Abstract
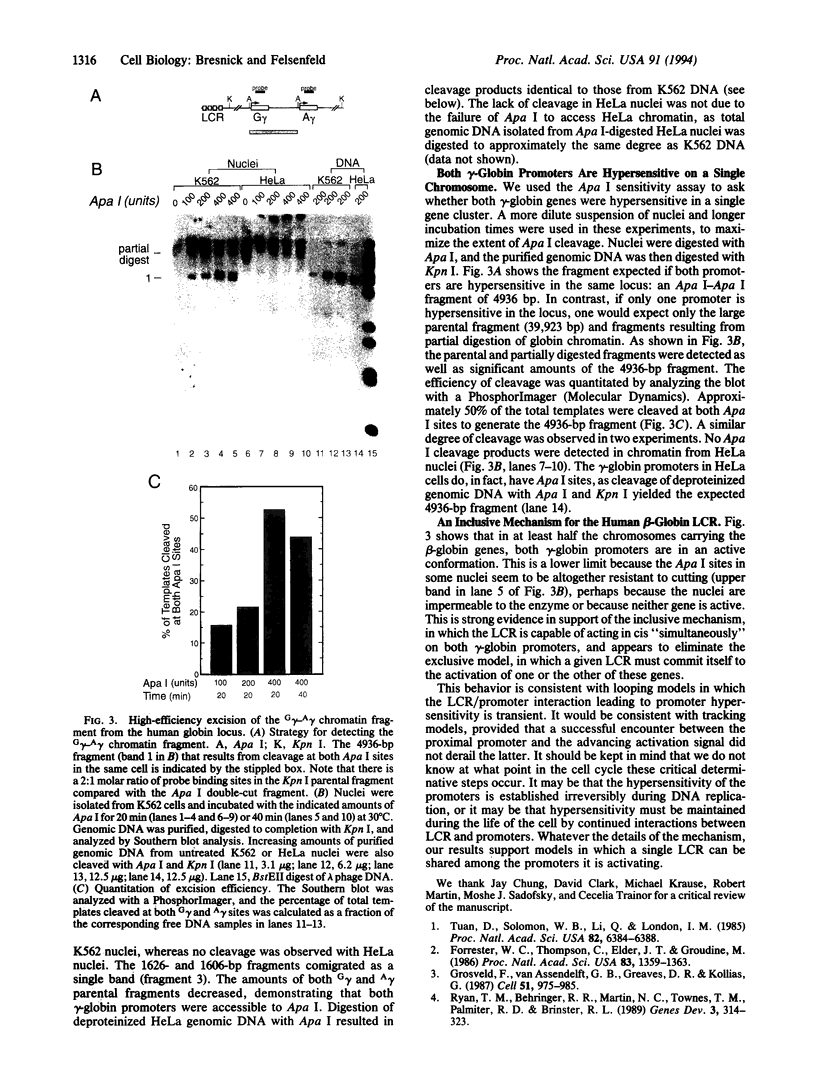
The human beta-globin locus control region (LCR) is necessary for high-level and position-independent expression of globin genes in erythroid cells. A variety of mechanisms have been proposed for the cis-activation of individual members of the beta-globin gene family by the LCR located 10-50 kilobases upstream. It is not known, however, whether a given LCR can activate all developmentally appropriate globin family members on its chromosome or whether, within a given chromosome, the LCR must be committed to activating only a single gene. We have devised an experiment to distinguish between these possibilities. This experiment takes advantage of the fact that if two genes in a cluster are transcriptionally active and their promoters, therefore, are in a conformation hypersensitive to nucleases, restriction enzymes that cleave the promoters will excise the intervening chromatin fragment. The Apa I sites on human fetal G gamma- and A gamma-globin gene promoters are accessible to cleavage in nuclei from the human erythroleukemia cell line K562, which expresses these genes, but not in HeLa cells. We find that Apa I digestion leads to excision in high yield of the fragment spanning these promoters, showing that a LCR element is capable of sharing its activating function among members of a gene cluster on a single chromosome.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behringer R. R., Ryan T. M., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Townes T. M. Human gamma- to beta-globin gene switching in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):380–389. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnick E. H., Bustin M., Marsaud V., Richard-Foy H., Hager G. L. The transcriptionally-active MMTV promoter is depleted of histone H1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):273–278. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnick E. H., Felsenfeld G. Evidence that the transcription factor USF is a component of the human beta-globin locus control region heteromeric protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18824–18834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S., Weissman S. M. The molecular genetics of human hemoglobin. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1984;31:315–462. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60382-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis P., Antoniou M., Grosveld F. Definition of the minimal requirements within the human beta-globin gene and the dominant control region for high level expression. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):233–240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08100.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A., Ley T. J., Humphries R. K., Fordis M., Schechter A. N. Inducible transcription of five globin genes in K562 human leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5515–5519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J., Talbot D., Dillon N., Grosveld F. Synthetic human beta-globin 5'HS2 constructs function as locus control regions only in multicopy transgene concatamers. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):127–134. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05638.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enver T., Raich N., Ebens A. J., Papayannopoulou T., Costantini F., Stamatoyannopoulos G. Developmental regulation of human fetal-to-adult globin gene switching in transgenic mice. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):309–313. doi: 10.1038/344309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Epner E., Driscoll M. C., Enver T., Brice M., Papayannopoulou T., Groudine M. A deletion of the human beta-globin locus activation region causes a major alteration in chromatin structure and replication across the entire beta-globin locus. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1637–1649. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Thompson C., Elder J. T., Groudine M. A developmentally stable chromatin structure in the human beta-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1359–1363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Kohwi-Shigematsu T., Gelinas R., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Papayannopoulou T. Human fetal to adult hemoglobin switching: changes in chromatin structure of the beta-globin gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7551–7555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanscombe O., Whyatt D., Fraser P., Yannoutsos N., Greaves D., Dillon N., Grosveld F. Importance of globin gene order for correct developmental expression. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1387–1394. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hug B. A., Moon A. M., Ley T. J. Structure and function of the murine beta-globin locus control region 5' HS-3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5771–5778. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. G., Epner E. M., Forrester W. C., Groudine M. Inactivation of the human beta-globin gene by targeted insertion into the beta-globin locus control region. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):928–938. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipsen S., Talbot D., Fraser P., Grosveld F. The beta-globin dominant control region: hypersensitive site 2. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2159–2167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. M., Behringer R. R., Martin N. C., Townes T. M., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. A single erythroid-specific DNase I super-hypersensitive site activates high levels of human beta-globin gene expression in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):314–323. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Collis P., Antoniou M., Vidal M., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. A dominant control region from the human beta-globin locus conferring integration site-independent gene expression. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):352–355. doi: 10.1038/338352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Grosveld F. The 5'HS2 of the globin locus control region enhances transcription through the interaction of a multimeric complex binding at two functionally distinct NF-E2 binding sites. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1391–1398. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Philipsen S., Fraser P., Grosveld F. Detailed analysis of the site 3 region of the human beta-globin dominant control region. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2169–2177. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. The reprogramming of transcriptional competence. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):573–575. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90218-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D. Y., Solomon W. B., London I. M., Lee D. P. An erythroid-specific, developmental-stage-independent enhancer far upstream of the human "beta-like globin" genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2554–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D., Kong S., Hu K. Transcription of the hypersensitive site HS2 enhancer in erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11219–11223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D., Solomon W., Li Q., London I. M. The "beta-like-globin" gene domain in human erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6384–6388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]