Abstract
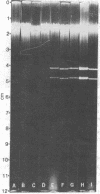
Mitochondrial DNAs were prepared from maize lines with normal cytoplasm and with the T, C, S, and EP sources of male-sterile cytoplasms. Agarose gel electrophoresis of these preparations revealed a main high-molecular-weight DNA band. In addition, the S cytoplasm was characterized by the presence of two faster migrating DNAs of molecular weight 3.42 to 3.48 × 106 and 4.01 to 4.10 × 106. Electron microscopy showed these unique DNAs to be of different length, but their molecular configuration was not clearly established. It is possible that these unique DNAs represent physical evidence of an episomal system previously postulated to function in the S male-sterile cytoplasm.
Keywords: episomal DNA, plasmid DNA, cytoplasmic inheritance
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Griffiths D. E., Lancashire W. E., Zanders E. D. Evidence for an extra-chromosomal element involved in mitochondrial function: a mitochondrial episome? FEBS Lett. 1975 May 1;53(2):126–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helling R. B., Goodman H. M., Boyer H. W. Analysis of endonuclease R-EcoRI fragments of DNA from lambdoid bacteriophages and other viruses by agarose-gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1235–1244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1235-1244.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levings C. S., 3rd, Pring D. R. Restriction endonuclease analysis of mitochondrial DNA from normal and Texas cytoplasmic male-sterile maize. Science. 1976 Jul 9;193(4248):158–160. doi: 10.1126/science.193.4248.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson U., Mulder C., Deluis H., Sharp P. A. Cleavage of adenovirus type 2 DNA into six unique fragments by endonuclease R-RI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):200–204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Air G. M., Barrell B. G., Brown N. L., Coulson A. R., Fiddes C. A., Hutchison C. A., Slocombe P. M., Smith M. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage phi X174 DNA. Nature. 1977 Feb 24;265(5596):687–695. doi: 10.1038/265687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A., Laughnan J. R. Instability of s male-sterile cytoplasm in maize. Genetics. 1972 Aug;71(4):607–620. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.4.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., Davis R. W. Studies on the cleavage of bacteriophage lambda DNA with EcoRI Restriction endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 25;91(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuring R. W., Sanders J. P., Borst P. A freeze-squeeze method for recovering long DNA from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 26;66(1):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90739-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]