Abstract
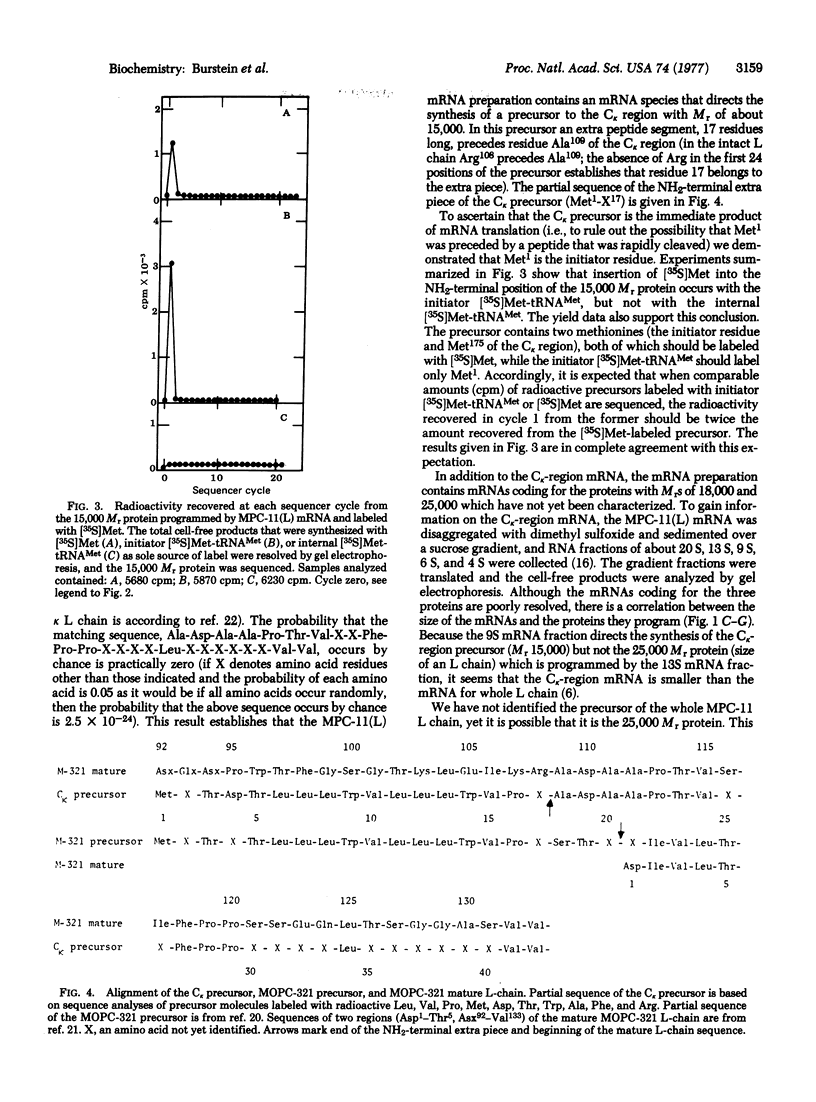
The mRNA coding for the κ-type constant region (Cκ) was purified from two clones derived from the MPC-11 mouse myeloma. This mRNA directs the cell-free synthesis of a Cκ precursor (molecular weight, about 15,000) in which an extra piece, 17 residues long, precedes the NH2-terminal residue (Ala109) of the Cκ region. The partial sequence of the extra piece is: Met-X-Thr-Asp-Thr-Leu-Leu-Leu-Trp-Val-Leu-Leu-Leu-Trp-Val-Pro-X- (X is unknown). Met1 was shown to be the initiator methionine. The sequence of the Cκ extra piece is completely different from any known sequence preceding residue Ala109 in whole light (L) chains, thus establishing that the Cκ-region mRNA could not have originated from mRNA coding for the whole L chain. The structural features of the Cκ extra piece (marked hydrophobicity, size, and a methionine at the NH2-terminus) are identical to those characteristic of the NH2-terminal extra piece linked to the variable (V) region of whole L-chain precursors. In addition, the Cκ extra piece and the extra piece linked to the V region of MOPC-321 L chain have 70% sequence homology. These findings can be explained by the two genes-one Ig chain hypothesis, if we assume that the DNA coding for the extra piece (xp-DNA) is a constitutive part of the V gene. According to this model, the Cκ-region mRNA could have originated from: (i) translocation of this V gene to the C gene, deletion of the entire mature V gene, and “end-to-end” repair of the remaining xp-DNA to the C gene; (ii) translocation to the C gene only of the xp-DNA portion of the V gene. Alternatively, we may assume that the xp-DNA is not covalently linked to the mature V gene at all times, as might be the case for the DNA of hypervariable regions presumed to be in episomes. This raises the intriguing speculation that the xp-DNA represents a third distinct gene, designated xp-gene. The presumed xp-gene may be involved in the regulation of gene transcription: when linked to the mature V gene it initiates a chain of events leading to whole L-chain mRNA formation; when attached to the C gene it leads to its transcription to provide the C-region mRNA.
Keywords: gene translocation, transcription control, initiator methionine, mRNA translation, sequence of cell-free protein product
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burstein Y., Schechter I. Amino acid sequence of the NH2-terminal extra piece segments of the precursors of mouse immunoglobulin lambda1-type and kappa-type light chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):716–720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein Y., Schechter I. Amino acid-sequence variability at the N-terminal extra piece of mouse immunoglobulin light-chain precursors of the same and different subgroups. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):145–151. doi: 10.1042/bj1570145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffino P., Scharff M. D. Rate of somatic mutation in immunoglobulin production by mouse myeloma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):219–223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer W. J., Bennett J. C. The molecular basis of antibody formation: a paradox. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):864–869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B. A new immunoglobulin variant: gamma3 heavy chain disease protein CHI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1552–1555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gally J. A., Edelman G. M. Somatic translocation of antibody genes. Nature. 1970 Jul 25;227(5256):341–348. doi: 10.1038/227341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh K., Ghosh H. P., Simsek M., Raj Bhandary U. L. Initiator methionine transfer ribonucleic acid from wheat embryo. Purification, properties, and partial nucleotide sequences. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4720–4729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hozumi N., Tonegawa S. Evidence for somatic rearrangement of immunoglobulin genes coding for variable and constant regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3628–3632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehl W. M., Kaplan B. A., Scharff M. D. Characterization of light chain and light chain constant region fragment mRNAs in MPC 11 mouse myeloma cells and variants. Cell. 1975 Jun;5(2):139–147. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehl W. M., Scharff M. D. Synthesis of a carboxyl-terminal (constant region) fragment of the immunoglobulin light chain by a mouse myeloma cell line. J Mol Biol. 1974 Nov 5;89(3):409–421. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskov R., Scharff M. D. Synthesis, assembly, and secretion of gamma globulin by mouse myeloma cells. I. Adaptation of the Merwin plasma cell tumor-11 to culture, cloning, and characterization of gamma globulin subunits. J Exp Med. 1970 Mar 1;131(3):515–541. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.3.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean D., Potter M., Hood L. Mouse immunoglobulin chains. Pattern of sequence variation among kappa chains with limited sequence differences. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):760–771. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Biologically and chemically pure mRNA coding for a mouse immunoglobulin L-chain prepared with the aid of antibodies and immobilized oligothymidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2256–2260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Burstein Y. Identification of N-terminal methionine in the precursor of immunoglobulin light chain. Initiation of translation of messenger ribonucleic acid in plants and animals. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 1;153(3):543–550. doi: 10.1042/bj1530543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Burstein Y. Marked hydrophobicity of the NH2-terminal extra piece of immunoglobulin light-chain precursors: possible physiological functions of the extra piece. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3273–3277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Further characterization of the mRNA coding for immunoglobulin light-chain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):228–235. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Partial amino acid sequence of the precursor of immunoglobulin light chain programmed by messenger RNA in vitro. Science. 1975 Apr 11;188(4184):160–162. doi: 10.1126/science.803715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Use of antibodies for the isolation of biologically pure messenger ribonucleic acid from fully functional eukaryotic cells. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 23;13(9):1875–1885. doi: 10.1021/bi00706a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Cohn M. Immunoglobulin biosynthesis. V. Light chain assembly. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 14;53(3):305–320. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90067-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Mouse immunoglobulin kappa chain MPC 11: extra amino-terminal residues. Science. 1973 Sep 7;181(4103):941–943. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4103.941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gibson D., Fanning E. M., Goodfliesh R. M., Gilman J. G., Ballantyne D. L. Quantitative procedures for use with the Edman-Begg sequenator. Partial sequences of two unusual immunoglobulin light chains, Rzf and Sac. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 21;10(26):4912–4921. doi: 10.1021/bi00802a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svasti J., Milstein C. The complete amino acid sequence of a mouse kappa light chain. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(2):427–444. doi: 10.1042/bj1280427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A. An analysis of the sequences of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and myeloma light chains and their implications for antibody complementarity. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):211–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]