Abstract
Retroviruses are commonly considered to be restricted to vertebrates. However, the genome of many eukaryotes contains mobile sequences known as retrotransposons with long terminal repeats (LTR retrotransposons) or viral retrotransposons, showing similarities with integrated proviruses of retroviruses, such as Ty elements in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, copia-like elements in Drosophila, and endogenous proviruses in vertebrates. The gypsy element of Drosophila melanogaster has LTRs and contains three open reading frames, one of which encodes potential products similar to gag-specific protease, reverse transcriptase, and endonuclease. It is more similar to typical retroviruses than to LTR retrotransposons. We report here experiments showing that gypsy can be transmitted by microinjecting egg plasma from embryos of a strain containing actively transposing gypsy elements into embryos of a strain originally devoid of transposing elements. Horizontal transfer is also observed when individuals of the "empty" stock are raised on medium containing ground pupae of the stock possessing transposing elements. These results suggest that gypsy is an infectious retrovirus and provide evidence that retroviruses also occur in invertebrates.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayev A. A., Jr, Lyubomirskaya N. V., Dzhumagaliev E. B., Ananiev E. V., Amiantova I. G., Ilyin Y. V. Structural organization of transposable element mdg4 from Drosophila melanogaster and a nucleotide sequence of its long terminal repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3707–3723. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucheton A., Paro R., Sang H. M., Pelisson A., Finnegan D. J. The molecular basis of I-R hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: identification, cloning, and properties of the I factor. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90536-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucheton A., Vaury C., Chaboissier M. C., Abad P., Pélisson A., Simonelig M. I elements and the Drosophila genome. Genetica. 1992;86(1-3):175–190. doi: 10.1007/BF00133719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clare J., Farabaugh P. Nucleotide sequence of a yeast Ty element: evidence for an unusual mechanism of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2829–2833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crozatier M., Vaury C., Busseau I., Pelisson A., Bucheton A. Structure and genomic organization of I elements involved in I-R hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9199–9213. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Feng D. F., Johnson M. S., McClure M. A. Origins and evolutionary relationships of retroviruses. Q Rev Biol. 1989 Mar;64(1):1–30. doi: 10.1086/416128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evgen'ev M. B., Corces V. G., Lankenau D. H. Ulysses transposable element of Drosophila shows high structural similarities to functional domains of retroviruses. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 5;225(3):917–924. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90412-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund R., Meselson M. Long terminal repeat nucleotide sequence and specific insertion of the gypsy transposon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4462–4464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Nissen M. S. Gene organization and transcription of TED, a lepidopteran retrotransposon integrated within the baculovirus genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3067–3077. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gans M., Audit C., Masson M. Isolation and characterization of sex-linked female-sterile mutants in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1975 Dec;81(4):683–704. doi: 10.1093/genetics/81.4.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Yuki S., Saigo K. Complete nucleotide sequence and genome organization of a Drosophila transposable genetic element, 297. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jan 15;154(2):417–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
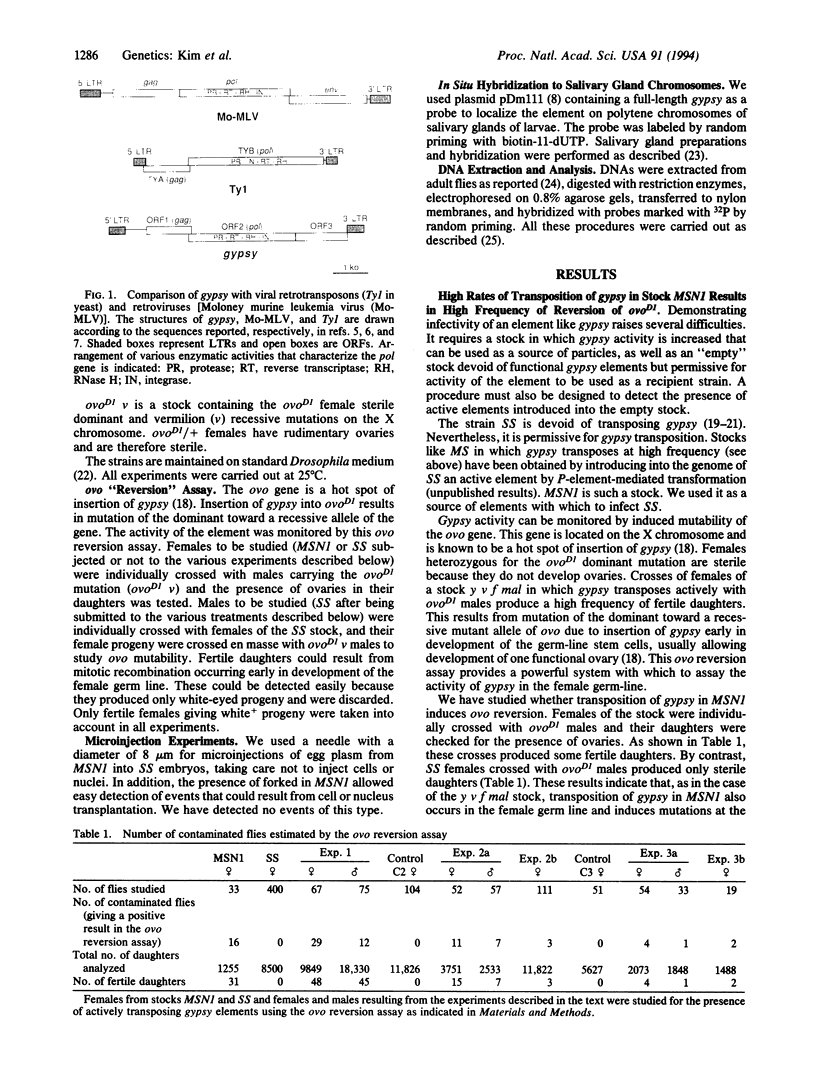
- Kim A. I., Belyaeva E. S., Aslanian M. M. Autonomous transposition of gypsy mobile elements and genetic instability in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Nov;224(2):303–308. doi: 10.1007/BF00271566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim A. I., Belyaeva E. S. Transposition of mobile elements gypsy (mdg4) and hobo in germ-line and somatic cells of a genetically unstable mutator strain of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Oct;229(3):437–444. doi: 10.1007/BF00267467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn D. T., Woods D. F., Andrew D. J. Deletion analysis of the tumorous-head (tuh-3) gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1981 Sep;99(1):99–107. doi: 10.1093/genetics/99.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim J. K., Simmons M. J., Raymond J. D., Cox N. M., Doll R. F., Culbert T. P. Homologue destabilization by a putative transposable element in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6624–6627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyubomirskaya N. V., Arkhipova I. R., Ilyin Y. V., Kim A. I. Molecular analysis of the gypsy (mdg4) retrotransposon in two Drosophila melanogaster strains differing by genetic instability. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Sep;223(2):305–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00265067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlor R. L., Parkhurst S. M., Corces V. G. The Drosophila melanogaster gypsy transposable element encodes putative gene products homologous to retroviral proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1129–1134. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modolell J., Bender W., Meselson M. Drosophila melanogaster mutations suppressible by the suppressor of Hairy-wing are insertions of a 7.3-kilobase mobile element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1678–1682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mével-Ninio M., Mariol M. C., Gans M. Mobilization of the gypsy and copia retrotransposons in Drosophila melanogaster induces reversion of the ovo dominant female-sterile mutations: molecular analysis of revertant alleles. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1549–1558. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03539.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saigo K., Kugimiya W., Matsuo Y., Inouye S., Yoshioka K., Yuki S. Identification of the coding sequence for a reverse transcriptase-like enzyme in a transposable genetic element in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):659–661. doi: 10.1038/312659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheen F., Lim J. K., Simmons M. J. Genetic instability in Drosophila melanogaster mediated by hobo transposable elements. Genetics. 1993 Feb;133(2):315–334. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaury C., Abad P., Pelisson A., Lenoir A., Bucheton A. Molecular characteristics of the heterochromatic I elements from a reactive strain of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Evol. 1990 Nov;31(5):424–431. doi: 10.1007/BF02106056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaury C., Bucheton A., Pelisson A. The beta heterochromatic sequences flanking the I elements are themselves defective transposable elements. Chromosoma. 1989 Sep;98(3):215–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00329686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Eickbush T. H. Origin and evolution of retroelements based upon their reverse transcriptase sequences. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3353–3362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuki S., Inouye S., Ishimaru S., Saigo K. Nucleotide sequence characterization of a Drosophila retrotransposon, 412. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jul 15;158(2):403–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]