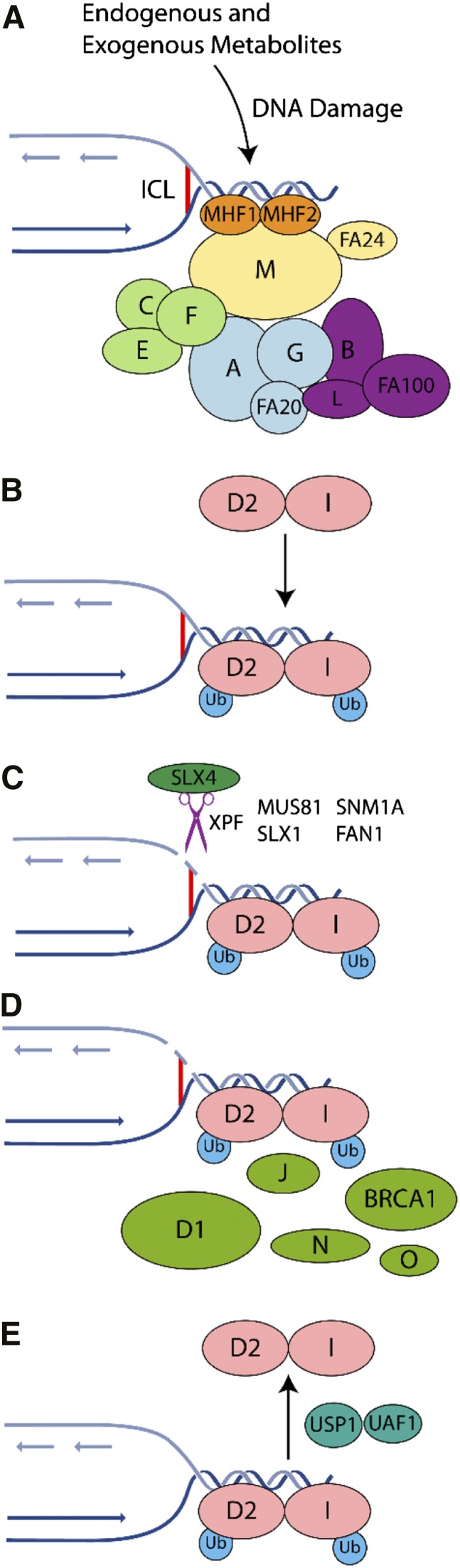
Figure 1.
Mechanism of ICL repair in the FA pathway on collision of a replication fork with an ICL. The FA pathway is composed of ≥16 genes (A, B, C, D1, D2, E, F, G, I, K, L, M, N, O, P, and Q). The encoded proteins can be subdivided within the FA pathway into 3 groups: (1) proteins that make up the core complex; (2) the FANCI and FANCD2 proteins, which compose the ID2 complex; and (3) downstream effector proteins. (A) The FA pathway is activated during S phase of the cell cycle or on the detection of ICLs and DNA damage caused by other agents, including endogenous acetaldehydes. The FA core complex is recruited to the damage site through its interaction with the MHF1-MHF2-FANCM complex. (B) The ID2 complex becomes monoubiquitinated and remains associated with the DNA damage. The B-L-100 complex mediates the ubiquitination reaction, with the other 2 core subcomplexes (A-G-20 and C-E-F) playing accessory roles that remain to be elucidated. (C) Specialized endonucleases, in particular XPF/FANCQ-ERCC1 in complex with SLX4/FANCP, incise the DNA. (D) Within chromatin, the monoubiquitinated ID2 complex recruits DNA repair proteins including BRCA1, BRCA2/FANCD1, FANCJ, PALB2/FANCN, and RAD51C/FANCO. (E) Following successful repair, deubiquitination of the ID2 complex by USP1-UAF1 promotes its release from chromatin.