Abstract
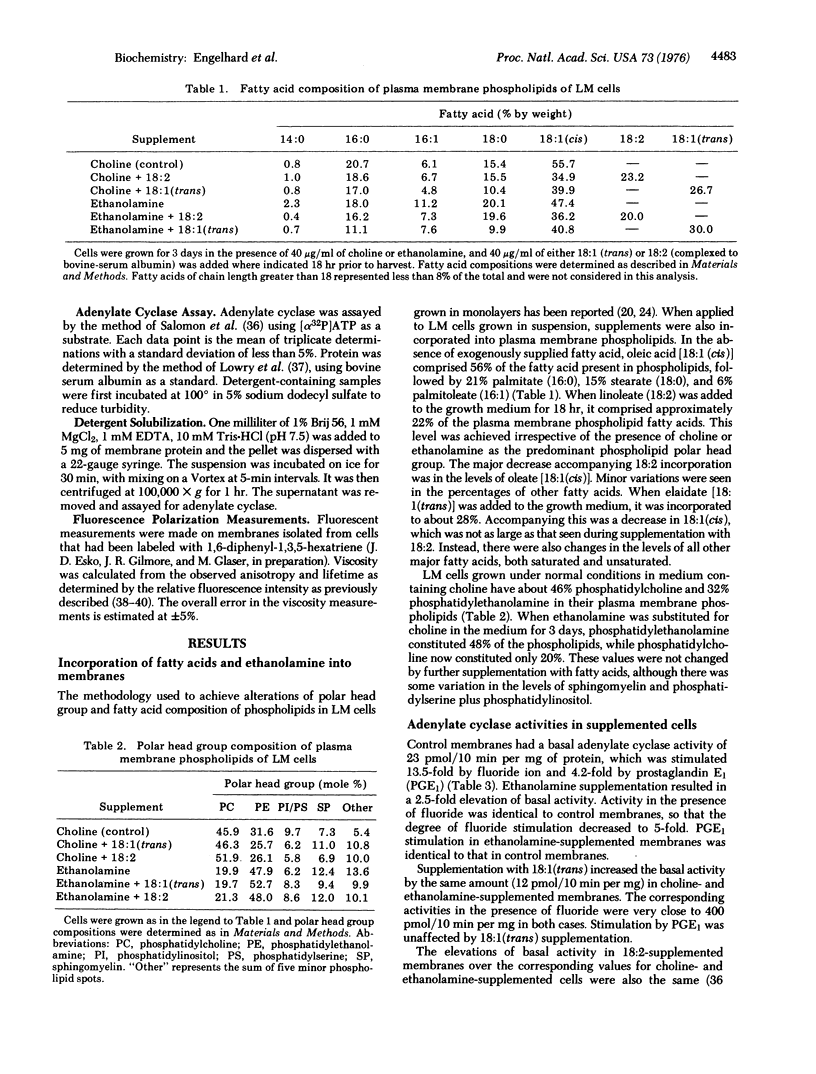
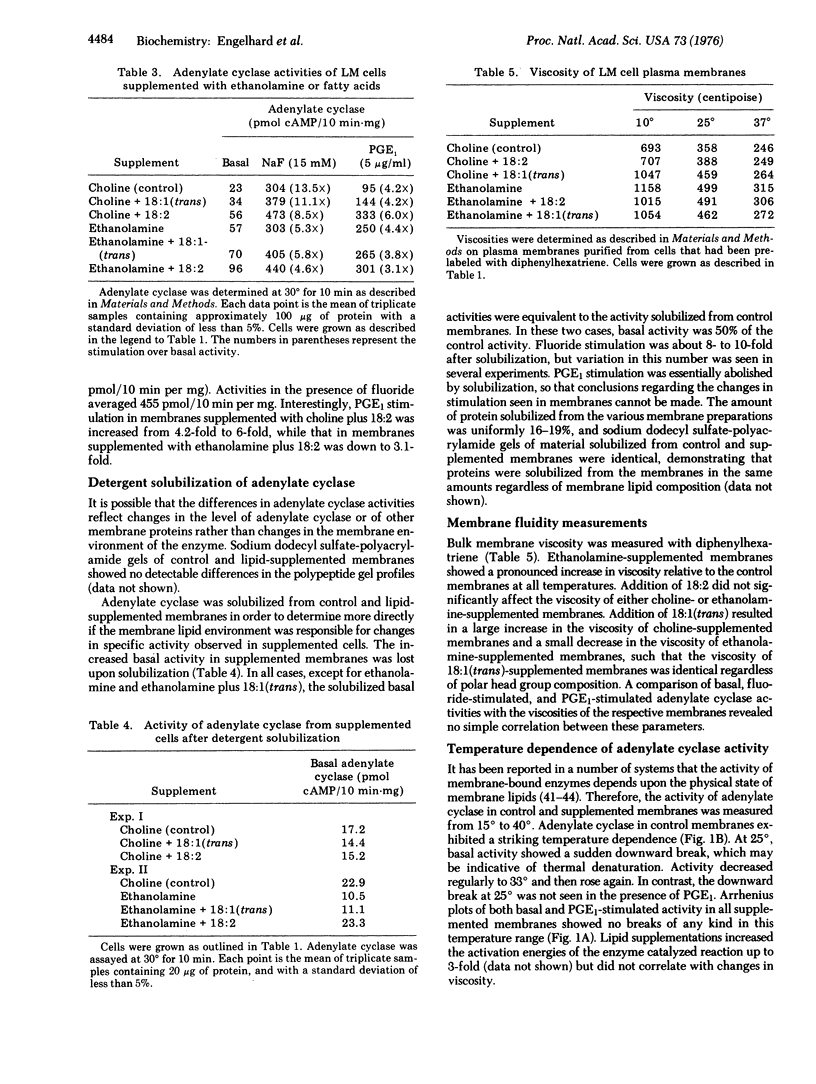
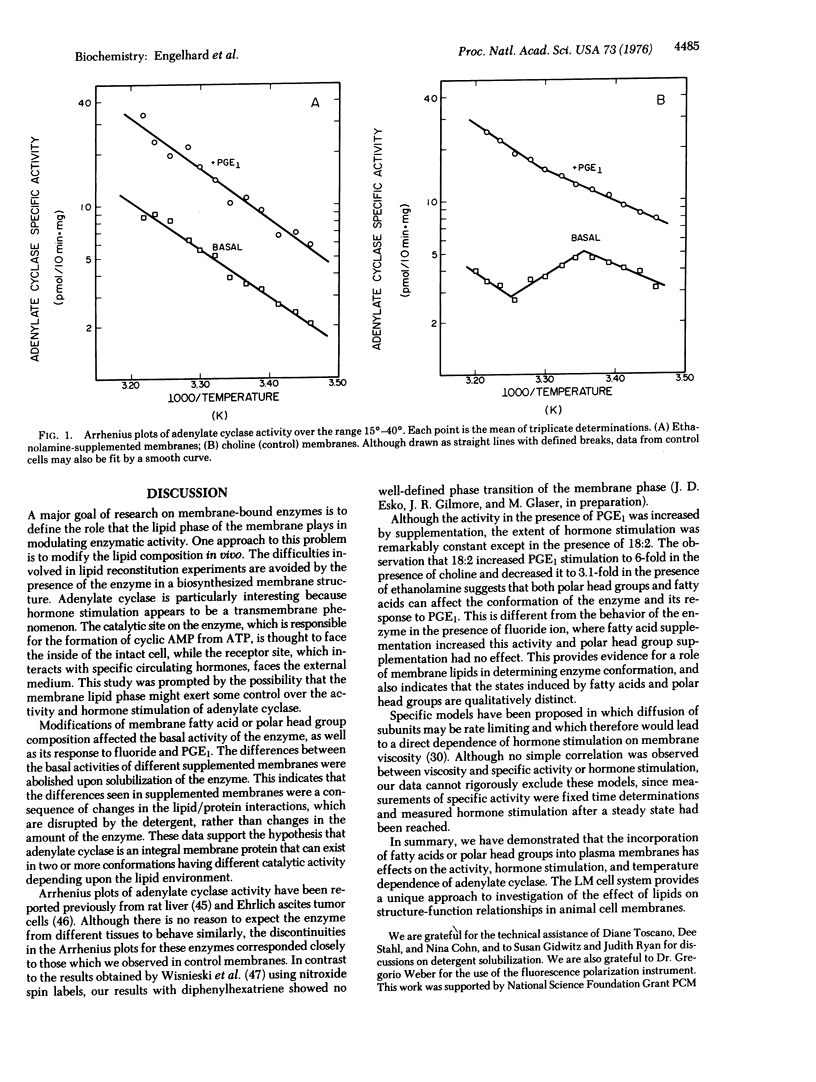
Adenylate cyclase [atp pyrophosphate-lyase (cyclizing): EC 4.6.4.4] activities were examined in mouse LM cell (fibroblast) membranes that were supplemented with ethanolamine and/or fatty acids. The supplements were incorporated into the plasma membrane phospholipids in significant amounts. Fatty acid supplementations had distinct effects as compared to polar head group supplementations. All lipid supplementations increased basal adenylate cyclase activity relative to control cells grown in choline-containing medium. Double supplementation with ethanolamine and linoleate increased the specific activity of adenylate cyclase up to 4-fold. Activity in the presence of fluoride was unaffected by ethanolamine supplementation, but was increased by fatty acid supplementation. In contrast, prostaglandin E1 stimulation was 4.2-fold in controls and ethanolamine and/or elaidate supplements, 6-fold in choline plus linoleate supplements, and 3.1-fold in ethanolamine plus linoleate supplements. Differences in activity could not be ascribed to changes in membrane protein composition in supplemented cells, and could be abolished by detergent solublization. Fluidity of the supplemented membranes was monitored by fluorescence polarization, and no correlation was observed between membrane viscosity and adenylate cyclase activity or hormone stimulation. These results emphasize the importance of the membrane lipid phase for this enzyme.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F. Lipids of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli: structure and metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):833–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.833-843.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V., O'Keefe E., Cuatrecasaş P. Mechanism of action of cholera toxin and the mobile receptor theory of hormone receptor-adenylate cyclase interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):33–37. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilezikian J. P., Aurbach G. D. The effects of nucleotides on the expression of beta-adrenergic adenylate cyclase activity in membranes from turkey erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):157–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L. Hormone-sensitive adenylyl cyclases. Useful models for studying hormone receptor functions in cell-free systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 10;300(2):129–158. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(73)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M. L., Piantadosi C., Ishaq K. S., Snyder F. Modification of glycerolipid metabolism in L-M fibroblasts by an unnatural amino-alcohol, N-isopropylethanolamine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 17;62(4):983–988. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90419-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brivio-Haugland R. P., Louis S. L., Musch K., Waldeck N., Williams M. A. Liver plasma membranes from essential fatty acid-deficient rats. Isolation, fatty acid composition, and activities of 5'-nucleotidase, ATPase and adenylate cyclase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 16;433(1):150–163. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90184-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher R. W., Ho R. J., Meng H. C., Sutherland E. W. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in biological materials. II. The measurement of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in tissues and the role of the cyclic nucleotide in the lipolytic response of fat to epinephrine. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4515–4523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson K. A., Glaser M., Bayer W. H., Vagelos P. R. Alteration of fatty acid composition of LM cells by lipid supplementation and temperature. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):146–151. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser M., Ferguson K. A., Vagelos P. R. Manipulation of the phospholipid composition of tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4072–4076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisham C. M., Barnett R. E. The role of lipid-phase transitions in the regulation of the (sodium + potassium) adenosine triphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 3;12(14):2635–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00738a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz A. F., Hatten M. E., Burger M. M. Membrane fatty acid replacements and their effect on growth and lectin-induced agglutinability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3115–3119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Warren G. B., Metcalfe J. C. The lipid environment of the glucagon receptor regulates adenylate cyclase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 17;436(2):495–504. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90211-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keirns J. J., Kreiner P. W., Bitensky M. W. An abrupt temperature-dependent change in the energy of activation of hormone-stimulated hepatic adenylyl cyclase. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(4):368–379. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. G., Birdsall N. J., Metcalfe J. C., Toon P. A., Warren G. B. Clusters in lipid bilayers and the interpretation of thermal effects in biological membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 27;13(18):3699–3705. doi: 10.1021/bi00715a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Mukherjee C., Coverstone M., Caron M. G. Stereospecific (3H)(minus)-alprenolol binding sites, beta-adrenergic receptors and adenylate cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 23;60(2):703–709. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey G. S., Fletcher M. A., Klein I., Ruiz E., Schenk A. Characterization of 125I-glucagon binding in a solubilized preparation of cat myocardial adenylate cyclase. Further evidence for a dissociable receptor site. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2665–2673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey G. S. Restoration of glucagon responsiveness of solubilized myocardial adenyl cyclase by phosphatidylserine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 2;43(1):108–113. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey G. S. Restoration of norepinephrine responsiveness of solubilized myocardial adenylate cyclase by phosphatidylinositol. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7405–7407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey G. S. Solubilization of myocardial adenyl cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 6;38(1):86–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. K., Williams R. E., Fox C. F. Effects of temperature and host lipid composition on the infection of cells by Newcastle disease virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 20;62(2):470–477. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden C. D., Wright K. L., McConnell H. M., Fox C. F. Lateral phase separations in membrane lipids and the mechanism of sugar transport in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2271–2275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overath P., Träuble H. Phase transitions in cells, membranes, and lipids of Escherichia coli. Detection by fluorescent probes, light scattering, and dilatometry. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 3;12(14):2625–2634. doi: 10.1021/bi00738a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L., Rodbell M. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. I. Properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1849–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl S. L., Krans H. M., Kozyreff V., Birnbaumer L., Rodbell M. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. VI. Evidence for a role of membrane lipids. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 25;246(14):4447–4454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puchwein G., Pfeuffer T., Helmreich E. J. Uncoupling of catecholamine activation of pigeon erythrocyte membrane adenylate cyclase by filipin. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3232–3240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethy A., Tomasi V., Trevisani A., Barnabei O. The role of phosphatidylserine in the hormonal control of adenylate cyclase of rat liver plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 1;290(1):58–69. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse H. G., Williams R. E., Fox C. F. Effect of membrane lipid composition and microtubule structure on lectin interactions of mouse LM cells. J Supramol Struct. 1974;2(5-6):629–645. doi: 10.1002/jss.400020510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubalcava B., Rodbell M. The role of acidic phospholipids in glucagon action on rat liver adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3831–3837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Réthy A., Tomasi V., Trevisani A. The role of lipids in the activity of adenylate cyclase of rat liver plasma membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Nov;147(1):36–40. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90306-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND E. W., RALL T. W., MENON T. Adenyl cylase. I. Distribution, preparation, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1220–1227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel S. D., Kent C., Bischoff R., Vagelos P. R. Plasma membranes from cultured muscle cells: isolation procedure and separation of putative plasma-membrane marker enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3195–3199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Barenholz Y. Dynamics of the hydrocarbon layer in liposomes of lecithin and sphingomyelin containing dicetylphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 25;249(8):2652–2657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Dianoux A. C., Gitler C., Weber G. Microviscosity and order in the hydrocarbon region of micelles and membranes determined with fluorescent probes. I. Synthetic micelles. Biochemistry. 1971 May 25;10(11):2106–2113. doi: 10.1021/bi00787a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Inbar M. Difference in microviscosity induced by different cholesterol levels in the surface membrane lipid layer of normal lymphocytes and malignant lymphoma cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;85(4):603–615. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90318-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silbert D. F. Genetic modification of membrane lipid. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:315–339. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellwagen E., Baker B. Proposed structure for brain adenylate cyclase purified using blue dextran-Sepharose chromatography. Nature. 1976 Jun 24;261(5562):719–720. doi: 10.1038/261719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm D. R., Chase R. A. Exploitation of hormone-induced conformational changes to label selectively a component of rat liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 10;250(7):2539–2545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm D. R., Dolginow Y. D. Glucagon stimulation of adenylate cyclase sulfhydryl reactivity. Evidence for hormone-induced conformational changes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):5208–5210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm D. R., Field S. O., Ryan J. The HLB dependency for detergent solubilization of hormonally sensitive adenylate cyclase. J Supramol Struct. 1976;4(2):221–231. doi: 10.1002/jss.400040209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. E., Wisnieski B. J., Rittenhouse H. G., Fox C. F. Utilization of fatty acid supplements by cultured animal cells. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 23;13(9):1969–1977. doi: 10.1021/bi00706a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisnieski B. J., Parkes J. G., Huang Y. O., Fox C. F. Physical and physiological evidence for two phase transitions in cytoplasmic membranes of animal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


