Abstract
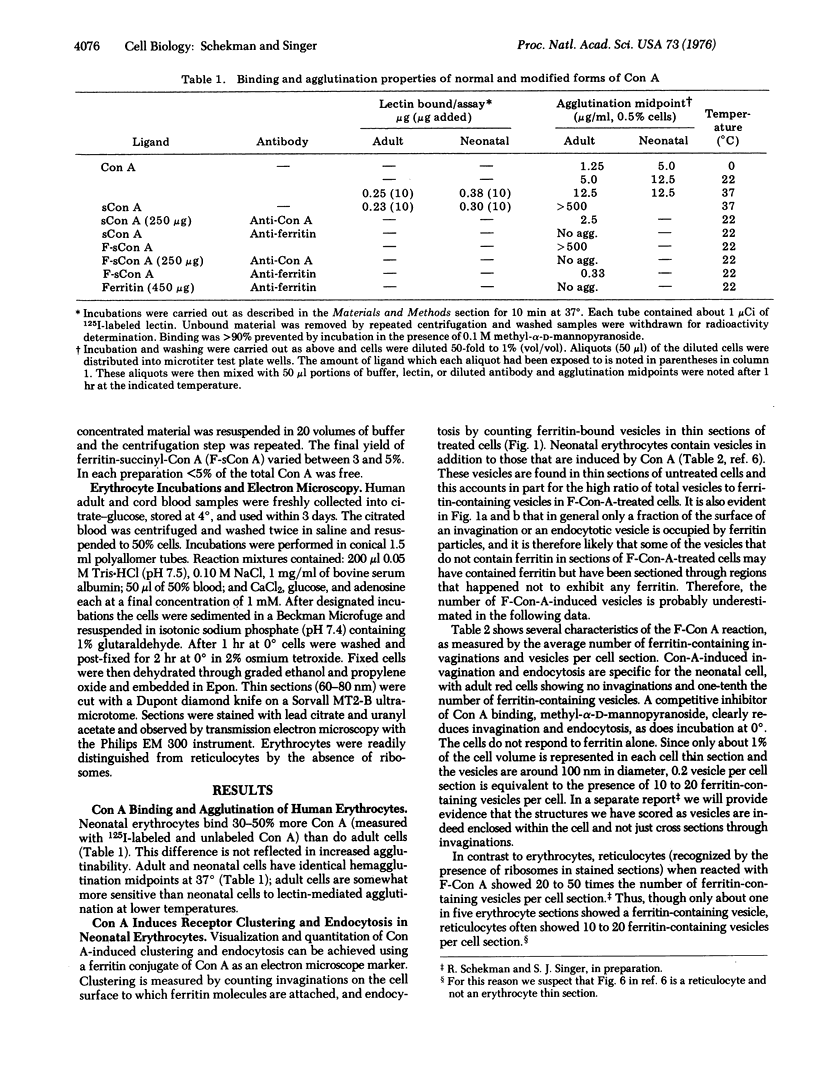
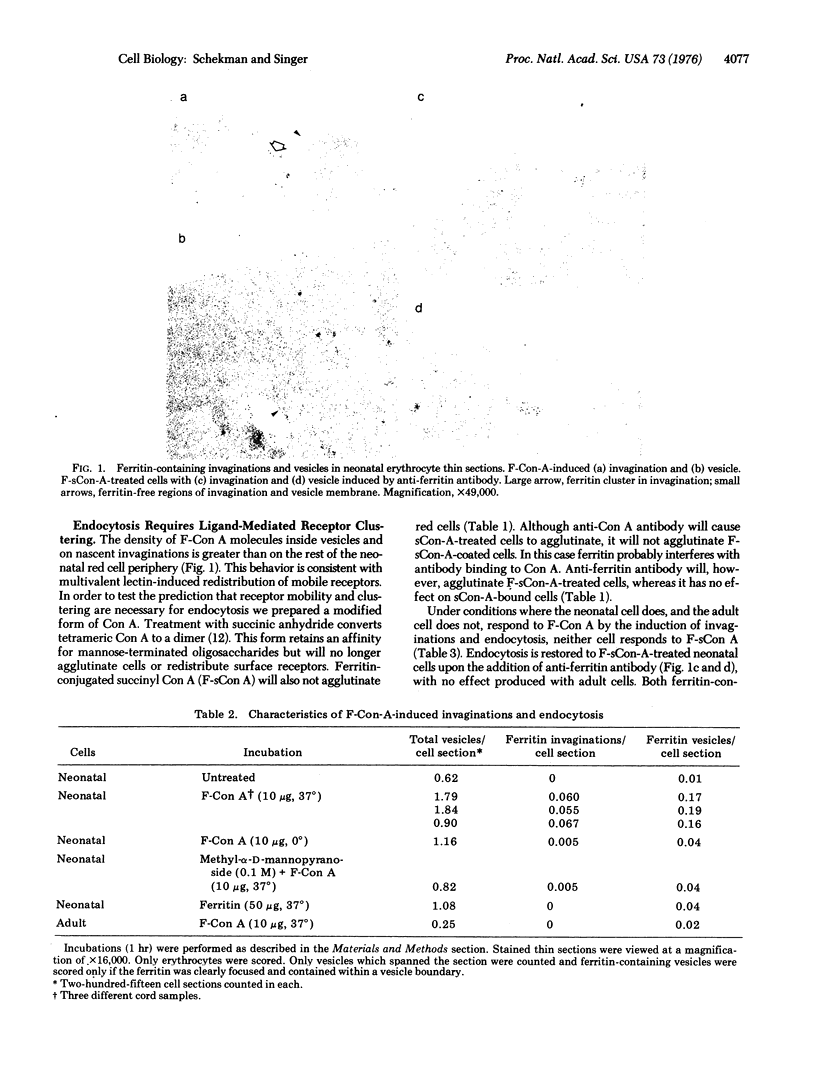
Concanavalin A (Con A) is taken up by endocytosis in mature erythrocytes of newborn humans but not in adult red cells. Thin sections of neonatal cells incubated with ferritin-conjugated Con A at 37 degrees show ferritin clusters on invaginations at the surface and in intracellular vesicles, but such invaginations and vesicles are absent with adult cells. The endocytosis induced by ferritin-conjugated Con A is inhibited at 0 degrees, and by methyl-alpha-D-mannopyranoside at 37 degrees. Succinylation of Con A, which is known to convert it from the tetrameric to dimeric form, renders Con A inactive in cell agglutination and endocytotic vesicle formation, presumably by reducing the number of oligosaccharide chains simultaneously bound by a single Con A molecule. Ferritin-conjugated succinyl Con A binds to neonatal erythrocytes but does not induce endocytosis; if, however, antibodies to ferritin are now added, endocytosis occurs. These results are consistent with a greater lateral mobility of at least a fraction of Con A recptors in the membrane of the intact neonatal erythrocyte compared to the adult. The results also support the hypothesis that the clustering of receptors is obligatory for endocytosis to occur. No discernible difference was found in the sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel patterns of the membrane proteins of the neonatal and adult cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal B. B., Goldstein I. J. Physical and chemical characterization of concanavalin A, the hemagglutinin from jack bean (Canavalia ensiformis). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 21;133(2):376–379. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Bassat I., Bensch K. G., Schrier S. L. Drug-induced erythrocyte membrane internalization. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1833–1844. doi: 10.1172/JCI106985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanton P. L., Martin J., Haberman S. Pinocytotic response of circulating erythrocytes to specific blood grouping antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jun;37(3):716–728. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.3.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L. N., Oliver J. M. Changes in number, mobility, and topographical distribution of lectin receptors during maturation of chick erythroid cells. J Cell Biol. 1976 Jun;69(3):647–658. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edidin M. Rotational and translational diffusion in membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1974;3(0):179–201. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.03.060174.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgsaeter A., Branton D. Intramembrane particle aggregation in erythrocyte ghosts. I. The effects of protein removal. J Cell Biol. 1974 Dec;63(3):1018–1036. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.3.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frye L. D., Edidin M. The rapid intermixing of cell surface antigens after formation of mouse-human heterokaryons. J Cell Sci. 1970 Sep;7(2):319–335. doi: 10.1242/jcs.7.2.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. A., Marquardt M. D. Erythrocyte morphology and clustering of fluorescent anti-A immunoglobulin. Nature. 1975 Nov 27;258(5533):346–347. doi: 10.1038/258346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunther G. R., Wang J. L., Yahara I., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Concanavalin A derivatives with altered biological activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1012–1016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY H. B., SOBER H. A. A simple chromatographic method for preparation of gamma globulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Jan;103:250–252. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen B. Redistribution of surface-bound polyelectrolytes on erythrocytes. Nature. 1975 Nov 27;258(5533):344–345. doi: 10.1038/258344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loor F., Forni L., Pernis B. The dynamic state of the lymphocyte membrane. Factors affecting the distribution and turnover of surface immunoglobulins. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Jun;2(3):203–212. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Painter R. G. Anionic sites of human erythrocyte membranes. II. Antispectrin-induced transmembrane aggregation of the binding sites for positively charged colloidal particles. J Cell Biol. 1973 Nov;59(2 Pt 1):395–406. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Singer S. J. The distribution and asymmetry of mammalian cell surface saccharides utilizing ferritin-conjugated plant agglutinins as specific saccharide stains. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jan;60(1):236–248. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.1.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter R. G., Sheetz M., Singer S. J. Detection and ultrastructural localization of human smooth muscle myosin-like molecules in human non-muscle cells by specific antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1359–1363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. Molecular biology of cellular membranes with applications to immunology. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):1–66. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. The molecular organization of membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):805–833. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. A review. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Detmers P. Actin in erythrocyte ghosts and its association with spectrin. Evidence for a nonfilamentous form of these two molecules in situ. J Cell Biol. 1975 Sep;66(3):508–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.3.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



