Abstract
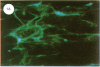
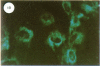
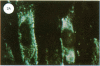
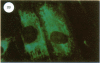
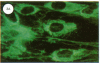
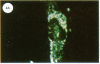
Specific antibodies against types I and III collagens and procollagens were used to localize these proteins in cultured human cells. These studies indicate that the same cell makes both proteins. No type III procollagen synthesis was observed in cells from two patients with two patients with the Ehlers-Danlos type IV syndrome.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker U., Nowack H., Gay S., Timpl R. Production and specificity of antibodies against the aminoterminal region in type III collagen. Immunology. 1976 Jul;31(1):57–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church R. L., Tanzer M. L., Lapiere C. M. Identification of two distinct species of procollagen synthesized by a clonal line of calf dermatosparactic cells. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 8;244(136):188–190. doi: 10.1038/newbio244188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E. H., Jr (Alpha1(3))3 human skin collagen. Release by pepsin digestion and preponderance in fetal life. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3225–3231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E. H., Jr, Munderloh N. H. Isolation and characterization of CNBr peptides of human (alpha 1 (III) )3 collagen and tissue distribution of (alpha 1 (I) )2 alpha 2 and (alpha 1 (III) )3 collagens. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 25;250(24):9304–9312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay S., Balleisen L., Remberger K., Fietzek P. P., Adelmann B. C., Kühn K. Immunohistochemical evidence for the presence of collagen type III in human arterial walls, arterial thrombi, and in leukocytes, incubated with collagen in vitro. Klin Wochenschr. 1975 Oct 1;53(19):899–902. doi: 10.1007/BF01468981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay S., Fietzek P. P., Remberger K., Eder M., Kühn K. Liver cirrhosis: immunofluorescence and biochemical studies demonstrate two types of collagen. Klin Wochenschr. 1975 Mar 1;53(5):205–208. doi: 10.1007/BF01468808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay S., Müller P. K., Meigel W. N., Kühn K. Polymorphie des Kollagens. Neue Aspekte für Struktur and Funktion des Bindegewebes. Hautarzt. 1976 May;27(5):196–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg B., Epstein E. H., Jr, Sherr C. J. Precursors of collagen secreted by cultured human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3655–3659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Todaro G. J., Goldberg B. Collagen synthesis in fibroblasts transformed by oncogenic viruses. Nature. 1966 Feb 26;209(5026):916–917. doi: 10.1038/209916a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn E., Nowack H., GOTZE D., Timpl R. H-2-linked genetic control of antibody response to soluble calf skin collagen in mice. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Apr;5(4):288–291. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A. Isolation of a collagen from basement membranes containing three identical - chains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Oct 1;45(1):226–234. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layman D. L., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R. The nature of the collagen synthesized by cultured human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):454–458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein J. R., Byers P. H., Smith B. D., Martin G. R. Identification of the collagenous proteins synthesized by cultured cells from human skin. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 22;14(8):1589–1594. doi: 10.1021/bi00679a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein J. R., Martin G. R., Kohn L. D., Byers P. H., McKusick V. A. Defect in conversion of procollagen to collagen in a form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Science. 1973 Oct 19;182(4109):298–300. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4109.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKusick V. A. Editorial notes: Molecular defects in collagen. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Apr;82(4):585–586. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-4-585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Epstein E. H., Jr, Piez K. A. Identification of three genetically distinct collagens by cyanogen bromide cleavage of insoluble human skin and cartilage collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Mar 19;42(6):1024–1029. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Matukas V. J. Biosynthesis of collagen. The biochemist's view. Fed Proc. 1974 May;33(5):1197–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penttinen R. P., Lichtenstein J. R., Martin G. R., McKusick V. A. Abnormal collagen metabolism in cultured cells in osteogenesis imperfecta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):586–589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky B. Regulation of collagen secretion by ascorbic acid in 3T3 and chick embryo fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Dec 4;49(5):1343–1350. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90614-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky B. The effect of ascorbic acid on collagen polypeptide synthesis and proline hydroxylation during the growth of cultured fibroblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Sep;152(1):318–328. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90221-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope F. M., Martin G. R., Lichtenstein J. R., Penttinen R., Gerson B., Rowe D. W., McKusick V. A. Patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV lack type III collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1314–1316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. D., Byers P. H., Martin G. R. Production of procollagen by human fibroblasts in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3260–3262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Wick G., Furthmayr H., Lapiére C. M., Kühn K. Immunochemical properties of procollagen from dermatosparactic calves. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 1;32(3):584–591. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02645.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]