Abstract
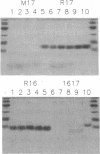
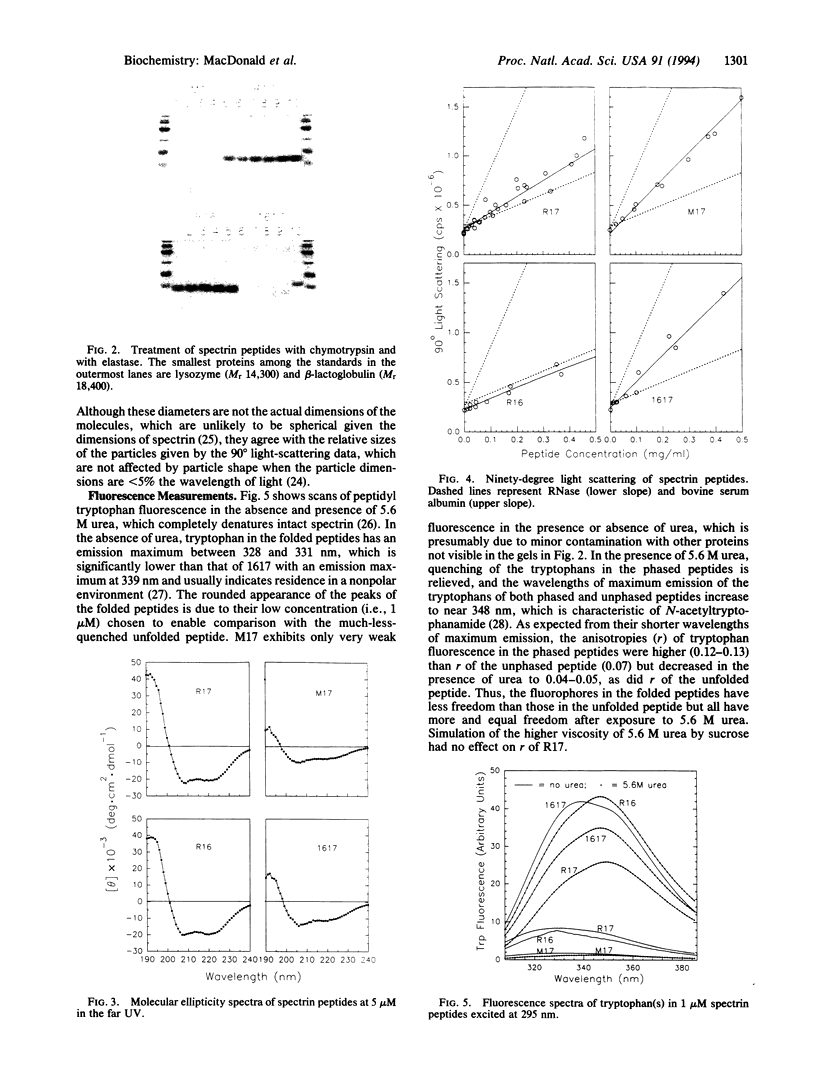
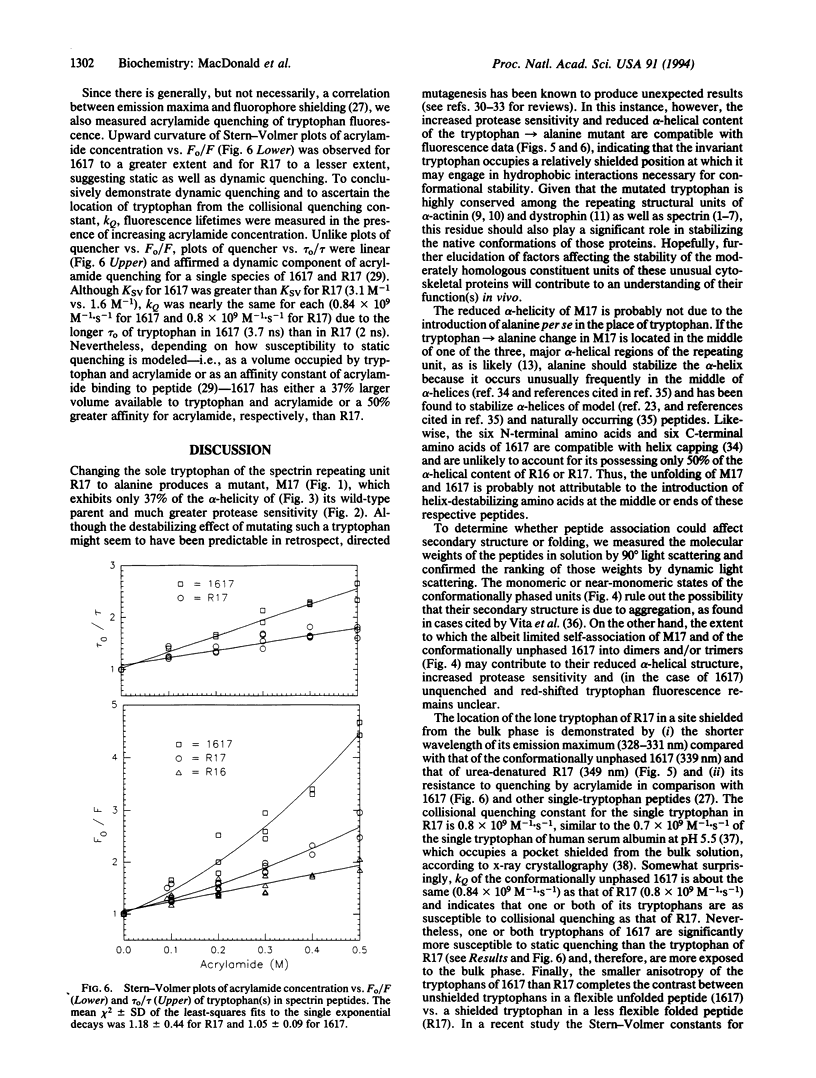
The tryptophan that is highly conserved among repeating structural units of spectrin is reported to promote the conformational stability of one such unit of chicken brain alpha-spectrin. Four constructs were inserted into pET vectors for overexpression in Escherichia coli of the following spectrin peptides: (i) two adjacent but separately expressed "conformationally phased" repeating units, R16 and R17, one of which (R17) contains a single tryptophan; (ii) a mutant, M17, of the single tryptophan-containing unit with alanine substituted for the tryptophan; and (iii) a conformationally unphased unit, 1617, composed of half of each of the phased units. Both the mutant unit and the unphased unit were much more readily digested by chymotrypsin and by elastase than the phased units and exhibited only 38% and 54% as much alpha-helical structure, respectively, as the phased units by their far UV CD spectra; 90 degrees light scattering measurements revealed the folded peptides to be predominantly monomeric in solution, whereas the unfolded, protease-sensitive peptides consisted of dimers and/or trimers. This trend was corroborated by their dynamic light scattering. Both the blue-shifted wavelength of maximal emission and the relative inaccessibility to acrylamide of the single tryptophan in the folded unit indicate that the invariant tryptophan occupies a site that is shielded from the aqueous phase.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alber T. Mutational effects on protein stability. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:765–798. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. D., Davison M. D., Jones P., Patel B., Critchley D. R. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding a chick alpha-actinin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2558–2561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaber M., Zhang X. J., Matthews B. W. Structural basis of amino acid alpha helix propensity. Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1637–1640. doi: 10.1126/science.8503008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers T. J., Husain-Chishti A., Dubreuil R. R., Branton D., Goldstein L. S. Sequence similarity of the amino-terminal domain of Drosophila beta spectrin to alpha actinin and dystrophin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1633–1641. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. A., Stewart M., Kendrick-Jones J. Structural predictions for the central domain of dystrophin. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 12;262(1):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80160-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubreuil R. R., Byers T. J., Sillman A. L., Bar-Zvi D., Goldstein L. S., Branton D. The complete sequence of Drosophila alpha-spectrin: conservation of structural domains between alpha-spectrins and alpha-actinin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2197–2205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eftink M. R. Fluorescence techniques for studying protein structure. Methods Biochem Anal. 1991;35:127–205. doi: 10.1002/9780470110560.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eftink M. R., Ghiron C. A. Exposure of tryptophanyl residues in proteins. Quantitative determination by fluorescence quenching studies. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):672–680. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson A. E., Baase W. A., Zhang X. J., Heinz D. W., Blaber M., Baldwin E. P., Matthews B. W. Response of a protein structure to cavity-creating mutations and its relation to the hydrophobic effect. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):178–183. doi: 10.1126/science.1553543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X. M., Carter D. C. Atomic structure and chemistry of human serum albumin. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):209–215. doi: 10.1038/358209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu R. J., Watanabe M., Bennett V. Characterization of human brain cDNA encoding the general isoform of beta-spectrin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18715–18722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahana E., Pinder J. C., Smith K. S., Gratzer W. B. Fluorescence quenching of spectrin and other red cell membrane cytoskeletal proteins. Relation to hydrophobic binding sites. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 15;282(Pt 1):75–80. doi: 10.1042/bj2820075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy S. P., Warren S. L., Forget B. G., Morrow J. S. Ankyrin binds to the 15th repetitive unit of erythroid and nonerythroid beta-spectrin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):267–277. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Monaco A. P., Kunkel L. M. The complete sequence of dystrophin predicts a rod-shaped cytoskeletal protein. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laws W. R., Contino P. B. Fluorescence quenching studies: analysis of nonlinear Stern-Volmer data. Methods Enzymol. 1992;210:448–463. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)10023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovejoy B., Choe S., Cascio D., McRorie D. K., DeGrado W. F., Eisenberg D. Crystal structure of a synthetic triple-stranded alpha-helical bundle. Science. 1993 Feb 26;259(5099):1288–1293. doi: 10.1126/science.8446897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W. Structural and genetic analysis of protein stability. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:139–160. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan S., Marqusee S., Ridgeway T., Laue T. M., Baldwin R. L. Relative helix-forming tendencies of nonpolar amino acids. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):268–270. doi: 10.1038/344268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. A., Dixon T. W., Cohen C. Analysis of the three-alpha-helix motif in the spectrin superfamily of proteins. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;61(4):858–867. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81893-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S., Richardson D. C. Amino acid preferences for specific locations at the ends of alpha helices. Science. 1988 Jun 17;240(4859):1648–1652. doi: 10.1126/science.3381086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahr K. E., Laurila P., Kotula L., Scarpa A. L., Coupal E., Leto T. L., Linnenbach A. J., Winkelmann J. C., Speicher D. W., Marchesi V. T. The complete cDNA and polypeptide sequences of human erythroid alpha-spectrin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4434–4443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D. Mutational studies of protein structures and their stabilities. Q Rev Biophys. 1992 May;25(2):205–250. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D. M., Burke B. E., Branton D. The molecular structure of human erythrocyte spectrin. Biophysical and electron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):303–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speicher D. W., Marchesi V. T. Erythrocyte spectrin is comprised of many homologous triple helical segments. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):177–180. doi: 10.1038/311177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEALE F. W., WEBER G. Ultraviolet fluorescence of the aromatic amino acids. Biochem J. 1957 Mar;65(3):476–482. doi: 10.1042/bj0650476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vita C., Fontana A., Jaenicke R. Folding of thermolysin fragments. Hydrodynamic properties of isolated domains and subdomains. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Aug 15;183(3):513–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb21079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasenius V. M., Saraste M., Salvén P., Erämaa M., Holm L., Lehto V. P. Primary structure of the brain alpha-spectrin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;108(1):79–93. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelmann J. C., Chang J. G., Tse W. T., Scarpa A. L., Marchesi V. T., Forget B. G. Full-length sequence of the cDNA for human erythroid beta-spectrin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11827–11832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winograd E., Hume D., Branton D. Phasing the conformational unit of spectrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10788–10791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witke W., Schleicher M., Lottspeich F., Noegel A. Studies on the transcription, translation, and structure of alpha-actinin in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):969–975. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y., Prabhakaran M., Johnson M. E., Fung L. W. Secondary structure prediction for the spectrin 106-amino acid segment, and a proposed model for tertiary structure. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1990 Aug;8(1):55–62. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1990.10507789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. T., Wu C. S., Martinez H. M. Calculation of protein conformation from circular dichroism. Methods Enzymol. 1986;130:208–269. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)30013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino H., Marchesi V. T. Isolation of spectrin subunits and reassociation in vitro. Analysis by fluorescence polarization. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4496–4500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]