Abstract
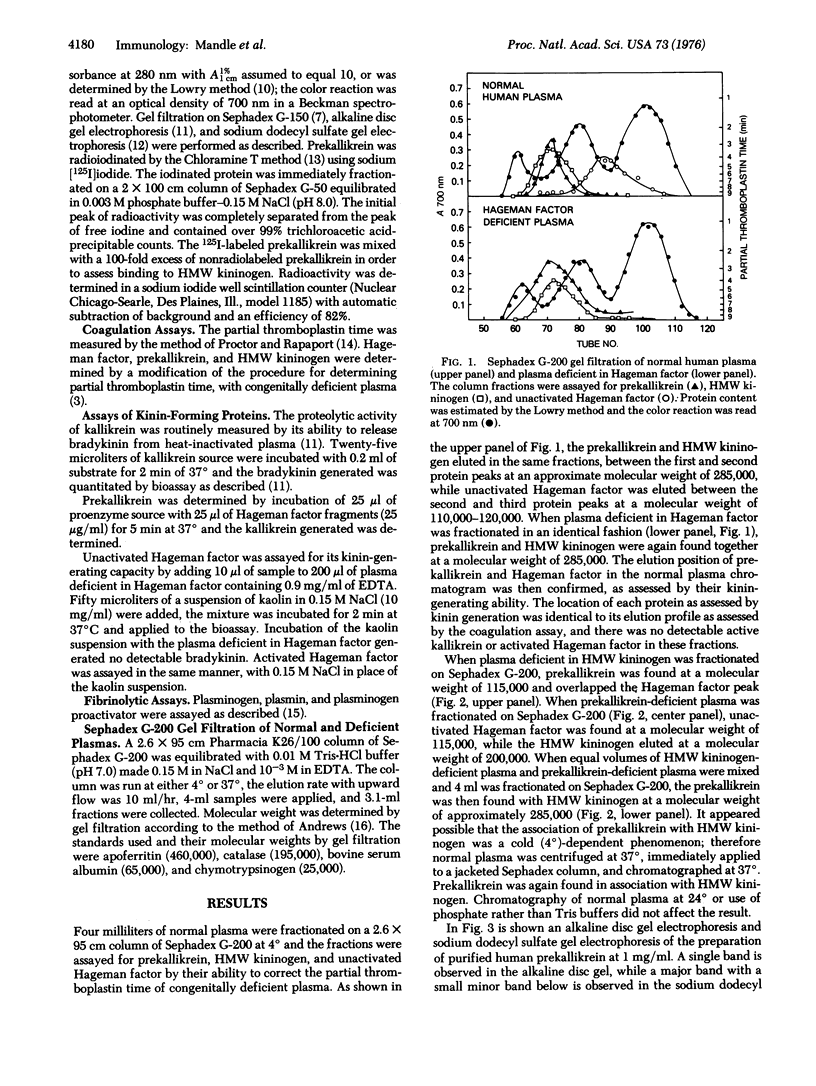
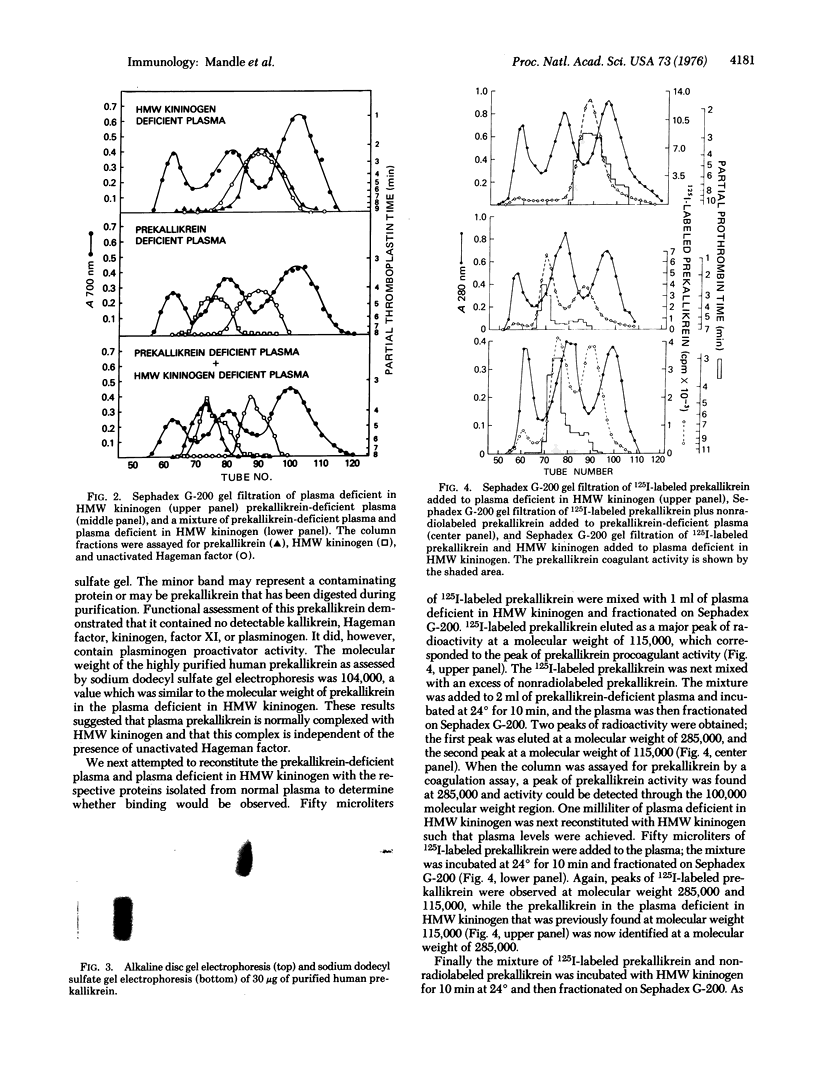
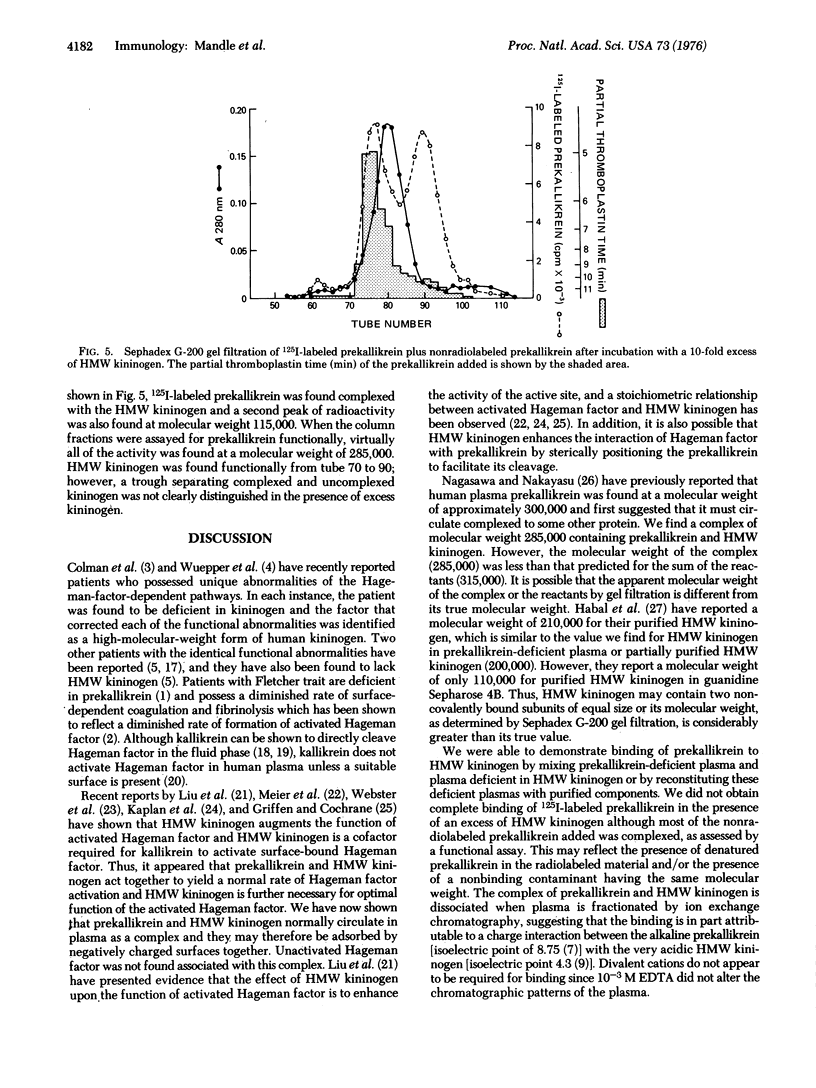
Prekallikrein and high-molecular-weight kininogen were found associated in normal human plasma at a molecular weight of 285,000 as assessed by gel filtration on Sephadex G-200. The molecular weight of prekallikrein in plasma that is deficient in high-molecular-weight kininogen was 115,000. This prekallikrein could be isolated at a molecular weight of 285,000 after plasma deficient in high-molecular-weight kininogen was combined with plasma that is congenitally deficient in prekallikrein. Addition of purified 125I-labeled prekallikrein and high-molecular-weight kininogen to the respective deficient plasma yielded a shift in the molecular weight of prekallikrein, and complex formation could be demonstrated by incubating prekallikrein with high-molecular weight kininogen. This study demonstrates that prekallikrein and high-molecular-weight kininogen are physically associated in plasma as a noncovalently linked complex and may therefore be adsorbed together during surface activation of Hageman factor. The complex is disrupted when these proteins are isolated by ion exchange chromatography.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axén R., Porath J., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of peptides and proteins to polysaccharides by means of cyanogen halides. Nature. 1967 Jun 24;214(5095):1302–1304. doi: 10.1038/2141302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdasarian A., Lahiri B., Colman R. W. Origin of the high molecular weight activator of prekallikrein. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7742–7747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Revak S. D., Wuepper K. D. Activation of Hageman factor in solid and fluid phases. A critical role of kallikrein. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1564–1583. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W., Bagdasarian A., Talamo R. C., Scott C. F., Seavey M., Guimaraes J. A., Pierce J. V., Kaplan A. P. Williams trait. Human kininogen deficiency with diminished levels of plasminogen proactivator and prekallikrein associated with abnormalities of the Hageman factor-dependent pathways. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1650–1662. doi: 10.1172/JCI108247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson V. H., Glueck H. I., Miller M. A., Movat H. Z., Habal F. Kininogen deficiency in Fitzgerald trait: role of high molecular weight kininogen in clotting and fibrinolysis. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Feb;87(2):327–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H., Cochrane C. G. Mechanisms for the involvement of high molecular weight kininogen in surface-dependent reactions of Hageman factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2554–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habal F. M., Movat H. Z., Burrowes C. E. Isolation of two functionally different kininogens from human plasma--separation from proteinase inhibitors and interaction with plasma kallikrein. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Aug 15;23(16):2291–2303. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90558-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habal F. M., Underdown B. J., Movat H. Z. Further characterization of human plasma kininogens. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Jun 15;24(11-12):1241–1243. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. A pre-albumin activator of prekallikrein. J Immunol. 1970 Oct;105(4):802–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. The fibrinolytic pathway of human plasma. Isolation and characterization of the plasminogen proactivator. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1378–1393. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Kay A. B., Austen K. F. A prealbumin activator of prekallikrein. 3. Appearance of chemotactic activity for human neutrophils by the conversion of human prekallikrein to kallikrein. J Exp Med. 1972 Jan;135(1):81–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Meier H. L., Mandle R., Jr The Hageman factor dependent pathways of coagulation, fibrinolysis, and kinin-generation. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1976 Jul;3(1):1–26. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1087162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa S., Nakayasu T. Human plasma prekallikrein as a protein complex. J Biochem. 1973 Aug;74(2):401–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROCTOR R. R., RAPAPORT S. I. The partial thromboplastin time with kaolin. A simple screening test for first stage plasma clotting factor deficiencies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1961 Sep;36:212–219. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/36.3.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Ratnoff O. D., Waldmann R., Abraham J. P. Fitzgerald Trait: Deficiency of a Hitherto Unrecognized Agent, Fitzgerald Factor, Participating in Surface-Mediated Reactions of Clotting, Fibrinolysis, Generation of Kinins, and the Property of Diluted Plasma Enhancing Vascular Permeability (PF/Dil). J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):1082–1089. doi: 10.1172/JCI108009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster M. E., Guimaraes J. A., Kaplan A. P., Colman R. W., Pierce J. V. Activation of surface-bound Hageman factor: pre-eminent role of high molecular weight kininogen and evidence for a new factor. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1976;70(00):285–299. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3267-1_35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. S., Gallin J. I., Kaplan A. P. Fletcher factor deficiency. A diminished rate of Hageman factor activation caused by absence of prekallikrein with abnormalities of coagulation, fibrinolysis, chemotactic activity, and kinin generation. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):622–633. doi: 10.1172/JCI107597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuepper K. D., Miller D. R., Lacombe M. J. Flaujeac trait. Deficiency of human plasma kininogen. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1663–1672. doi: 10.1172/JCI108248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuepper K. D. Prekallikrein deficiency in man. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1345–1355. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




