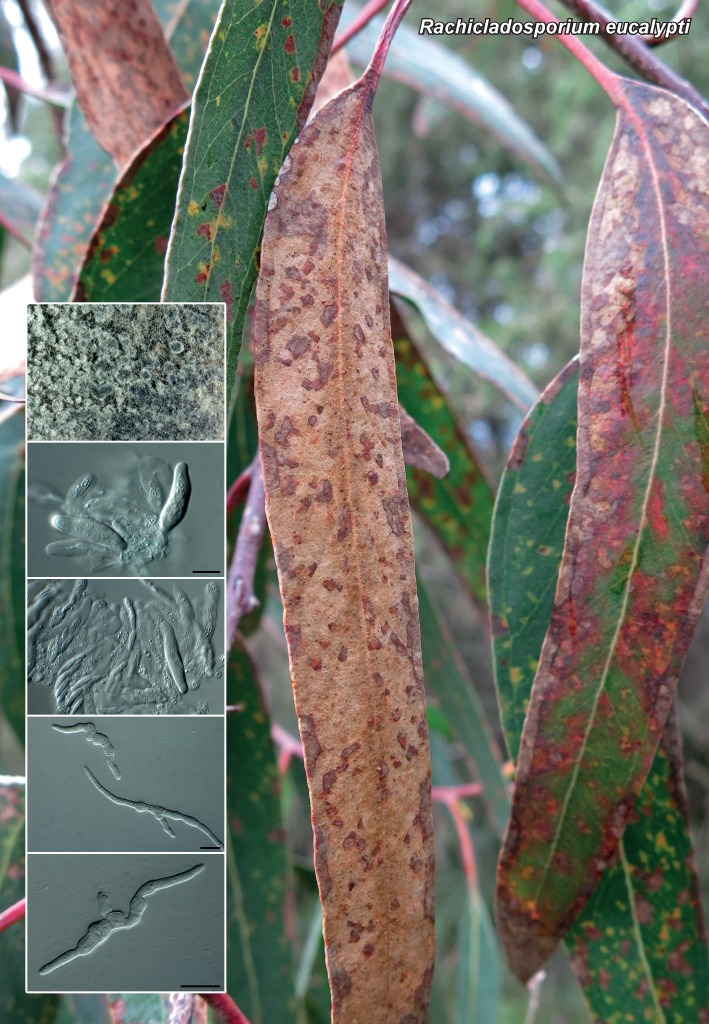
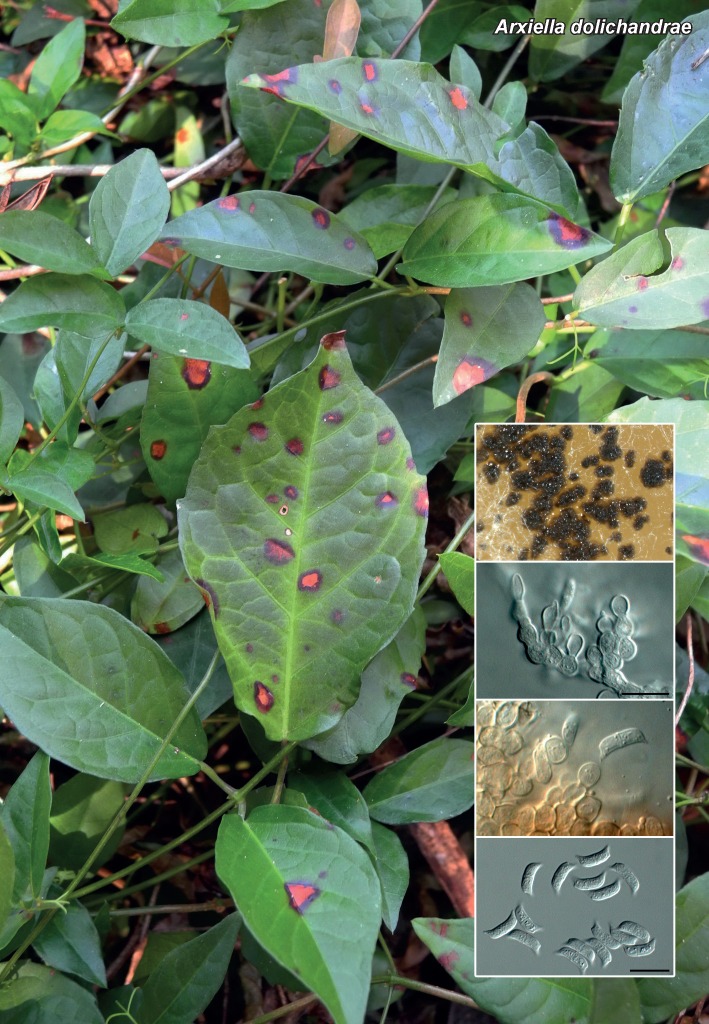
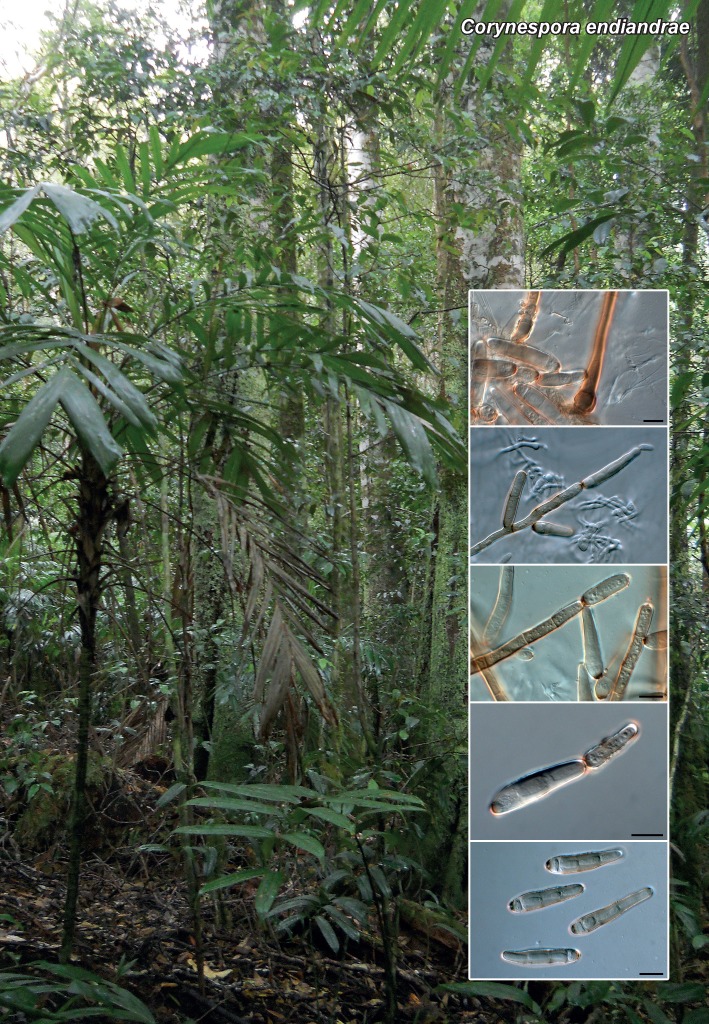
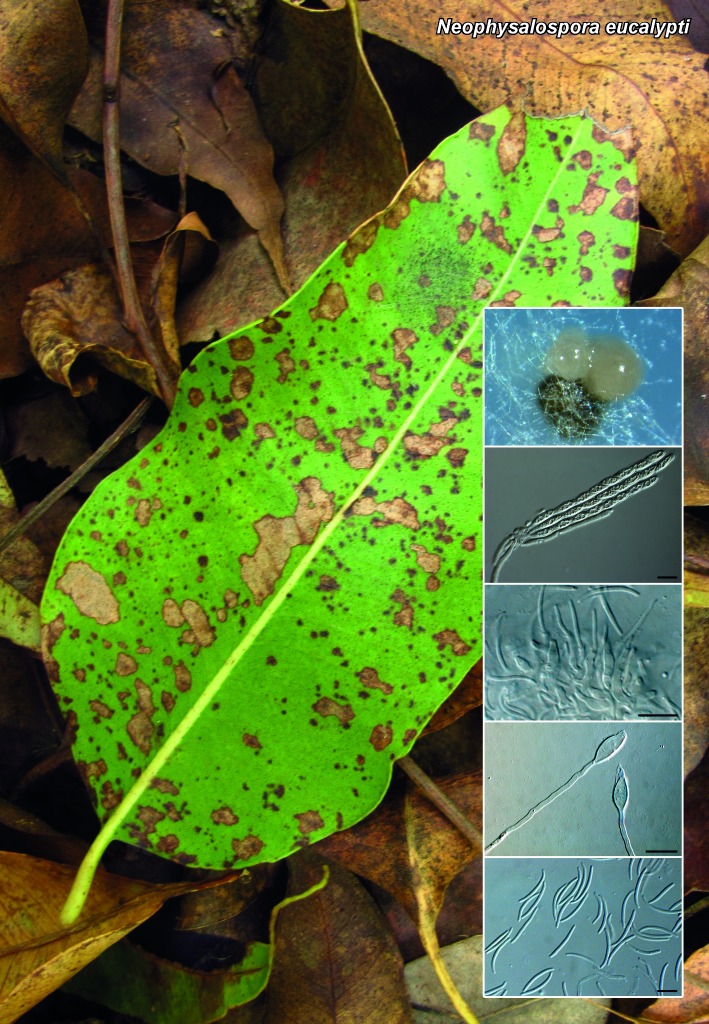
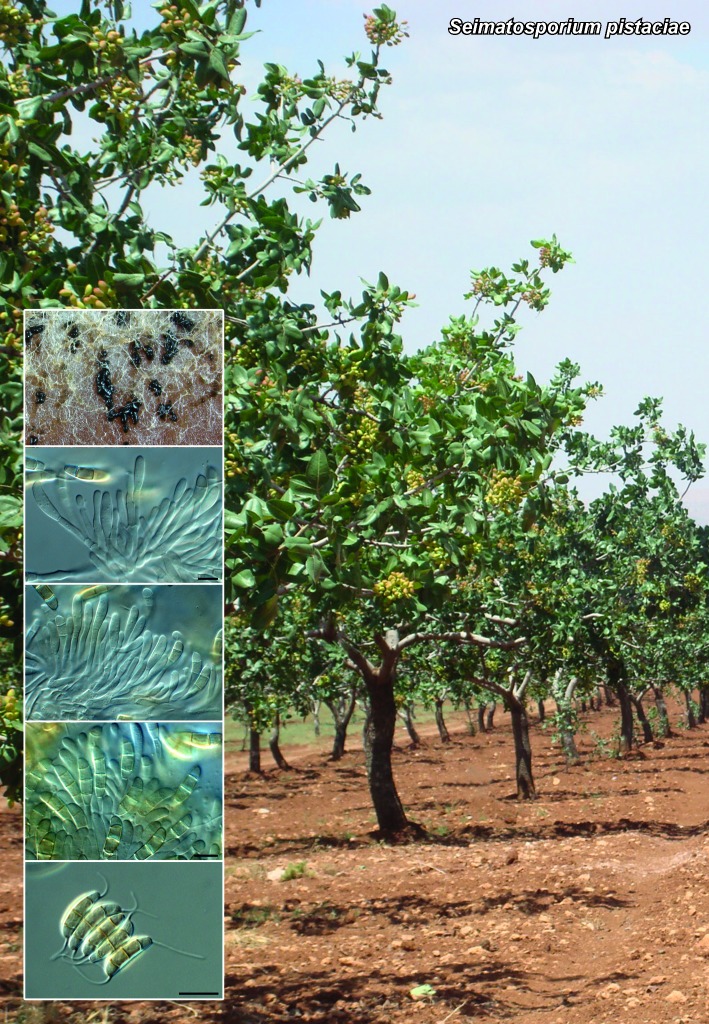
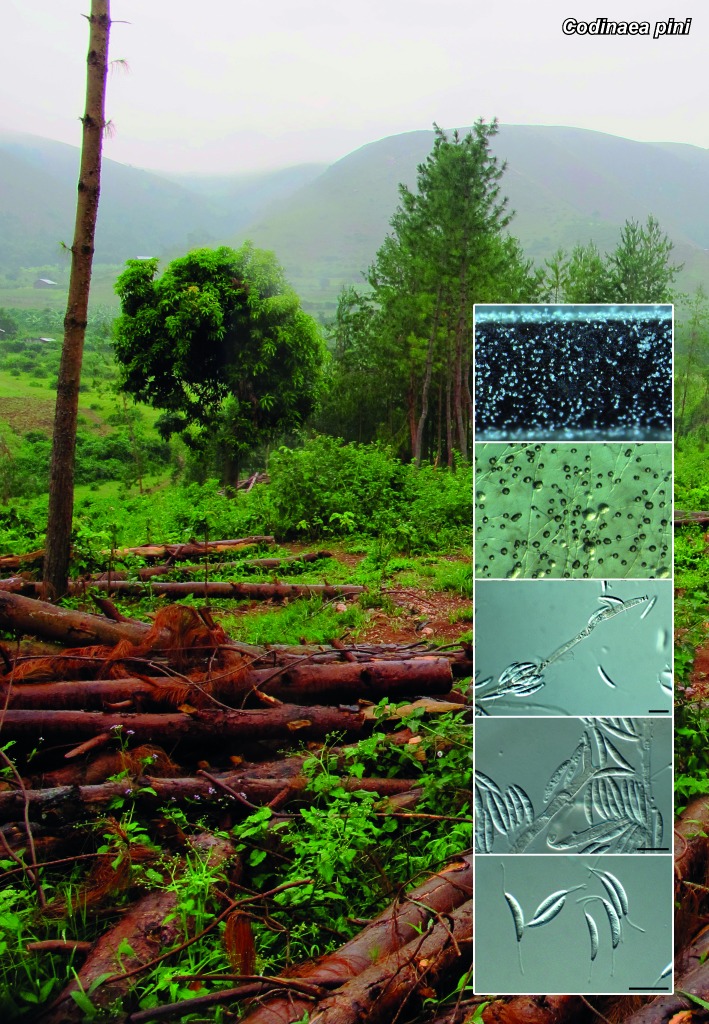
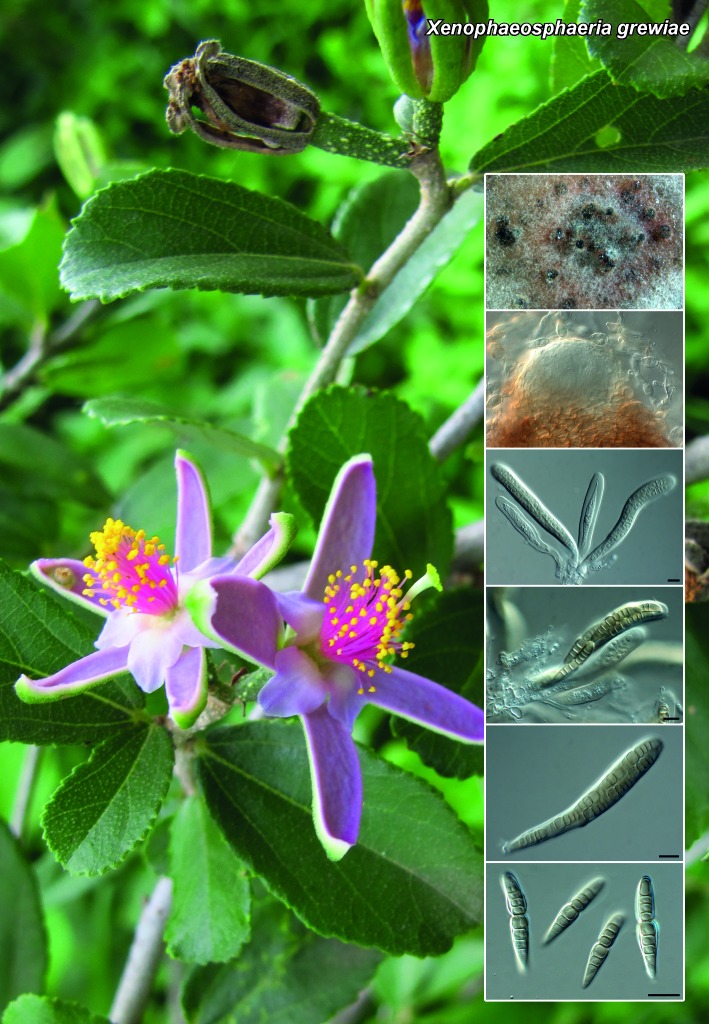
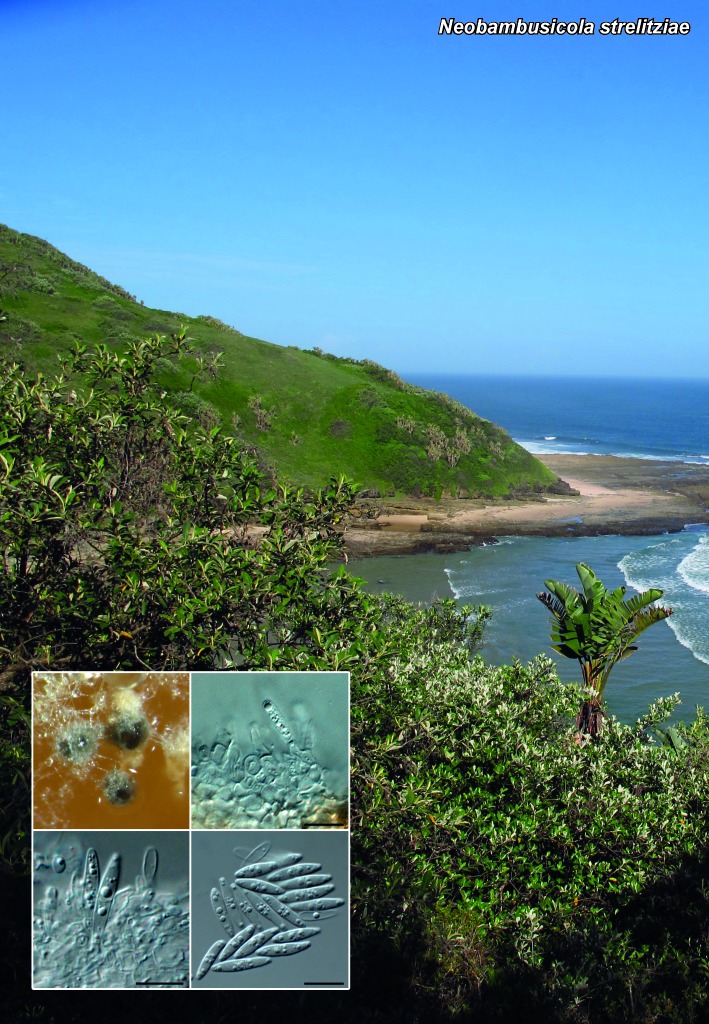
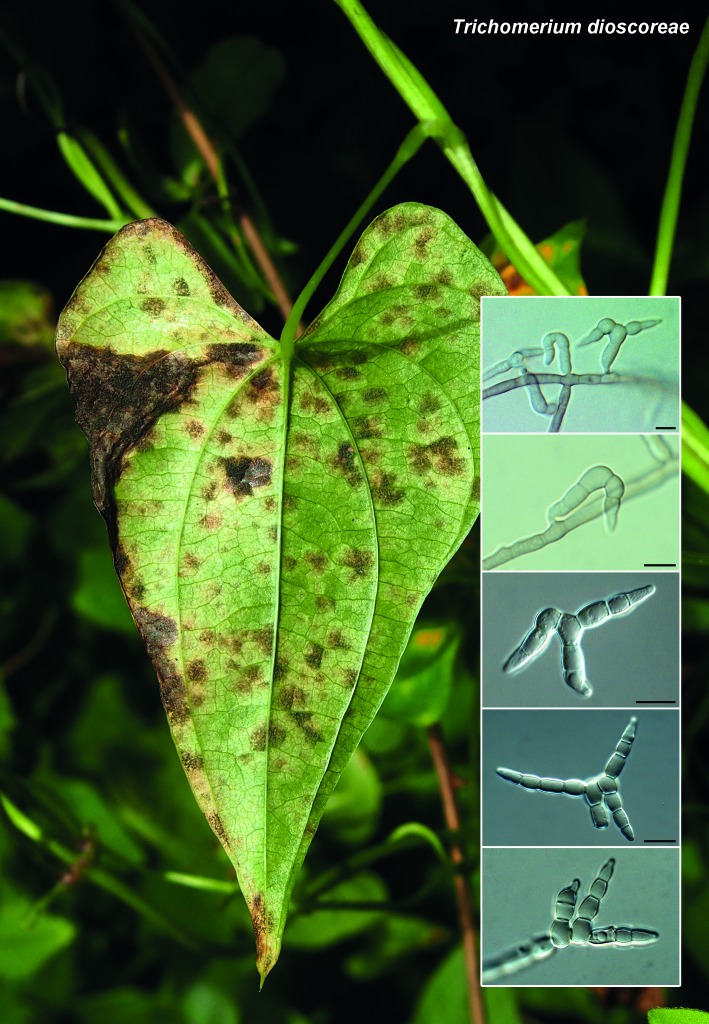
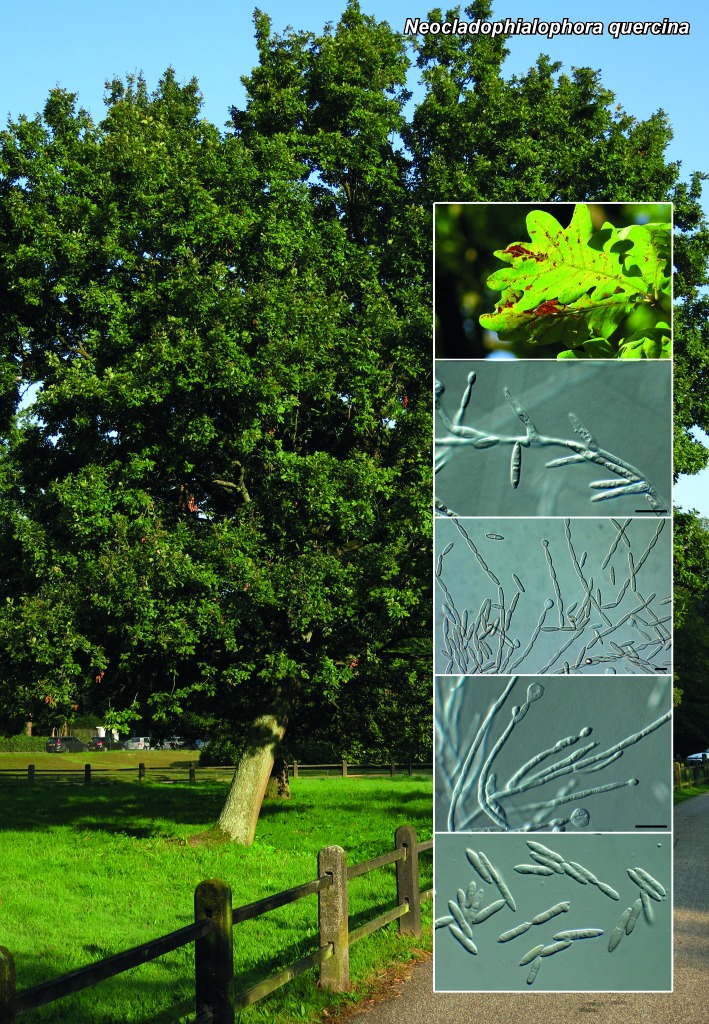
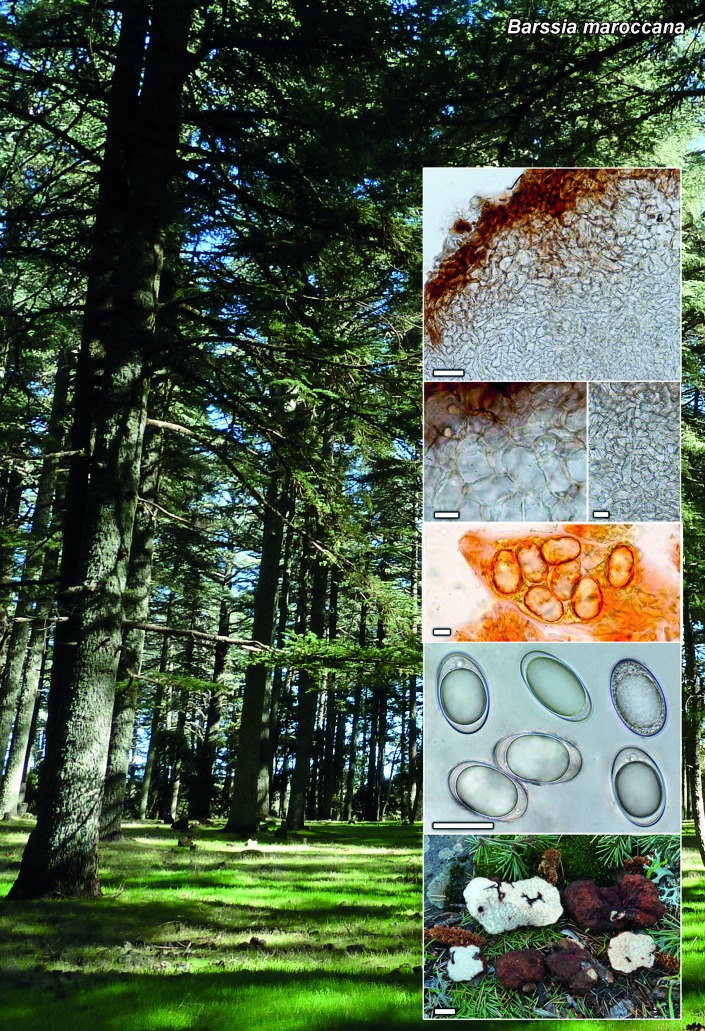
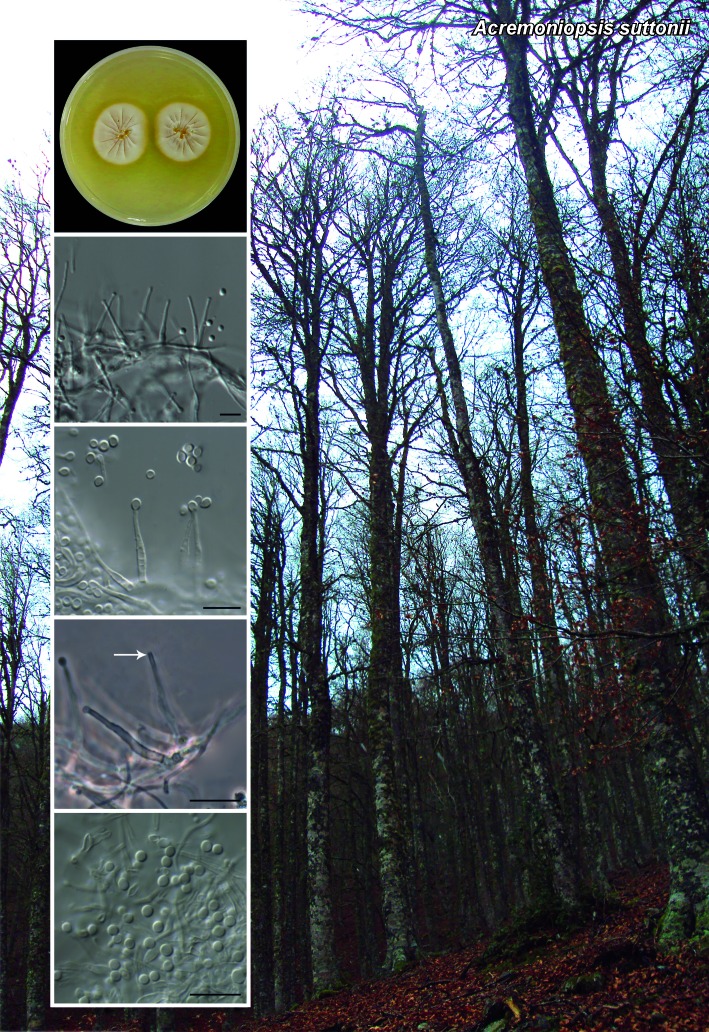
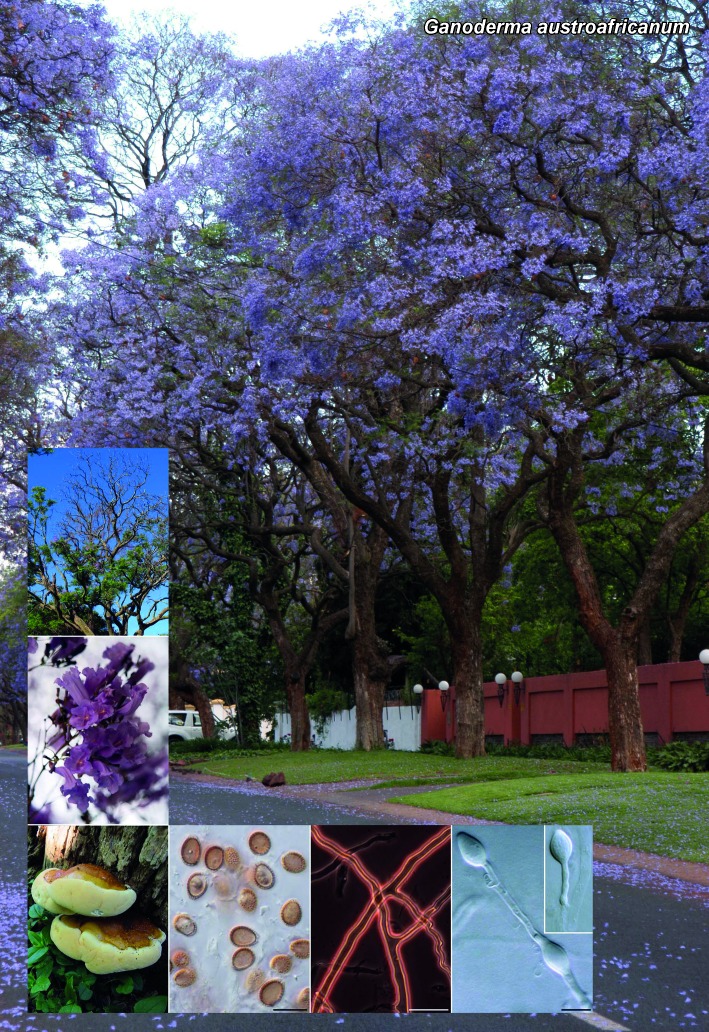
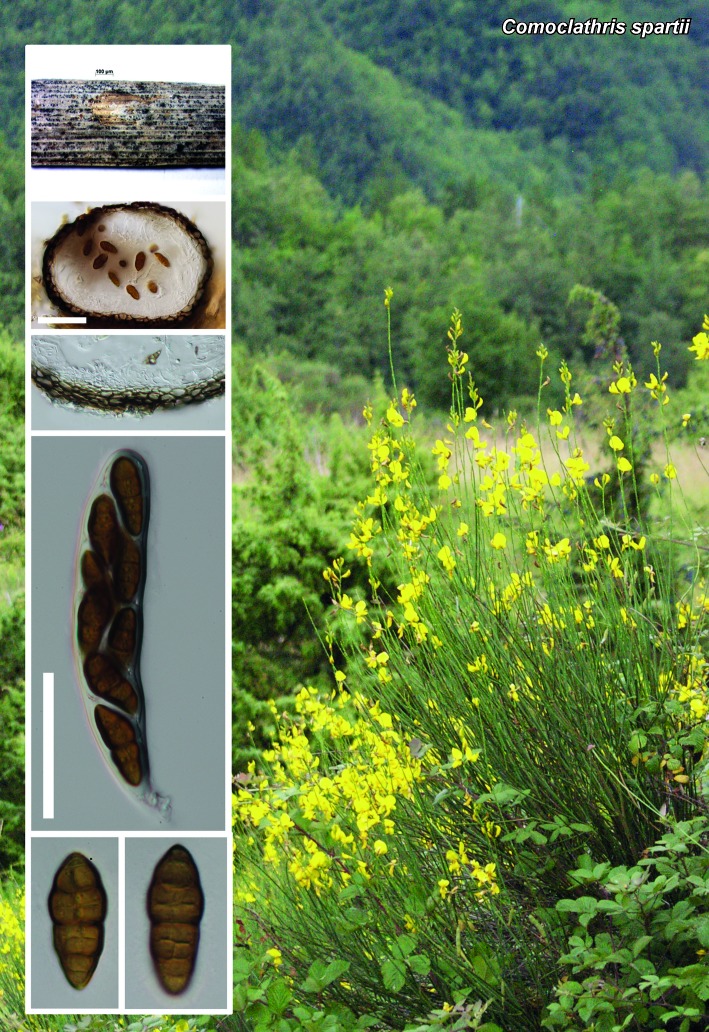
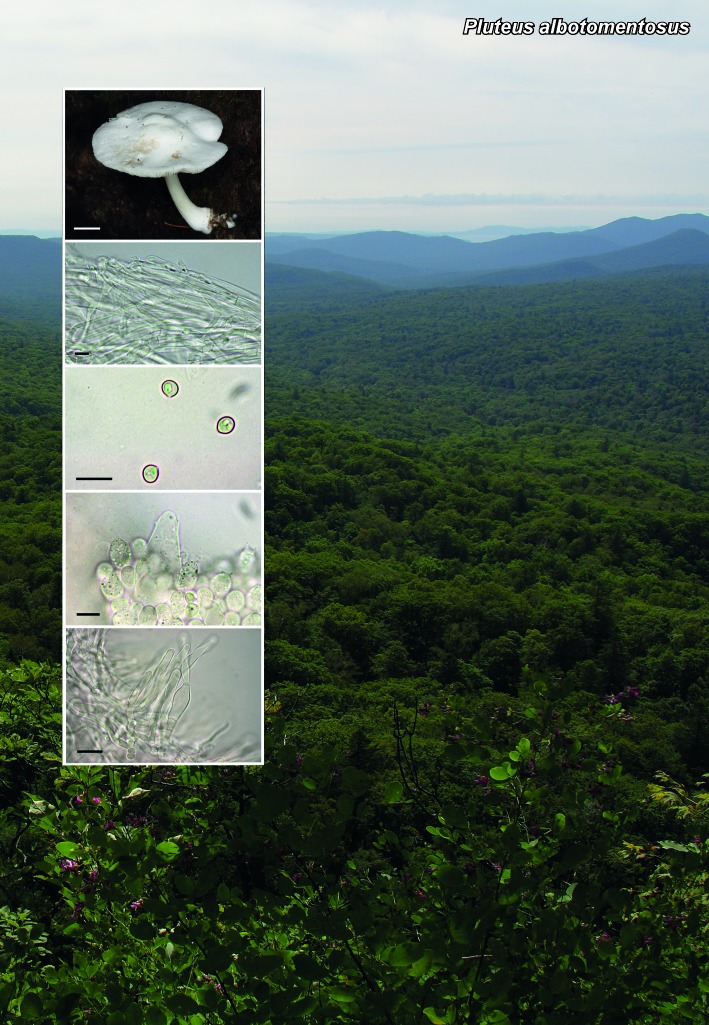
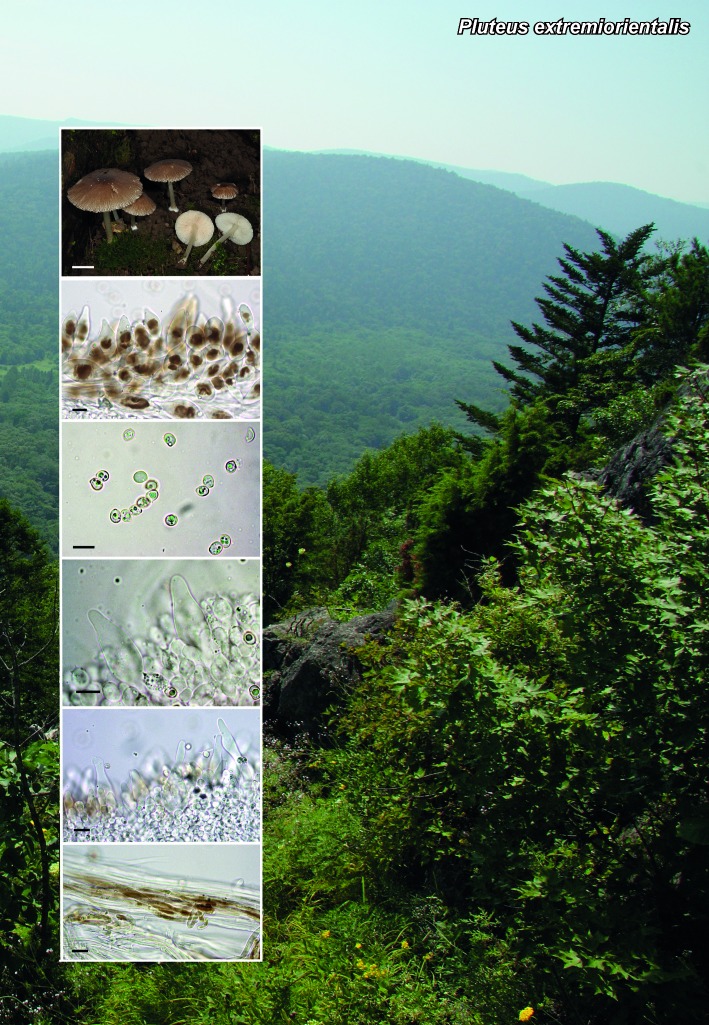
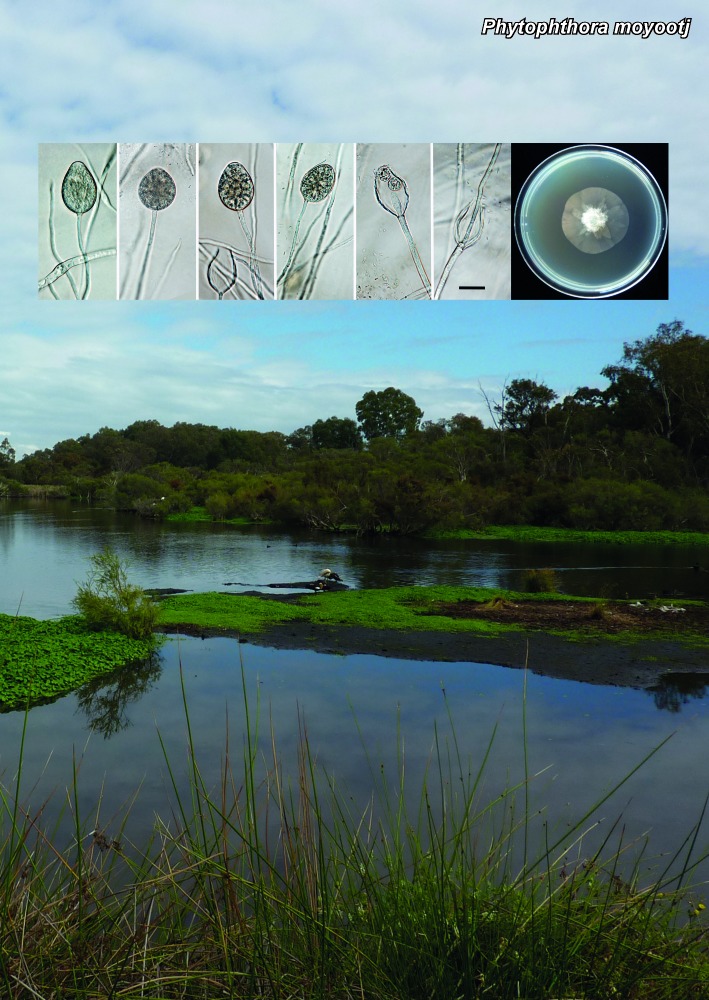
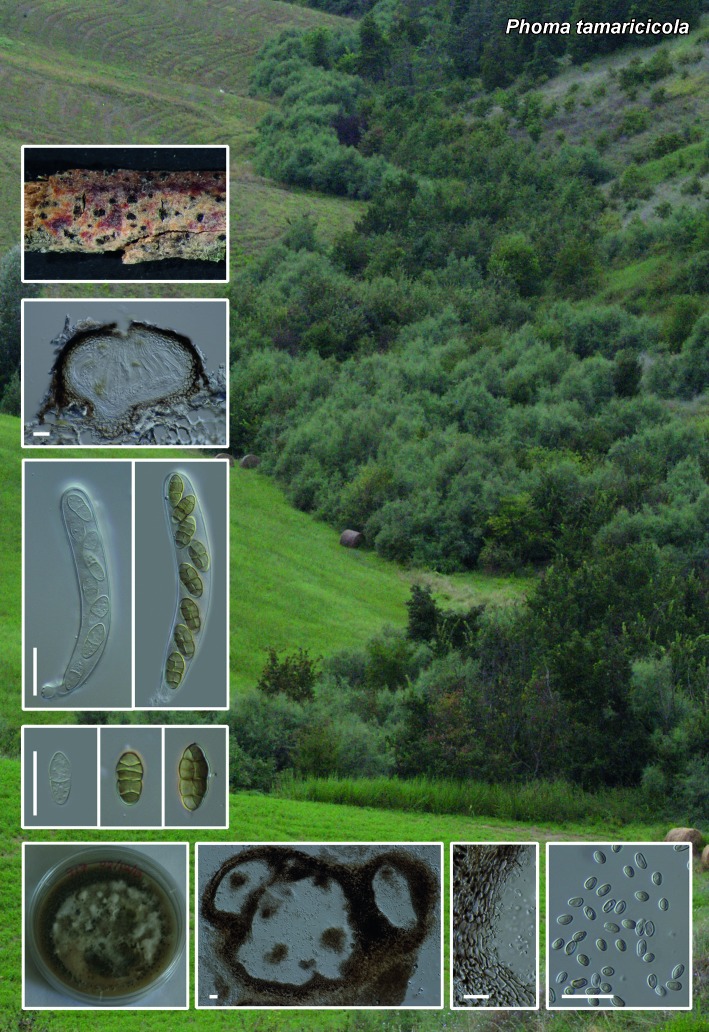
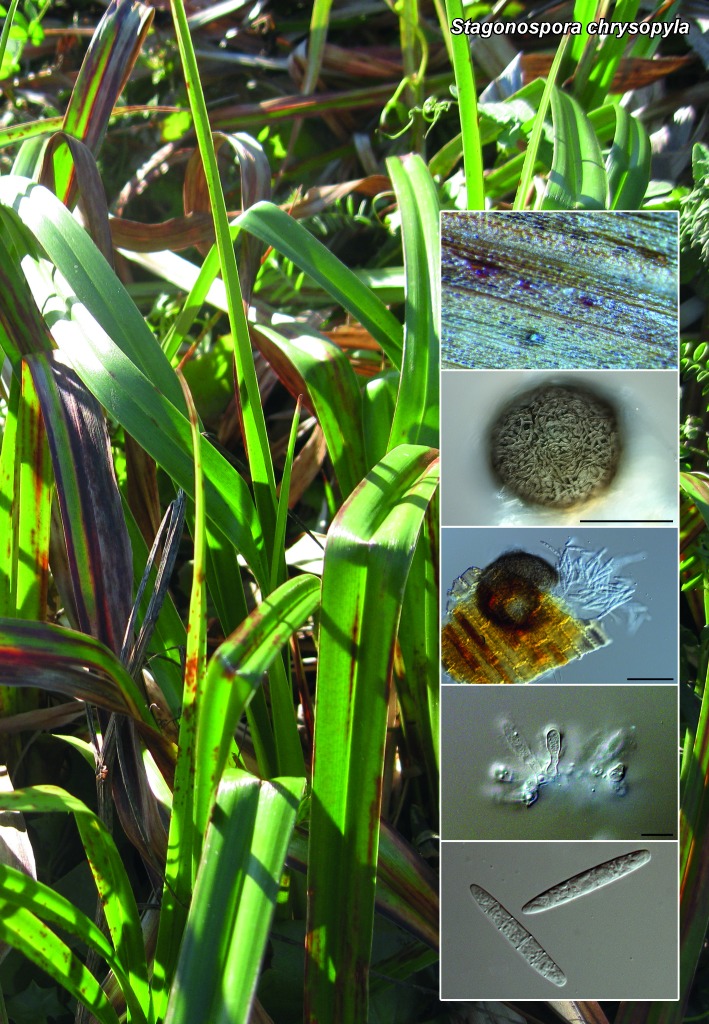
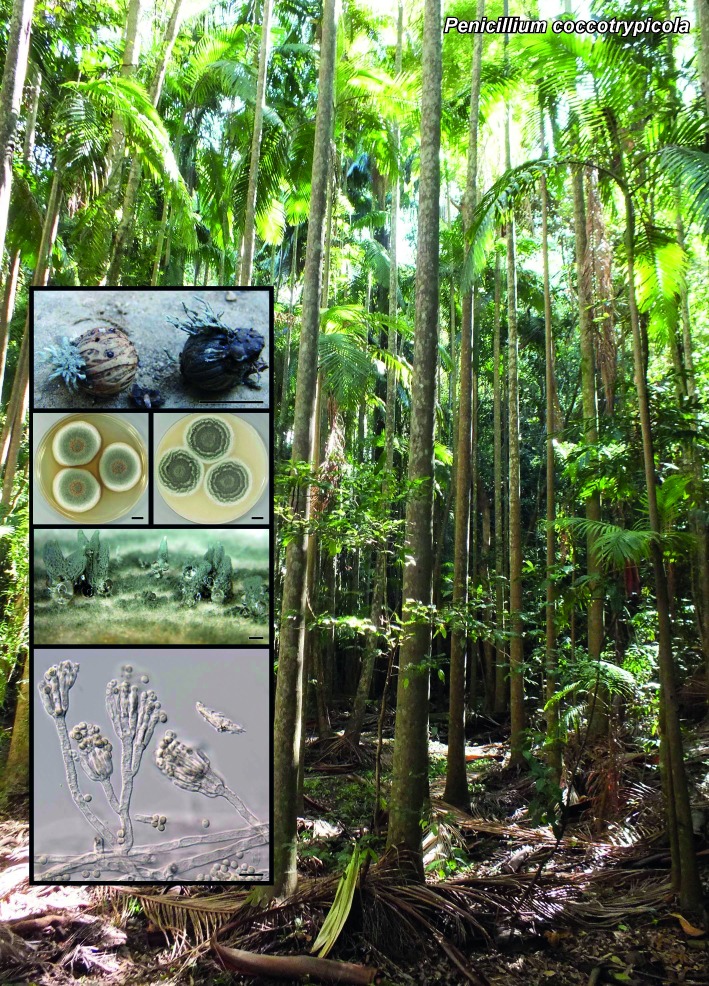
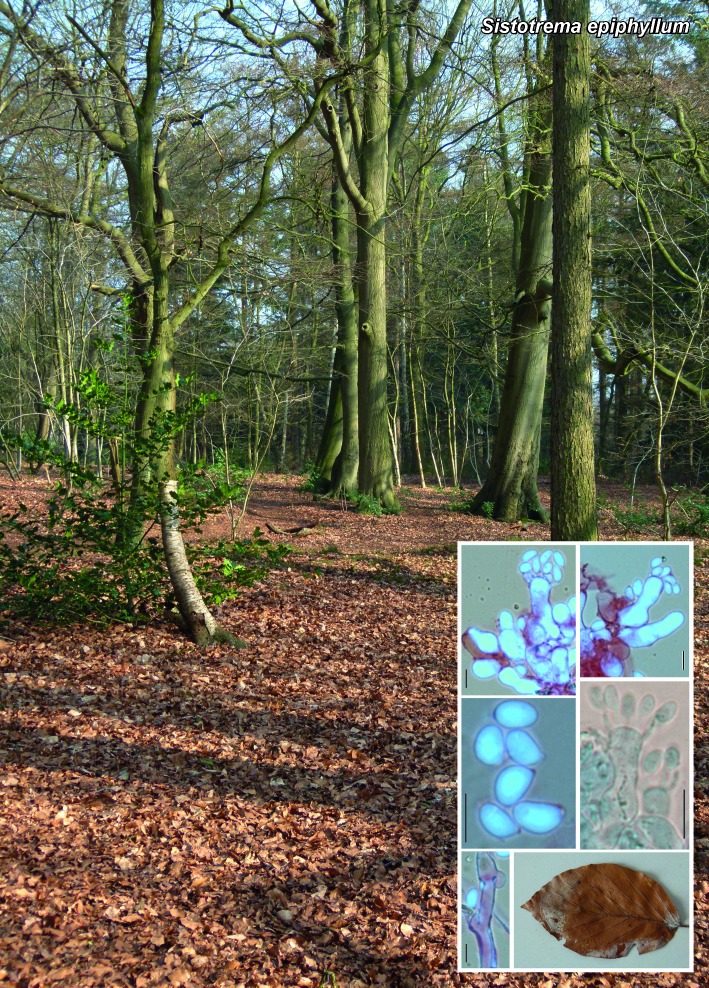
Novel species of fungi described in the present study include the following from South Africa: Alanphillipsia aloeicola from Aloe sp., Arxiella dolichandrae from Dolichandra unguiscati, Ganoderma austroafricanum from Jacaranda mimosifolia, Phacidiella podocarpi and Phaeosphaeria podocarpi from Podocarpus latifolius, Phyllosticta mimusopisicola from Mimusops zeyheri and Sphaerulina pelargonii from Pelargonium sp. Furthermore, Barssia maroccana is described from Cedrus atlantica (Morocco), Codinaea pini from Pinus patula (Uganda), Crucellisporiopsis marquesiae from Marquesia acuminata (Zambia), Dinemasporium ipomoeae from Ipomoea pes-caprae (Vietnam), Diaporthe phragmitis from Phragmites australis (China), Marasmius vladimirii from leaf litter (India), Melanconium hedericola from Hedera helix (Spain), Pluteus albotomentosus and Pluteus extremiorientalis from a mixed forest (Russia), Rachicladosporium eucalypti from Eucalyptus globulus (Ethiopia), Sistotrema epiphyllum from dead leaves of Fagus sylvatica in a forest (The Netherlands), Stagonospora chrysopyla from Scirpus microcarpus (USA) and Trichomerium dioscoreae from Dioscorea sp. (Japan). Novel species from Australia include: Corynespora endiandrae from Endiandra introrsa, Gonatophragmium triuniae from Triunia youngiana, Penicillium coccotrypicola from Archontophoenix cunninghamiana and Phytophthora moyootj from soil. Novelties from Iran include Neocamarosporium chichastianum from soil and Seimatosporium pistaciae from Pistacia vera. Xenosonderhenia eucalypti and Zasmidium eucalyptigenum are newly described from Eucalyptus urophylla in Indonesia. Diaporthe acaciarum and Roussoella acacia are newly described from Acacia tortilis in Tanzania. New species from Italy include Comoclathris spartii from Spartium junceum and Phoma tamaricicola from Tamarix gallica. Novel genera include (Ascomycetes): Acremoniopsis from forest soil and Collarina from water sediments (Spain), Phellinocrescentia from a Phellinus sp. (French Guiana), Neobambusicola from Strelitzia nicolai (South Africa), Neocladophialophora from Quercus robur (Germany), Neophysalospora from Corymbia henryi (Mozambique) and Xenophaeosphaeria from Grewia sp. (Tanzania). Morphological and culture characteristics along with ITS DNA barcodes are provided for all taxa.
Keywords: ITS DNA barcodes, LSU, novel fungal species, systematics
HIGHER ORDER CLASSIFICATION OF TAXONOMIC NOVELTIES.
| ASCOMYCOTA |
| Dothideomycetes |
| Acrospermales, Acrospermaceae |
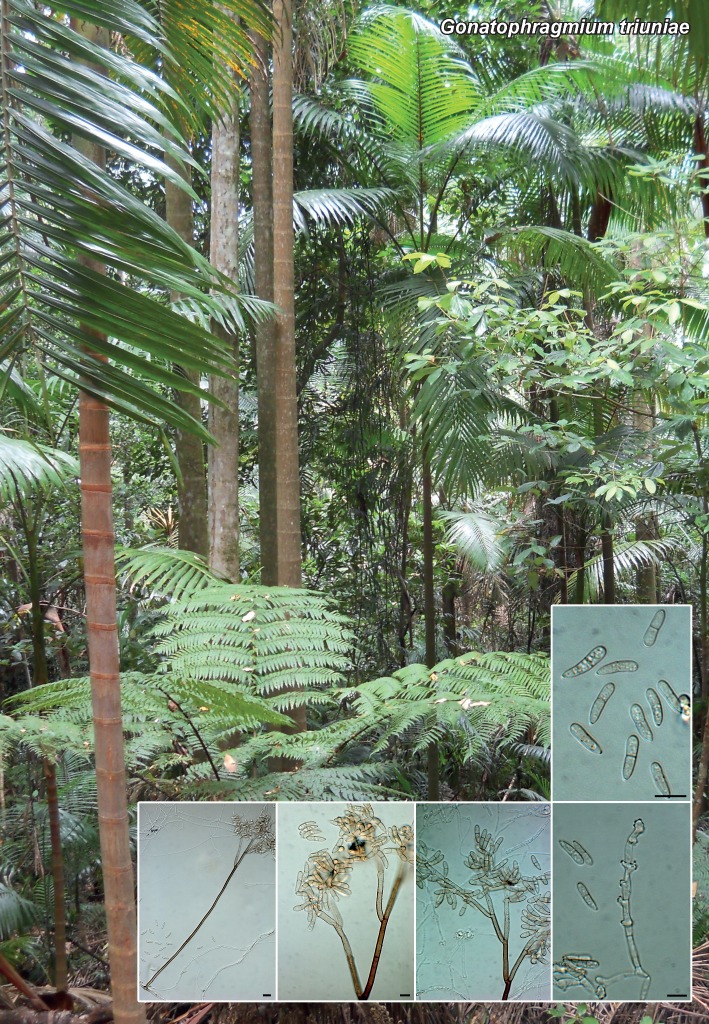
| Gonatophragmium triuniae |
| Botryosphaeriales, Botryosphaeriaceae |
| Alanphillipsia aloeicola |
| Botryosphaeriales, Phyllostictaceae |
| Phyllosticta mangiferae-indica |
| Phyllosticta mimusopisicola |
| Phyllosticta rubella |
| Capnodiales, Cladosporiaceae |
| Rachicladosporium eucalypti |
| Capnodiales, Mycosphaerellaceae |
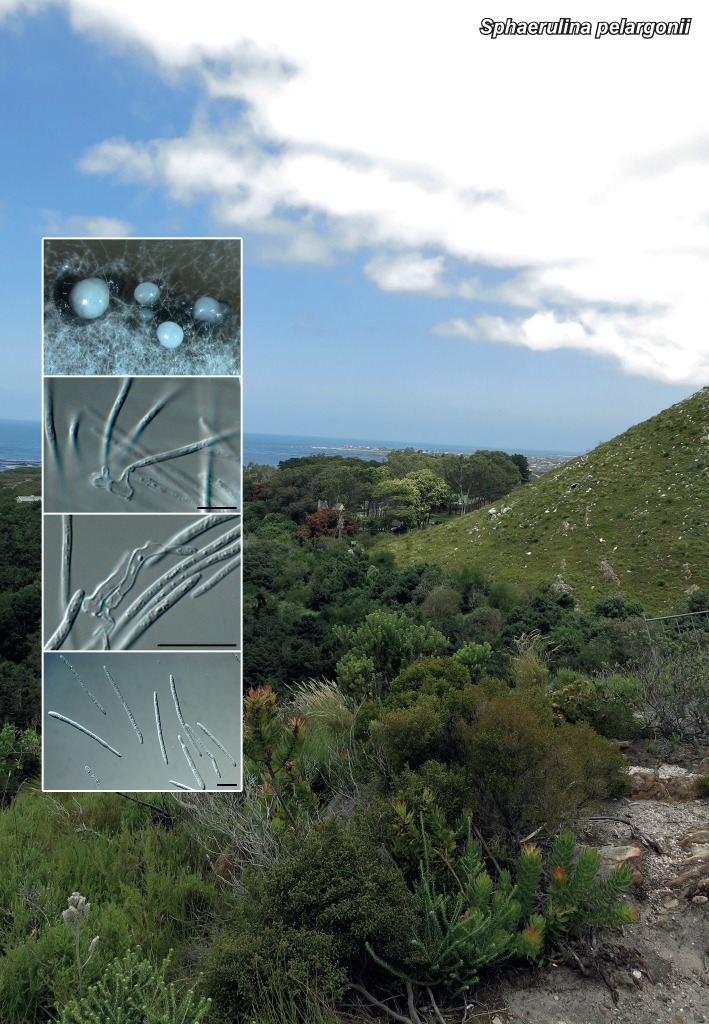
| Sphaerulina pelargonii |
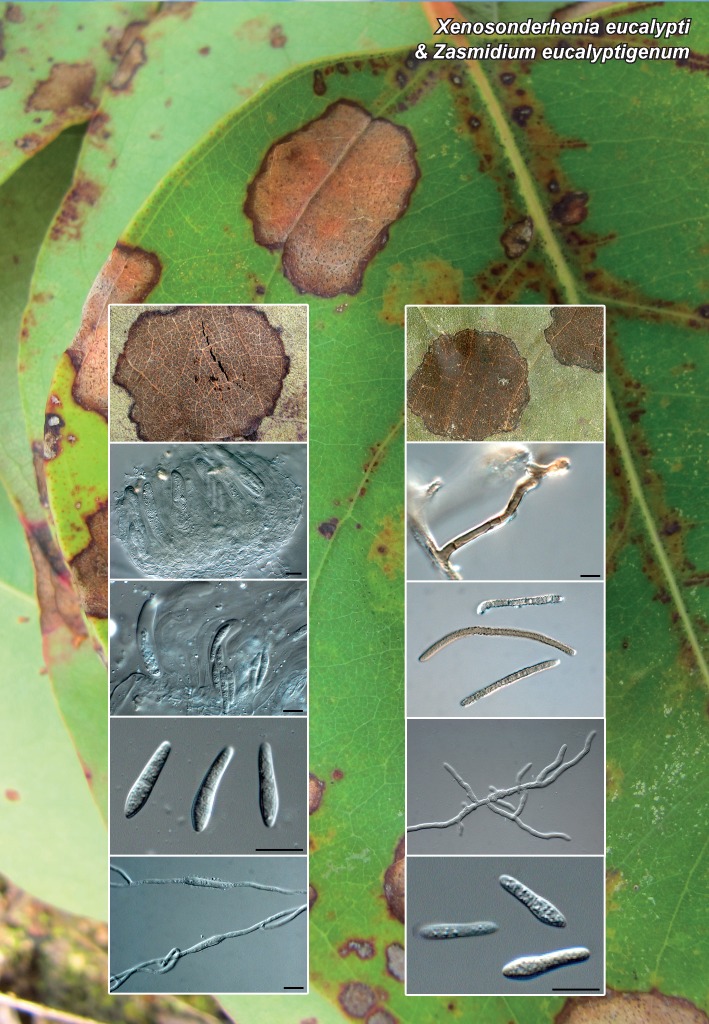
| Xenosonderhenia eucalypti |
| Zasmidium eucalyptigenum |
| Incertae sedis |
| Arxiella dolichandrae |
| Pleosporomycetidae, Pleosporales, Incertae |
| sedis |
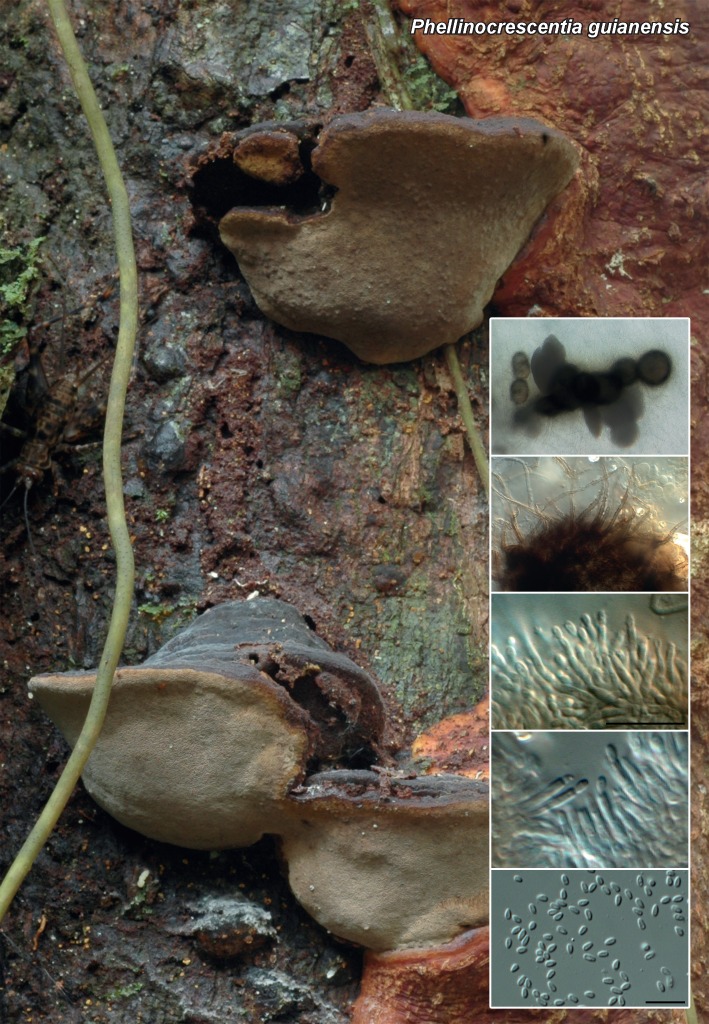
| Phellinocrescentia guianensis |
| Pleosporomycetidae, Pleosporales, Incertae |
| sedis, Corynesporascaceae |
| Corynespora endiandrae |
| Pleosporomycetidae, Pleosporales, Incertae |
| sedis, Roussoellaceae |
| Roussoella acaciae |
| Pleosporomycetidae, Pleosporales, |
| Massarineae, Bambusicolaceae |
| Neobambusicola strelitziae |
| Pleosporomycetidae, Pleosporales, |
| Massarineae, Massarinaceae |
| Stagonospora chrysopyla |
| Pleosporomycetidae, Pleosporales, |
| Pleosporineae, Didymellaceae |
| Phoma tamaricicola |
| Pleosporomycetidae, Pleosporales, |
| Pleosporineae, Phaeosphaeriaceae |
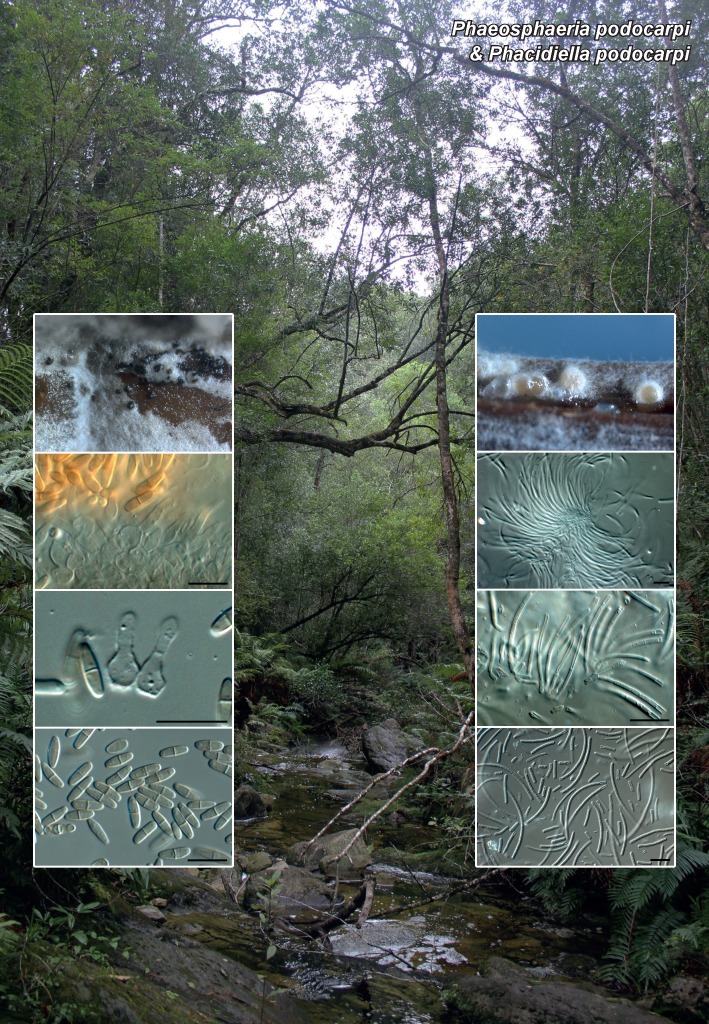
| Phaeosphaeria podocarpi |
| Xenophaeosphaeria grewiae |
| Pleosporomycetidae, Pleosporales, |
| Pleosporineae, Pleosporaceae |
| Comoclathris spartii |
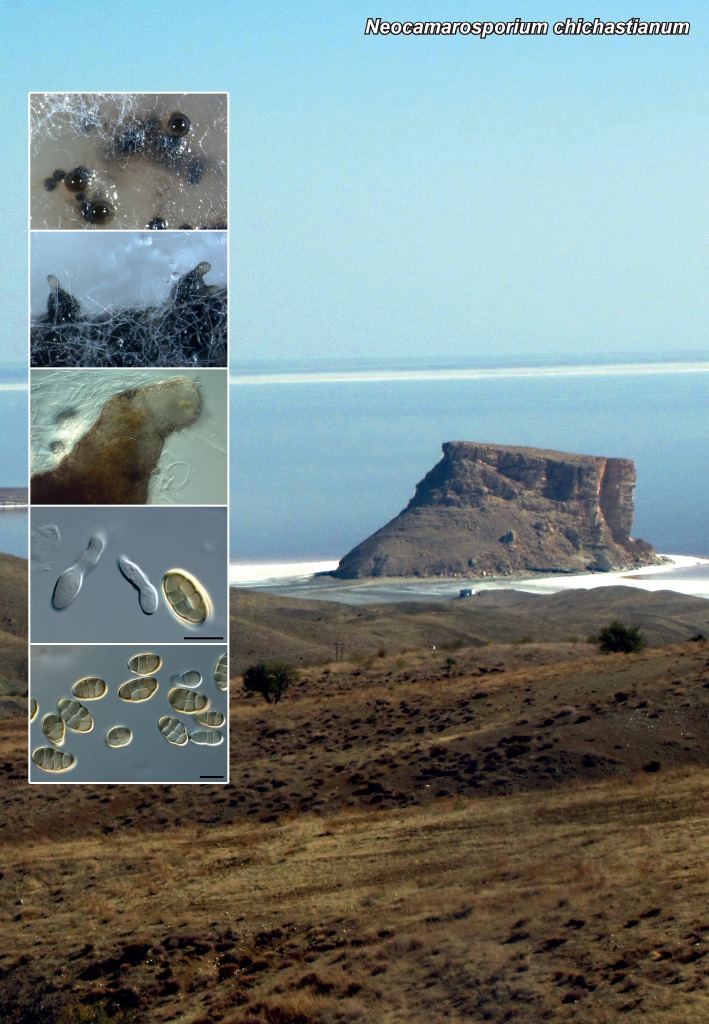
| Neocamarosporium chichastianum |
| Eurotiomycetes |
| Chaetothyriomycetidae, Chaetothyriales, |
| Trichomeriaceae |
| Trichomerium dioscoreae |
| Eurotiomycetidae, Eurotiales, Trichocomaceae |
| Penicillium coccotrypicola |
| Incertae sedis |
| Neocladophialophora quercina |
| Lecanoromycetes |
| Ostropomycetidae, Ostropales, Incertae sedis |
| Phacidiella podocarpi |
| Leotiomycetes |
| Helotiales, Hyaloscyphaceae |
| Crucellisporiopsis marquesiae |
| Pezizomycetes |
| Pezizomycetidae, Pezizales, Helvellaceae |
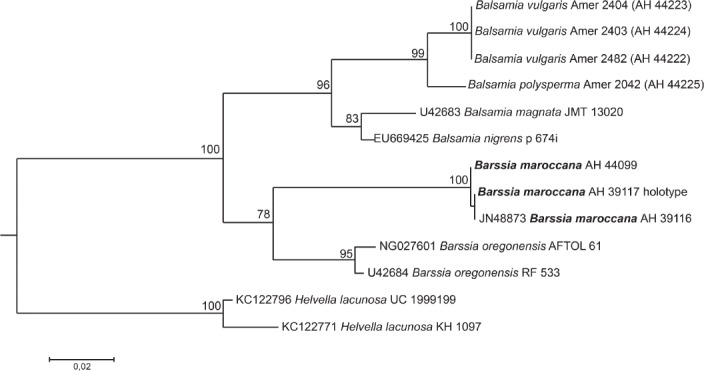
| Barssia maroccana |
| Sordariomycetes |
| Hypocreomycetidae, Hypocreales, |
| Clavicipitaceae |
| Collarina aurantiaca |
| Hypocreomycetidae, Hypocreales, Incertae |
| sedis |
| Acremoniopsis suttonii |
| Hypocreomycetidae, Incertae sedis |
| Neophysalospora eucalypti |
| Sordariomycetidae, Chaetosphaeriales, |
| Chaetosphaeriaceae |
| Codinaea pini |
| Dinemasporium ipomoeae |
| Sordariomycetidae, Diaporthales, |
| Diaporthaceae |
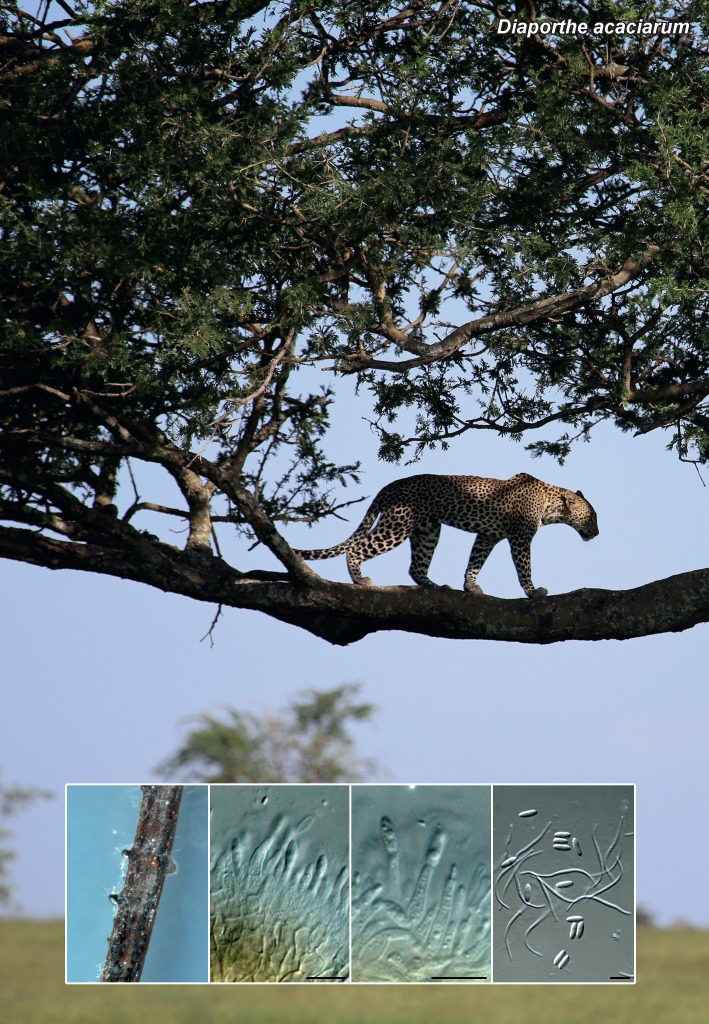
| Diaporthe acaciarum |
| Diaporthe phragmitis |
| Sordariomycetidae, Diaporthales, |
| Melanconidaceae |
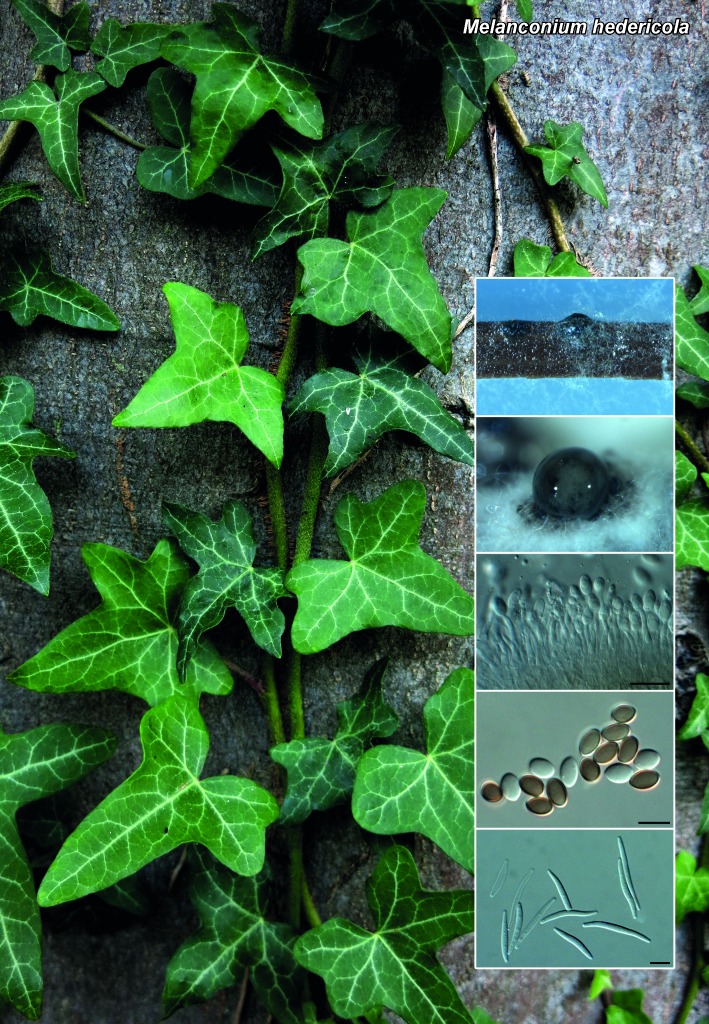
| Melanconium hedericola |
| Xylariomycetidae, Xylariales, |
| Amphisphaeriaceae |
| Seimatosporium pistaciae |
| BASIDIOMYCOTA |
| Agaricomycetes, Agaricomycetidae, Agaricales, |
| Marasmiaceae |
| Marasmius vladimirii |
| Agaricomycetes, Agaricomycetidae, Agaricales, |
| Pluteaceae |
| Pluteus albotomentosus |
| Pluteus extremiorientalis |
| Agaricomycetes, Agaricomycetidae, |
| Polyporales, Ganodermataceae |
| Ganoderma austroafricanum |
| Agaricomycetes, Incertae sedis, Cantharellales, |
| Hydnaceae |
| Sistotrema epiphyllum |
| CHROMISTA |
| Oomycota, Oomycetes, Pythiales, Pythiaceae |
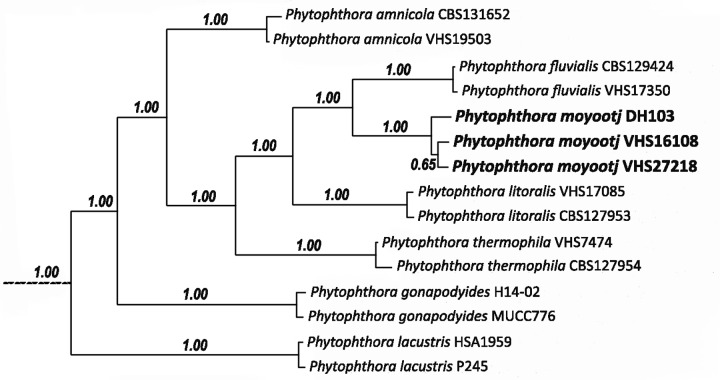
| Phytophthora moyootj |
Acknowledgments
Alejandra Giraldo acknowledges support from the Spanish Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad, grant CGL 2011-27185. Ekaterina F. Malysheva & Vera F. Malysheva thank Drs A. Kovalenko and N. Psurtseva (Komarov Botanical Institute) for help in collecting specimens. Financial support was provided by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (projects 13-04-00838a and 12-04-33018). Gabriel H. Moreno acknowledges financial support from the Spanish grant (project RTA2012-00007-00-00) and to Dr L. Monje and Mr A. Pueblas of the Department of Drawing and Scientific Photography at the Alcalá University for his help in the digital preparation of the photographs, and to Dr J. Rejos, curator of the AH herbarium for his assistance with the specimens examined in the present study. We also thank the technical staff, A. van Iperen (cultures), M. Vermaas (photographic plates), and M. Starink-Willemse (DNA isolation, amplification and sequencing) for their invaluable assistance. Cony Decock acknowledges the financial support received from the Belgian State – Belgian Federal Science Policy through the BCCM research programme and the FNRS / FRFC (convention FRFC 2.4544.10).
REFERENCES
- Aa HA van der, Vanev S. 2002. A revision of the species described in Phyllosticta. Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures, Utrecht, The Netherlands. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarado P, Moreno G, Manjón JL, et al. 2011. First molecular data on Delastria rosea, Fischerula macrospora and Hydnocystis piligera. Boletín de la Sociedad Micológica de Madrid 35: 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Antonín V, Ryoo R, Shin HD. 2012. Marasmioid and gymnopoid fungi of the Republic of Korea. 4. Marasmius sect. Sicci. Mycological Progress 11: 615–638. [Google Scholar]
- Ariyawansa HA, Phookamsak R, Tibpromma S, et al. 2014. A molecular and morphological reassessment of Diademaceae. The Scientific World Journal: doi.org/10.1155/2014/675348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arzanlou M, Groenewald JZ, Gams W, et al. 2007. Phylogenetic and morphotaxonomic revision of Ramichloridium and allied genera. Studies in Mycology 58: 57–93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aveskamp MM, Gruyter J de, Woudenberg JHC, et al. 2010. Highlights of the Didymellaceae: A polyphasic approach to characterize Phoma and related pleosporalean genera. Studies in Mycology 65: 1–60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensch K, Braun U, Groenewald JZ, et al. 2012. The genus Cladosporium. Studies in Mycology 72: 1–401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun U, Crous PW, Schubert K, et al. 2010. Some reallocations of Stenella species to Zasmidium. Schlechtendalia 20: 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Braun U, Hill CF. 2008. New species and new records of foliicolous hyphomycetes from New Zealand. Australasian Mycologist 27: 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Castellani E, Germano G. 1977. Le Stagonosporae graminicole. Annali della Facoltà di Scienze Agrarie della Universitá degli Studi di Torino 10: 1–135. [Google Scholar]
- Chomnunti P, Bhat DJ, Gareth Jones EB, et al. 2012. Trichomeriaceae, a new sooty mould family of Chaetothyriales. Fungal Diversity 56: 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Corner EJH. 1996. The agaric genera Marasmius, Chaetocalathus, Crinipellis, Heimiomyces, Resupinatus, Xerula and Xerulina in Malesia. Nova Hedwigia Beihefte 111: 1–175. [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Braun U, Groenewald JZ. 2007a. Mycosphaerella is polyphyletic. Studies in Mycology 58: 1–32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Braun U, Schubert K, et al. 2007b. Delimiting Cladosporium from morphologically similar genera. Studies in Mycology 58: 33–56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Shivas RG, et al. 2011. Fungal Planet description sheets: 69–91. Persoonia 26: 108–156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Schoch CL, Hyde KD, et al. 2009a. Phylogenetic lineages in the Capnodiales. Studies in Mycology 64: 17–47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Schubert K, Braun U, et al. 2007c. Opportunistic, human-pathogenic species in the Herpotrichiellaceae are phenotypically similar to saprobic or phytopathogenic species in the Venturiaceae. Studies in Mycology 58: 185–217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Shivas RG, Quaedvlieg W, et al. 2014. Fungal Planet description sheets: 214–280. Persoonia 32: 184–306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Summerell BA, Carnegie AJ, et al. 2009b. Unravelling Mycosphaerella: do you believe in genera? Persoonia 23: 99–118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Summerell BA, Shivas RG, et al. 2012a. Fungal Planet description sheets: 107–127. Persoonia 28: 138–182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Verkley GJM, Christensen M, et al. 2012b. How important are conidial appendages? Persoonia 28: 126–137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Wingfield MJ, Guarro J, et al. 2013. Fungal Planet description sheets: 154–213. Persoonia 31: 188–296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Wingfield MJ, Koch SH. 1990. New and interesting records of South African fungi. X. New records of Eucalyptus leaf fungi. South African Journal of Botany 56: 583–586. [Google Scholar]
- Cunnell GJ. 1957. Stagonospora spp. on Phragmites communis Trin. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 40: 443–445. [Google Scholar]
- Dai DQ, Jayarama Bhat D, Liu JK, et al. 2012. Bambusicola, a new genus from bamboo with asexual and sexual morphs. Cryptogamie, Mycologie 33: 363–379. [Google Scholar]
- Doidge EM. 1942. Revised descriptions of South African species of Phyllachora and related genera. Bothalia 4: 421–463. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis MB. 1971. Dematiaceous Hyphomycetes. CMI, Kew, England. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis MB. 1976. More Dematiaceous Hyphomycetes. CMI, Kew, England. [Google Scholar]
- Gams W. 1971. Cephalosporium-artige Schimmelpilze (Hyphomycetes). Stuttgart, Gustav Fischer Verlag. [Google Scholar]
- Gams W, Turham G. 1996. An extreme modification of Monocillium: Monocillium curvisetosum n. sp. Mycotaxon 59: 343–348. [Google Scholar]
- Gilkey HM. 1925. Five new hypogaeous fungi. Mycologia 17: 250–255. [Google Scholar]
- Gilkey HM. 1961. New species and revisions in the order Tuberales. Mycologia 53: 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Giordano L, Garbelotto M, Nicolotti G, et al. 2013. Characterization of fungal communities associated with the bark beetle Ips typographus varies depending on detection method, location, and beetle population levels. Mycological Progress 12: 127–140. [Google Scholar]
- Giraldo A, Gené J, Cano J, et al. 2012. Two new species of Acremonium from Spanish soils. Mycologia 104: 1456–1465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraldo A, Gené J, Cano J, et al. 2014. Acremonium with catenate elongate conidia: phylogeny of Acremonium fusidioides and related species. Mycologia 106: 328–338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girlanda M, Luppi-Mosca AM. 1998. Monocillium ligusticum, a new species from mycorrhizal roots in Mediterranean north Italy. Mycotaxon 67: 265–274. [Google Scholar]
- Glenn A, Bacon CW, Price R, et al. 1996. Molecular phylogeny of Acremonium and its taxonomic implications. Mycologia 88: 369–383. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes RR, Glienke C, Videira SIR, et al. 2013. Diaporthe: a genus of endophytic, saprobic and plant pathogenic fungi. Persoonia 31: 1–41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruyter J de,, Aveskamp MM, Woudenberg JHC, et al. 2009. Molecular phylogeny of Phoma and allied anamorph genera: Towards a re-classification of the Phoma complex. Mycological Research 113: 508–519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruyter J de, Woudenberg JHC, Aveskamp MM, et al. 2010. Systematic reappraisal of species in Phoma section Paraphoma, Pyrenochaeta and Pleurophoma. Mycologia 102: 1066–1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruyter J de,, Woudenberg JHC, Aveskamp MM, et al. 2013. Redisposition of Phoma-like anamorphs in Pleosporales. Studies in Mycology 75: 1–36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto A, Sato G, Matsuda T, et al. 2014. Molecular taxonomy of Dinemasporium and its allied genera. Mycoscience (in press) doi.org/10.1016/j.myc.2014.04.001. [Google Scholar]
- Hirooka Y, Rossman AY, Samuels GJ, et al. 2012. A monograph of Allantonectria, Nectria, and Pleonectria (Nectriaceae, Hypocreales, Ascomycota) and their pycnidial, sporodochial, and synnematous anamorphs. Studies in Mycology 71: 1–210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houbraken J, Samson RA. 2011. Phylogeny of Penicillium and the segregation of Trichocomaceae into three families. Studies in Mycology 70: 1–51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes SJ, Kendrick WB. 1968. New Zealand fungi 12. Menispora, Codinaea, Menisporopsis. New Zealand Journal of Botany 6: 323–375. [Google Scholar]
- Hyde KD, Jones EBG, Lui J-K, et al. 2013. Families of Dothideomycetes. Fungal Diversity 63: 1–313. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P, Seifert KA, Stone J, et al. 2014. Recommendations on generic names competing for use in Leotiomycetes (Ascomycota). IMA Fungus 5: 91–120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung T, Stukely MJC, Hardy GEStJ, et al. 2011. Multiple new Phytophthora species from ITS Clade 6 associated with natural ecosystems in Australia: evolutionary and ecological implications. Persoonia 26: 13–39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimbrough JW, Li LTL, Wu CG. 1996. Ultrastructural evidence for the placement of the truffle Barssia in the Helvellaceae (Pezizales). Mycologia 88: 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kornerup A, Wanscher JH. 1978. Methuen handbook of colour. 3rd ed London, Eyre Methuen. [Google Scholar]
- Kuthubutheen AJ, Nawawi A. l991. A key to Dictyochaeta and Codinaea species. Mycological Research 95: 1224–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Ławrynowicz M, Skirgiello A. 1984. Barssia, a new genus in Europe. Acta Mycologia 20: 277–280. [Google Scholar]
- Liu J-K, Phooksamsak R, Dai D-Q, et al. 2014. Roussoellaceae, a new pleosporalean family to accommodate the genera Neoroussoella gen. nov., Roussoella and Roussoellopsis. Phytotaxa 181: 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Lombard L, Leeuwen GCM van, Guarnaccia V, et al. 2014. Diaporthe species associated with Vaccinium, with specific reference to Europe. Phytopathologia Mediterranea 53: 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Mel’nik V, Lee S, Groenewald JZE, et al. 2004. New hyphomycetes from Restionaceae in fynbos: Parasarcopodium ceratocaryi gen. et sp. nov., and Rhexodenticula elegiae sp. nov. Mycological Progress 3: 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Minnis AM, Sundberg WJ. 2010. Pluteus section Celluloderma in the U.S.A. North American Fungi 5: 1–107. [Google Scholar]
- Montecchi A, Sarasini M. 2000. Funghi ipogei d’Europa. Associazione Micologica Bresadola. Fondazione Centro Studi Micologici; Trento. [Google Scholar]
- Nag Raj TR. 1993. Coelomycetous anamorphs with appendage-bearing conidia. Mycologue Publications, Waterloo,Ontario. [Google Scholar]
- Papendorf MC. 1967. Two new genera of soil fungi from South Africa. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 50: 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Park RF, Keane PJ, Wingfield MJ, et al. 2000. Fungal diseases of eucalypt foliage. In: Keane PJ, Kile GA, Podger FD, et al. (eds), Diseases and pathogens of eucalypts: 153–239 CSIRO publishing, Australia. [Google Scholar]
- Pascoe IG. 1990. Observations on ascus structure of Plectosphaera eucalypti (Phyllachoraceae). Mycological Research 94: 675–684. [Google Scholar]
- Percudani R, Trevisi A, Zambonelli A, et al. 1999. Molecular phylogeny of truffles (Pezizales: Terfeziaceae, Tuberaceae) derived from nuclear rDNA sequence analysis. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 13: 169–180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdomo H, Sutton DA, García D, et al. 2011. Spectrum of clinically relevant Acremonium species in the United States. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 49: 243–256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson SW, Pérez J, Vega FE, et al. 2003. Penicillium brocae, a new species associated with the coffee berry borer in Chipas, Mexico. Mycologia 95: 141–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips AJL, Alves A, Abdollahzadeh J, et al. 2013. The Botryosphaeriaceae: genera and species known from culture. Studies in Mycology 76: 51–167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt JI. 1979. The genus Penicillium and its teleomorphic states Eupenicillium and Talaromyces. Academic Press, London. [Google Scholar]
- Quaedvlieg W, Verkley GJM, Shin H-D, et al. 2013. Sizing up Septoria. Studies in Mycology 75: 307–390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaley AW. 2001. Hyaloseta nolinae, its anamorph Monocillium nolinae and Niesslia agavacearum, new members of the Niessliaceae, Hypocreales, from leaves of Agavaceae. Mycotaxon 79: 267–274. [Google Scholar]
- Rayner RW. 1970. A mycological colour chart. Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew, Surrey, UK. [Google Scholar]
- Reblová M, Winka K. 2000. Phylogeny of Chaetosphaeria and its anamorphs based on morphological and molecular data. Mycologia 92: 939–954. [Google Scholar]
- Ruscoe QW. 1970. Arxiella lunata sp. nov. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 55: 506–509. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert KA, Hoekstra ES, Frisvad JC, et al. 2004. Penicillium cecidicola, a new species on cynipid insect galls on Quercus pacifica in the western United States. Studies in Mycology 50: 517–523. [Google Scholar]
- Siboe GM, Kirk PM, Cannon PF. 1999. New dematiaceous hyphomycetes from Kenyan rare plants. Mycotaxon 73: 283–302. [Google Scholar]
- Sigler L, Gibas CFC, Kokotovic B, et al. 2010. Disseminated mycosis in veiled Chameleons (Chamaeleo calyptratus) caused by Chamaeleomyces granulomatis, a new fungus related to Paecilomyces viridis. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 48: 3182–3192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summerbell RC, Gueidan C, Schroers HJ, et al. 2011. Acremonium phylogenetic overview and revision of Gliomastix, Trichothecium and Sarocladium. Studies in Mycology 68: 139–162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung GH, Hywel-Jones NL, Sung JM, et al. 2007. Phylogenetic classification of Cordyceps and the clavicipitaceous fungi. Studies in Mycology 57: 5–63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton BC. 1980. The Coelomycetes: Fungi imperfecti with pycnidia, acervuli and stromata. Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew, Surrey, England. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H. 2000. Three new species of Marasmius section Sicci from eastern Honshu, Japan. Mycoscience 41: 313–321. [Google Scholar]
- Tehon LR. 1933. Notes on the parasitic fungi of Illinois. Mycologia 4: 237–257. [Google Scholar]
- Trappe JM. 1979. The orders, families, and genera of hypogenous Ascomycotina (truffles and their relatives). Mycotaxon 9: 297–340. [Google Scholar]
- Uecker FA. 1988. A world list of Phomopsis names with notes on nomenclature, morphology, and biology. Mycologia Memoirs 13: 1–231. [Google Scholar]
- Vellinga EC. 1990. Pluteus. In: Bas C, Kuyper ThW, Noordeloos ME, et al. (eds), Flora Agaricina Neerlandica, vol. 2: 31–55 Balkema, Rotterdam. [Google Scholar]
- Verkley GJM, Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, et al. 2004. Mycosphaerella punctiformis revisited: morphology, phylogeny, and epitypification of the type species of the genus Mycosphaerella (Dothideales, Ascomycota). Mycological Research 108: 1271–1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkley GJM, Quaedvlieg W, Shin HD, et al. 2013. A new approach to species delimitation in Septoria. Studies in Mycology 75: 213–305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannathes N, Desjardin DE, Hyde KD, et al. 2009. A monograph of Marasmius(Basidiomycota) from Northern Thailand based on morphological and molecular (ITS sequences) data. Fungal Diversity 37: 209–306. [Google Scholar]
- Warcup JH, Talbot PHB. 1962. Ecology and identity of mycelia isolated from soil. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 45: 495–518. [Google Scholar]
- Weresub LK, LeClair PM. 1971. On Papulaspora and bulbilliferous basidiomycetes Burgoa and Minimedusa. Canadian Journal of Botany 49: 2203–2213. [Google Scholar]
- Whitton SR, McKenzie EHC, Hyde KD. 2000. Dictyochaeta and Dictyochaetopsis species from the Pandanaceae. Fungal Diversity 4: 133–158. [Google Scholar]
- Wijayawardene NN, Crous PW, Kirk PM, et al. 2014. Naming and outline of Dothideomycetes – 2014. Fungal Diversity (in press). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikee S, Lombard L, Nakashima C, et al. 2013. A phylogenetic re-evaluation of Phyllosticta (Botryosphaeriales). Studies in Mycology 76: 1–29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woudenberg JHC, Groenewald JZ, Binder M, et al. 2013. Alternaria redefined. Studies in Mycology 75: 171–212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zare R, Gams W, Evans HC. 2001. A revision of Verticillium section Prostrata. V. The genus Pochonia, with notes on Rotiferophthora. Nova Hedwigia 73: 51–86. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y, Crous PW, Schoch CL, et al. 2012. Pleosporales. Fungal Diversity 53: 1–221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y, Schoch CL, Fournier J, et al. 2009. Multi-locus phylogeny of Pleosporales: a taxonomic, ecological and evolutionary re-evaluation. Studies in Mycology 64: 85–102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]