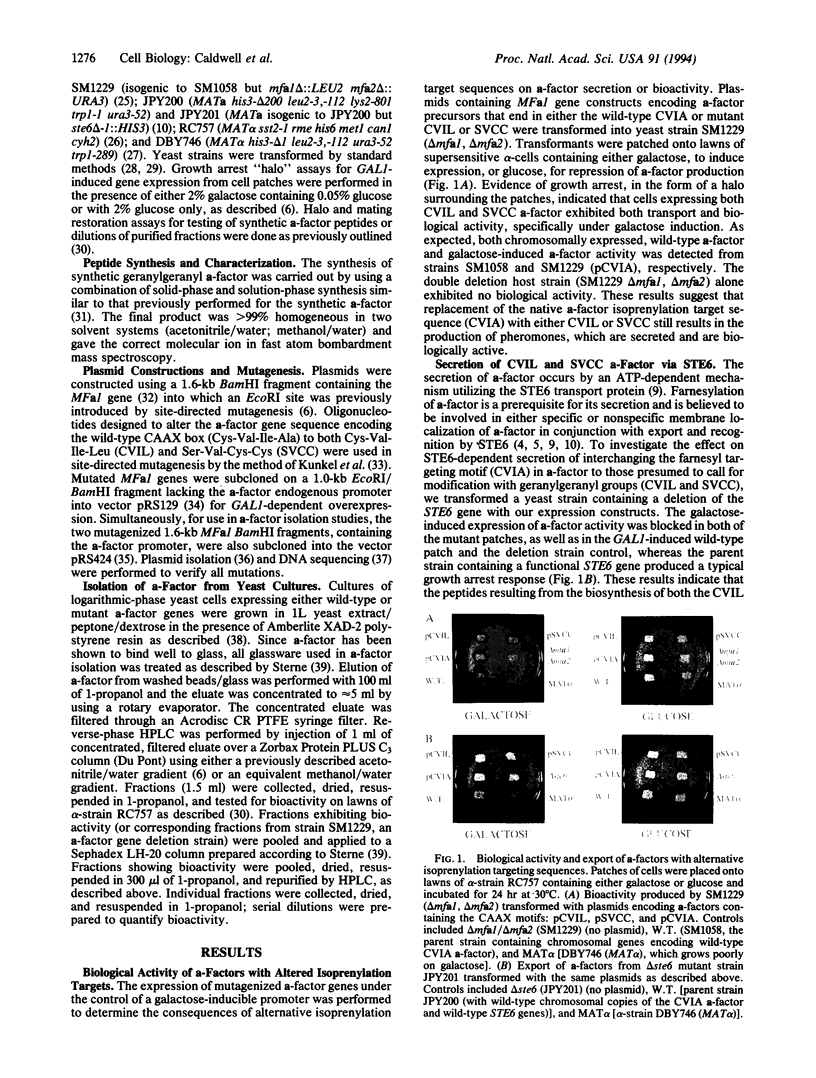
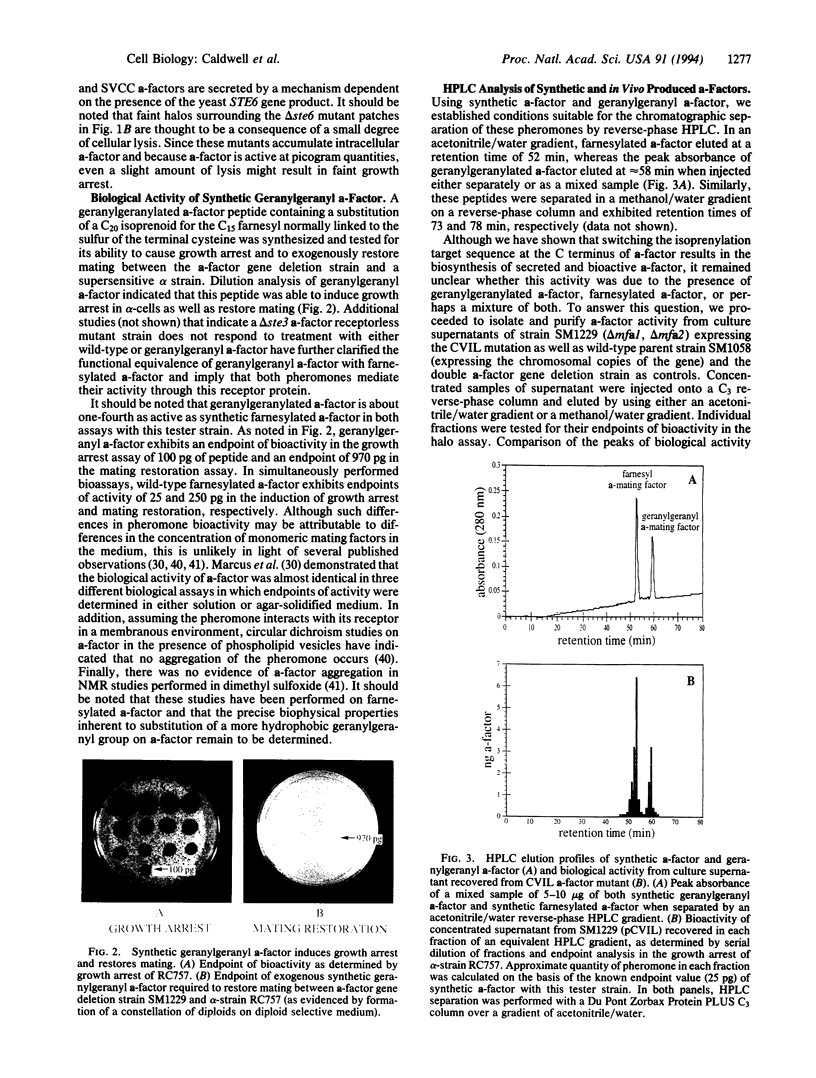
Abstract
Cysteine-containing amino acid sequences (CAAX, CC, and CXC; C is cysteine, A is any aliphatic amino acid, and X is any amino acid) are targets for the attachment of C15 (farnesyl) and C20 (geranylgeranyl) isoprenoids to peptides and proteins by specific prenyltransferases. Although much work has centered on the enzymatic mechanisms of these enzymes, the biological consequences of the differential isoprenylation they catalyze remain to be elucidated. Farnesylation of the a-factor mating pheromone of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a known prerequisite for its biological activity and its secretion through a pathway utilizing the yeast STE6 protein, a homolog of the mammalian multidrug resistance (MDR) P-glycoprotein. We generated specific mutations in the a-factor gene to encode isoprenylation targets for geranylgeranylation [Cys-Val-Ile-Leu (CVIL) and Ser-Val-Cys-Cys (SVCC)] in place of the natural farnesylation motif [Cys-Val-Ile-Ala (CVIA)]. The a-factors containing these modified prenylation sites were successfully exported by a STE6-dependent mechanism. Furthermore, these peptides, as well as synthetic geranylgeranyl a-factor, retained bioactivity. Chromatographic comparisons of synthetic and biosynthetic pheromones suggest that, in vivo, a peptide substrate containing the geranylgeranylation target CVIL can be both farnesylated and geranylgeranylated. These results clearly demonstrate that in vivo (i) different prenyltransferases may recognize the same substrate; (ii) both farnesylated and geranylgeranylated a-factor peptides are substrates for export via STE6, a MDR-like protein; and (iii) farnesylated and geranylgeranylated pheromones are both biologically active.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson P., Marshall C. J., Hall A., Tilbrook P. A. Post-translational modifications of p21rho proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20033–20038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker D. M., Guarente L. High-efficiency transformation of yeast by electroporation. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:182–187. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Falco S. C., Stewart S. E., Brennan M., Scherer S., Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Sterile host yeasts (SHY): a eukaryotic system of biological containment for recombinant DNA experiments. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R. K., Otte C. A. Isolation and genetic analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants supersensitive to G1 arrest by a factor and alpha factor pheromones. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;2(1):11–20. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christianson T. W., Sikorski R. S., Dante M., Shero J. H., Hieter P. Multifunctional yeast high-copy-number shuttle vectors. Gene. 1992 Jan 2;110(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90454-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. Protein isoprenylation and methylation at carboxyl-terminal cysteine residues. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:355–386. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox A. D., Hisaka M. M., Buss J. E., Der C. J. Specific isoprenoid modification is required for function of normal, but not oncogenic, Ras protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2606–2615. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epand R. F., Xue C. B., Wang S. H., Naider F., Becker J. M., Epand R. M. Role of prenylation in the interaction of the a-factor mating pheromone with phospholipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 17;32(32):8368–8373. doi: 10.1021/bi00083a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold A. A., Johnson D. I., Farnsworth C. C., Gelb M. H., Judd S. R., Glomset J. A., Tamanoi F. Protein geranylgeranyltransferase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is specific for Cys-Xaa-Xaa-Leu motif proteins and requires the CDC43 gene product but not the DPR1 gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4448–4452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Sterne R. E., Thorner J. Enzymes required for yeast prohormone processing. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:345–362. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz D., St Jean A., Woods R. A., Schiestl R. H. Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1425–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez R., Goodman L. E., Tripathy S. K., O'Rourke E., Manne V., Tamanoi F. Purified yeast protein farnesyltransferase is structurally and functionally similar to its mammalian counterpart. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 1;289(Pt 1):25–31. doi: 10.1042/bj2890025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gounarides J. S., Broido M. S., Xue C. B., Becker J. M., Naider F. R. The conformation of a-factor is not influenced by the S-prenylation of Cys12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 31;181(3):1125–1130. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)92055-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., McCaffrey G., Sprague G. F., Jr Evidence the yeast STE3 gene encodes a receptor for the peptide pheromone a factor: gene sequence and implications for the structure of the presumed receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1418–1422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara M., Akasaka K., Akinaga S., Okabe M., Nakano H., Gomez R., Wood D., Uh M., Tamanoi F. Identification of Ras farnesyltransferase inhibitors by microbial screening. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2281–2285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He B., Chen P., Chen S. Y., Vancura K. L., Michaelis S., Powers S. RAM2, an essential gene of yeast, and RAM1 encode the two polypeptide components of the farnesyltransferase that prenylates a-factor and Ras proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11373–11377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F. ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:67–113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi H., Kawata M., Katayama M., Yoshida Y., Musha T., Ando S., Takai Y. A novel prenyltransferase for a small GTP-binding protein having a C-terminal Cys-Ala-Cys structure. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):16981–16984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrycyna C. A., Clarke S. Maturation of isoprenylated proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Multiple activities catalyze the cleavage of the three carboxyl-terminal amino acids from farnesylated substrates in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10457–10464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Cox A. D., Hisaka M. M., Graham S. M., Buss J. E., Der C. J. Isoprenoid addition to Ras protein is the critical modification for its membrane association and transforming activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6403–6407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khosravi-Far R., Clark G. J., Abe K., Cox A. D., McLain T., Lutz R. J., Sinensky M., Der C. J. Ras (CXXX) and Rab (CC/CXC) prenylation signal sequences are unique and functionally distinct. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24363–24368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Diehl R. E., Schaber M. D., Rands E., Soderman D. D., He B., Moores S. L., Pompliano D. L., Ferro-Novick S., Powers S. Structural homology among mammalian and Saccharomyces cerevisiae isoprenyl-protein transferases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18884–18888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchler K., Sterne R. E., Thorner J. Saccharomyces cerevisiae STE6 gene product: a novel pathway for protein export in eukaryotic cells. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):3973–3984. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J. Pheromone response in yeast. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1097–1129. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda Y., Suzuki N., Kataoka T. The effect of posttranslational modifications on the interaction of Ras2 with adenylyl cyclase. Science. 1993 Jan 29;259(5095):683–686. doi: 10.1126/science.8430318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus S., Caldwell G. A., Miller D., Xue C. B., Naider F., Becker J. M. Significance of C-terminal cysteine modifications to the biological activity of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae a-factor mating pheromone. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3603–3612. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus S., Caldwell G. A., Xue C. B., Naider F., Becker J. M. Total in vitro maturation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae a-factor lipopeptide mating pheromone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1310–1316. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91592-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Varshavsky A. The yeast STE6 gene encodes a homologue of the mammalian multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):400–404. doi: 10.1038/340400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Herskowitz I. The a-factor pheromone of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is essential for mating. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1309–1318. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar C. M., Prange R., Gallwitz D. A carboxyl-terminal cysteine residue is required for palmitic acid binding and biological activity of the ras-related yeast YPT1 protein. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):971–976. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02903.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moomaw J. F., Casey P. J. Mammalian protein geranylgeranyltransferase. Subunit composition and metal requirements. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17438–17443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., Michaelis S., Broek D., Santa Anna S., Field J., Herskowitz I., Wigler M. RAM, a gene of yeast required for a functional modification of RAS proteins and for production of mating pheromone a-factor. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90598-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss Y., Goldstein J. L., Seabra M. C., Casey P. J., Brown M. S. Inhibition of purified p21ras farnesyl:protein transferase by Cys-AAX tetrapeptides. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi G., Yu J. A., Newman A. P., Ferro-Novick S. Dependence of Ypt1 and Sec4 membrane attachment on Bet2. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):158–161. doi: 10.1038/351158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer W. R., Kim R., Sterne R., Thorner J., Kim S. H., Rine J. Genetic and pharmacological suppression of oncogenic mutations in ras genes of yeast and humans. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):379–385. doi: 10.1126/science.2569235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer W. R., Rine J. Protein prenylation: genes, enzymes, targets, and functions. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:209–237. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer W. R., Trueblood C. E., Yang C. C., Mayer M. P., Rosenberg S., Poulter C. D., Kim S. H., Rine J. Enzymatic coupling of cholesterol intermediates to a mating pheromone precursor and to the ras protein. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1133–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.2204115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabra M. C., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Retinal degeneration in choroideremia: deficiency of rab geranylgeranyl transferase. Science. 1993 Jan 15;259(5093):377–381. doi: 10.1126/science.8380507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinensky M., Lutz R. J. The prenylation of proteins. Bioessays. 1992 Jan;14(1):25–31. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strazdis J. R., MacKay V. L. Reproducible and rapid methods for the isolation and assay of a-factor, a yeast mating hormone. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1153–1161. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1153-1161.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trueblood C. E., Ohya Y., Rine J. Genetic evidence for in vivo cross-specificity of the CaaX-box protein prenyltransferases farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase-I in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4260–4275. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue C. B., Caldwell G. A., Becker J. M., Naider F. Total synthesis of the lipopeptide a-mating factor of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jul 14;162(1):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91989-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama K., Goodwin G. W., Ghomashchi F., Glomset J. A., Gelb M. H. A protein geranylgeranyltransferase from bovine brain: implications for protein prenylation specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5302–5306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]