Abstract
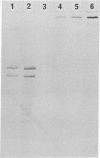
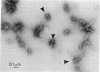
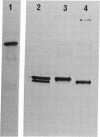
Type I procollagen secreted by matrix-free cells from chick embryo tendons was purified by DEAE-cellulose chromatography. Electron microscopy of segment-long-spacing aggregates of the procollagen demonstrated the presence of both NH2-terminal and COOH-terminal extensions not found in collagen. The procollagen was digested with bacterial collagenase and the COOH-terminal fragments were isolated by gel filtration and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate. Analysis of tryptic peptides demonstrated that the COOH-terminal extensions on the pro alpha 1 and pro alpha 2 chains had different primary structures.
Full text
PDF
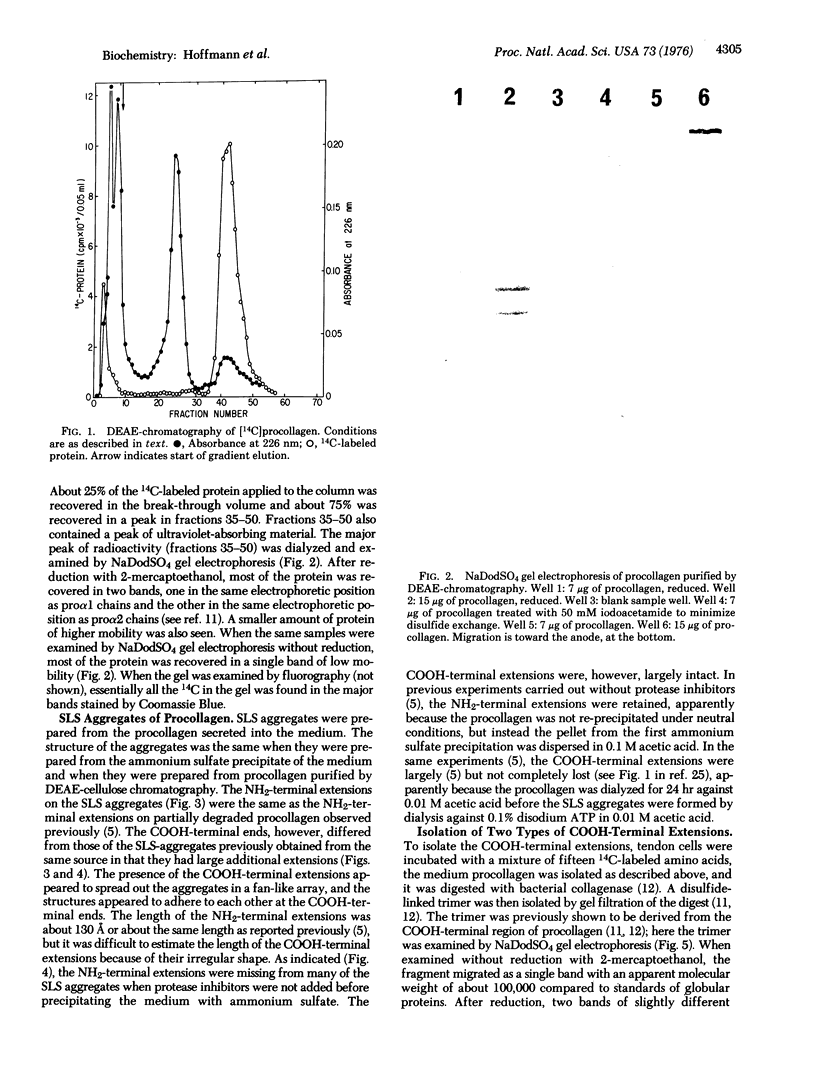

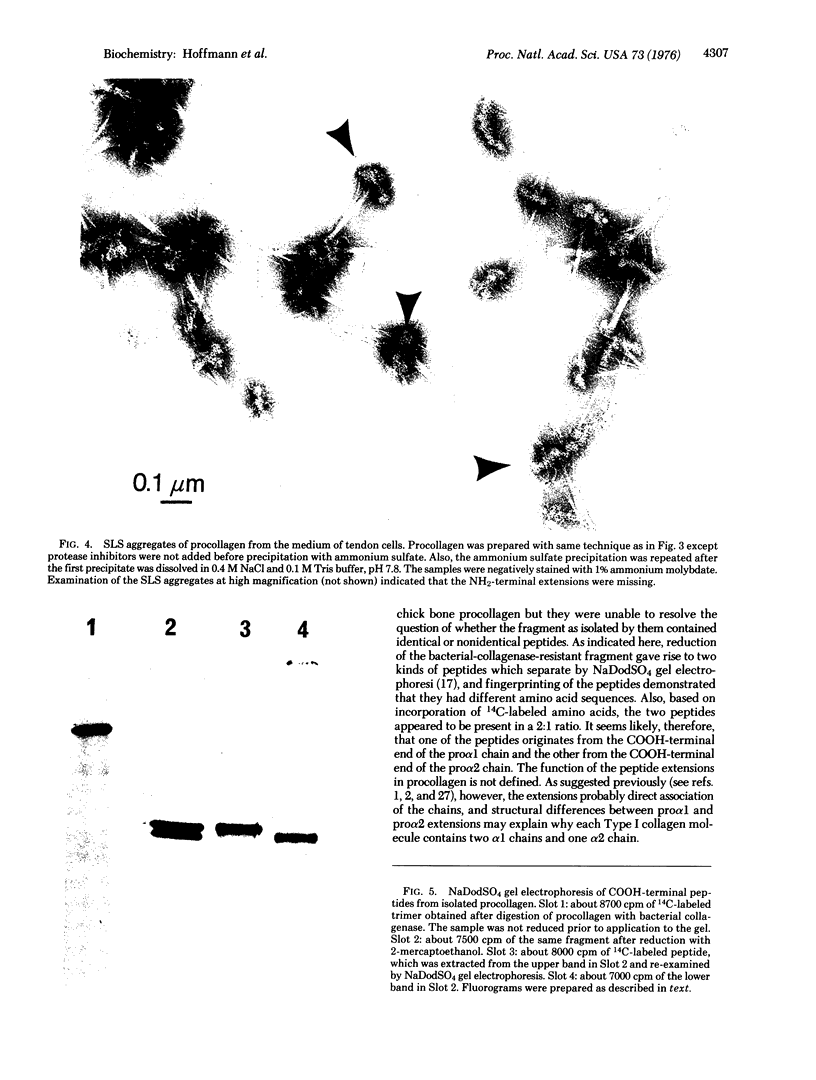
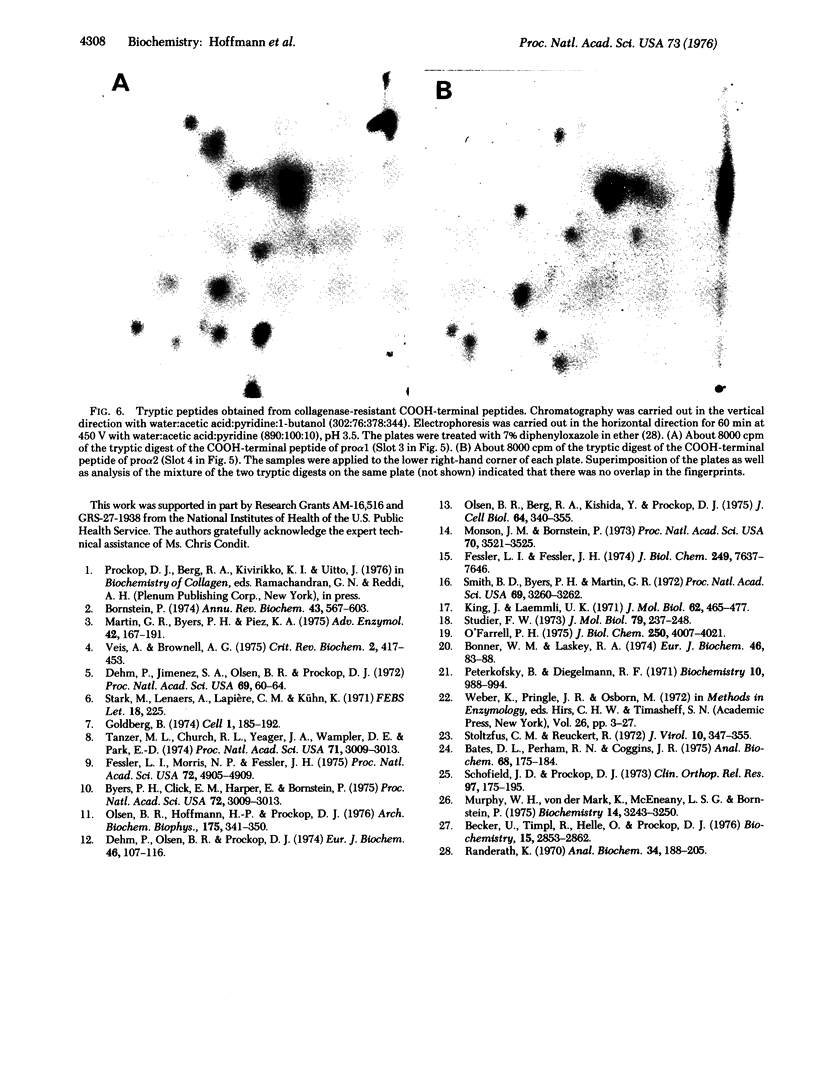
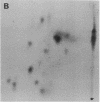
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bates D. L., Perham R. N., Coggins J. R. Methods for obtaining peptide maps of proteins on a subnanomole scale. Anal Biochem. 1975 Sep;68(1):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90692-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker U., Timpl R. NH2-terminal extensions on skin collagen from sheep with a genetic defect in conversion of procollagen into collagen. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2853–2862. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P. The biosynthesis of collagen. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):567–603. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., Click E. M., Harper E., Bornstein P. Interchain disulfide bonds in procollagen are located in a large nontriple-helical COOH-terminal domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3009–3013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehm P., Jimenez S. A., Olsen B. R., Prockop D. J. A transport form of collagen from embryonic tendon: electron microscopic demonstration of an NH 2 -terminal extension and evidence suggesting the presence of cystine in the molecule (chick embryo-tropocollagen-gel filtration). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):60–64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehm P., Olsen B. R., Prockop D. J. Antibodies to chick-tendon procollagen. Affinity purification with the isolated disulfide-linded NH2-terminal extensions and reactivity with a component in embryonic serum. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):107–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fessler L. I., Fessler J. H. Protein assembly of procollagen and effects of hydroxylation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7637–7646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fessler L. I., Morris N. P., Fessler J. H. Procollagen: biological scission of amino and carboxyl extension peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4905–4909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Laemmli U. K. Polypeptides of the tail fibres of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 28;62(3):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Byers P. H., Piez K. A. Procollagen. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1975;42:167–191. doi: 10.1002/9780470122877.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monson J. M., Borstein P. Identification of a disulfide-linked procollagen as the biosynthetic precursor of chick-bone collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3521–3525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy W. H., von der Mark K., McEneany L. S., Bornstein P. Characterization of procollagen-derived peptides unique to the precursor molecule. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 15;14(14):3243–3250. doi: 10.1021/bi00685a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen B. R., Berg R. A., Kishida Y., Prockop D. J. Further characterization of embryonic tendon fibroblasts and the use of immunoferritin techniques to study collagen biosynthesis. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):340–355. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen B. R., Hoffmann H., Prockop D. J. Interchain disulfide bonds at the COOH-terminal end of procollagen synthesized by matrix-free cells from chick embryonic tendon and cartilage. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jul;175(1):341–350. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90516-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky B., Diegelmann R. Use of a mixture of proteinase-free collagenases for the specific assay of radioactive collagen in the presence of other proteins. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 16;10(6):988–994. doi: 10.1021/bi00782a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath K. An evaluation of film detection methods for weak beta-emitters, particularly tritium. Anal Biochem. 1970 Mar;34:188–205. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield J. D., Prockop D. J. Procollagen-a precursor form of collagen. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1973 Nov-Dec;(97):175–195. doi: 10.1097/00003086-197311000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. D., Byers P. H., Martin G. R. Production of procollagen by human fibroblasts in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3260–3262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M., Lenaers A., Lapiere C., Kühn K. Electronoptical studies of procollagen from the skin of dermatosparaxic calves. FEBS Lett. 1971 Nov 1;18(2):225–227. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80450-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus C. M., Rueckert R. Capsid polypeptides of mouse Elberfeld virus. I. Amino acid compositions and molar ratios in the virion. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):347–355. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.347-355.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer M. L., Church R. L., Yaeger J. A., Wampler D. E., Park E. Procollagen: intermediate forms containing several types of peptide chains and non-collagen peptide extensions at NH2 and COOH ends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3009–3013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veis A., Brownell A. G. Collagen biosynthesis. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1975 Feb;2(4):417–453. doi: 10.3109/10409237509102549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]