Abstract
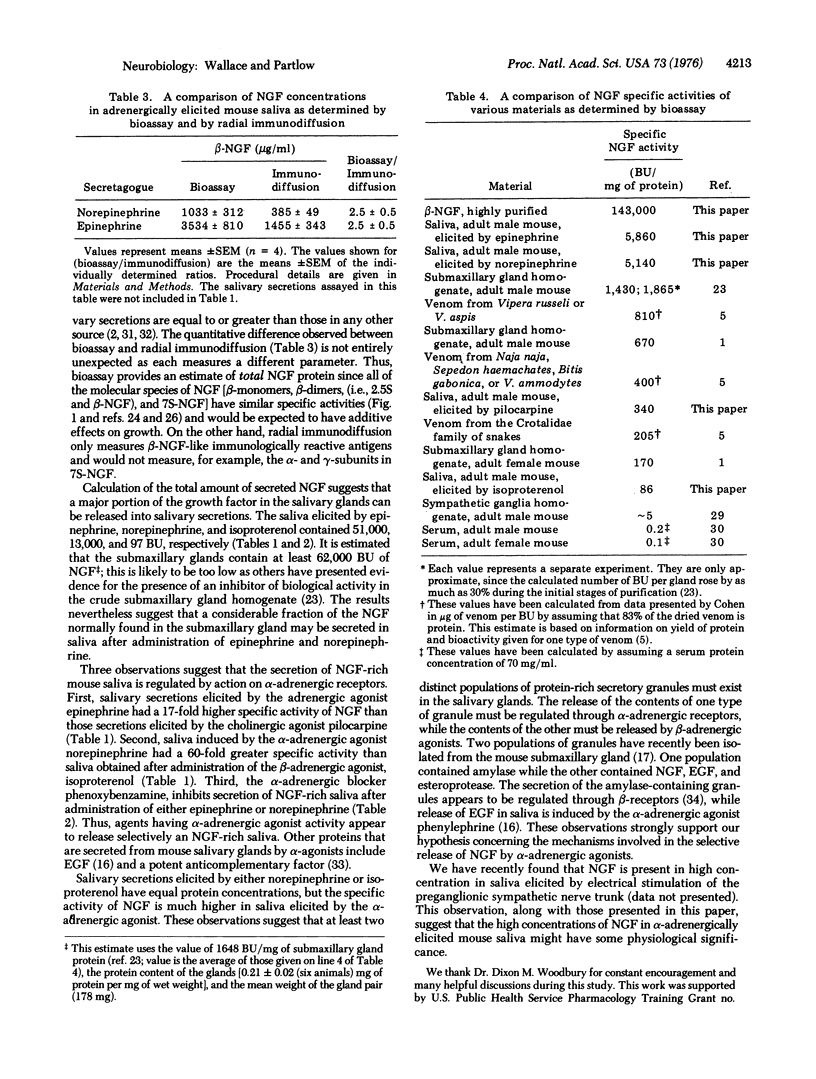
Nerve growth factor has been quantified by both bioassay and radial immunodiffusion in mouse saliva elicited by several secretagogues. The concentrations by bioassay of nerve growth factor in both epinephrine- and norepinephrine-induced saliva (3400 and 900 mug/ml, respectively) are higher than reported in any other source. In contrast, the concentrations of nerve growth factor in isoproterenol- and pilocarpine-induced saliva are relatively low (17 and 2 mug/ml, respectively). The specific activity of the salivary nerve growth factor was 41, 36, 2, and 0.6 mug/mg of protein in secretions elicited by epinephrine, norepinephrine, pilocarpine, and isoproterenol, respectively. Salivation after administration of either epinephrine or norepinephrine was completely inhibited by the alpha-adrenergic blocker, phenoxybenzamine. These results suggest that the release of saliva rich in nerve growth factor is primarily regulated through alpha-adrenergic receptors.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BING J. LOCATION OF RENIN (OR A RENIN-LIKE SUBSTANCE) IN THE SUBMAXILLARY GLANDS OF ALBINO MICE. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64:203–212. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.64.2.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks B. E., Banthorpe D. V., Charlwood K. A., Pearce F. L., Vernon C. A., Edwards D. C. Distribution and immunology of mammalian nerve growth factor. Nature. 1973 Dec 21;246(5434):503–504. doi: 10.1038/246503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byyny R. L., Orth D. N., Cohen S., Doyne E. S. Epidermal growth factor: effects of androgens and adrenergic agents. Endocrinology. 1974 Sep;95(3):776–782. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-3-776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. Purification and metabolic effects of a nerve growth-promoting protein from snake venom. J Biol Chem. 1959 May;234(5):1129–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Levi-Montalcini R. A NERVE GROWTH-STIMULATING FACTOR ISOLATED FROM SNAKE VENOM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Sep;42(9):571–574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.9.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. PURIFICATION OF A NERVE-GROWTH PROMOTING PROTEIN FROM THE MOUSE SALIVARY GLAND AND ITS NEURO-CYTOTOXIC ANTISERUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Mar;46(3):302–311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.3.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dische Z., Kahn N., Rothschild C., Danilchenko A., Licking J., Wang S. C. Glycoproteins of submaxillary saliva of the cat: differences in composition produced by sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve stimulation. J Neurochem. 1970 May;17(5):649–658. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb00544.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton E. L. Tissue culture assay of nerve growth factor and of the specific antiserum. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Mar;59(3):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90645-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN M. N., BURDMAN J. A. STUDIES OF THE NERVE GROWTH FACTOR IN SUBMANDIBULAR GLANDS OF FEMALE MICE TREATED WITH TESTOSTERONE. Anat Rec. 1965 Feb;151:199–207. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091510210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry I. A. Developmental changes in tissue and plasma concentrations of the biologically active species of nerve growth factor in the mouse, by using a two-site radioimmunoassay. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1265–1272. doi: 10.1042/bj1281265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUNQUEIRA L. C., FAJER A. Biochemical and histochemical observations on the sexual dimorphism of mice submaxillary glands. J Cell Physiol. 1949 Aug;34(1):129-58, incl 6 pl. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030340109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. G., Gorden P., Kopin I. J. A sensitive radioimmunoassay for 7S nerve growth factor antigens in serum and tissues. J Neurochem. 1971 Dec;18(12):2355–2362. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn N., Mandel I., Licking J., Wasserman A., Morea D. Comparison of the effects of parasympathetic nervous stimulation on cat submaxillary gland saliva. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jan;130(1):314–318. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVI-MONTALCINI R., ANGELETTI P. U. Growth control of the sympathetic system by a specific protein factor. Q Rev Biol. 1961 Jun;36:99–108. doi: 10.1086/403331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVI-MONTALCINI R., COHEN S. Effects of the extract of the mouse submaxillary salivary glands on the sympathetic system of mammals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Mar 29;85:324–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb49963.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVI-MONTALCINI R., MEYER H., HAMBURGER V. In vitro experiments on the effects of mouse sarcomas 180 and 37 on the spinal and sympathetic ganglia of the chick embryo. Cancer Res. 1954 Jan;14(1):49–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masseyeff R. F., Zisswiller M. C. A versatile method of radial immunodiffusion assay employing microquantities of antiserum. Anal Biochem. 1969 Aug;30(2):180–189. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90388-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelakis A. M., Yoshida H., Menzie J., Murakami K., Inagami T. A radioimmunoassay for the direct measurement of renin in mice and its application to submaxillary gland and kidney studies. Endocrinology. 1974 Apr;94(4):1101–1105. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-4-1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. B., Jr, Mobley W. C., Shooter E. M. Proteolytic modification of the beta nerve growth factor protein. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 12;13(4):833–840. doi: 10.1021/bi00701a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partlow L. M., Larrabee M. G. Effects of a nerve-growth factor, embryo age and metabolic inhibitors on growth of fibres and on synthesis of ribonucleic acid and protein in embryonic sympathetic ganglia. J Neurochem. 1971 Nov;18(11):2101–2118. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb05069.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasquini F., Petris A., Sbaraglia G., Scopelliti R., Cenci G., Frati L. Biological activities in the granules isolated from the mouse submaxillary gland. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Jun;86(2):233–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90708-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce F. L., Banthorpe D. V., Cook J. M., Vernon C. A. Adsorption of nerve growth factor onto surfaces. Implications for the assay in tissue culture. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 1;32(3):569–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohto P. Effect of isoprenaline, pilocarpine and prenylamine on amylase secretion in rat parotid saliva. J Oral Ther Pharmacol. 1968 May;4(6):467–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turkington R. W., Males J. L., Cohen S. Synthesis and storage of epithelial-epidermal growth factor in submaxillary gland. Cancer Res. 1971 Mar;31(3):252–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace L. J., Partlow L. M., Ellis M. E., Woodbury D. M. Alpha-adrenergic regulation of the secretion of an anticomplementary factor in mouse saliva. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 May;152(1):99–104. doi: 10.3181/00379727-152-39337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wlodawer A., Hodgson K. O., Shooter E. M. Crystallization of nerve growth factor from mouse submaxillary glands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):777–779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]