Abstract
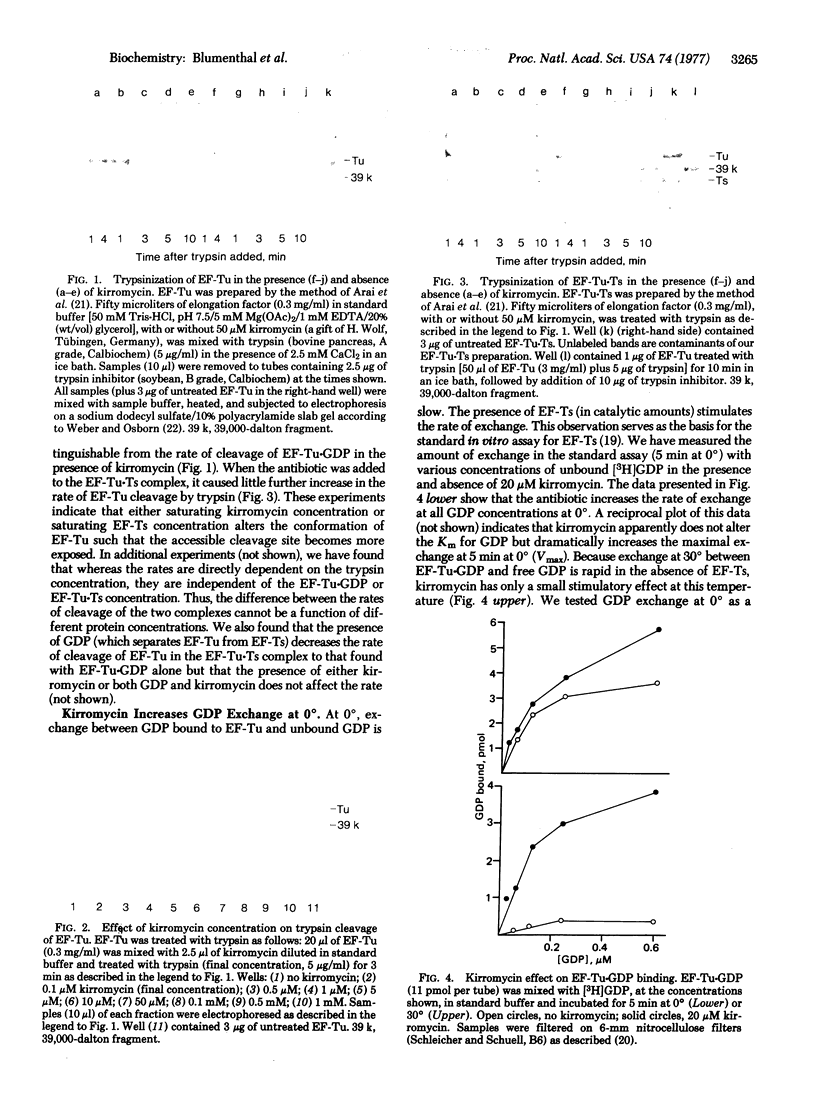
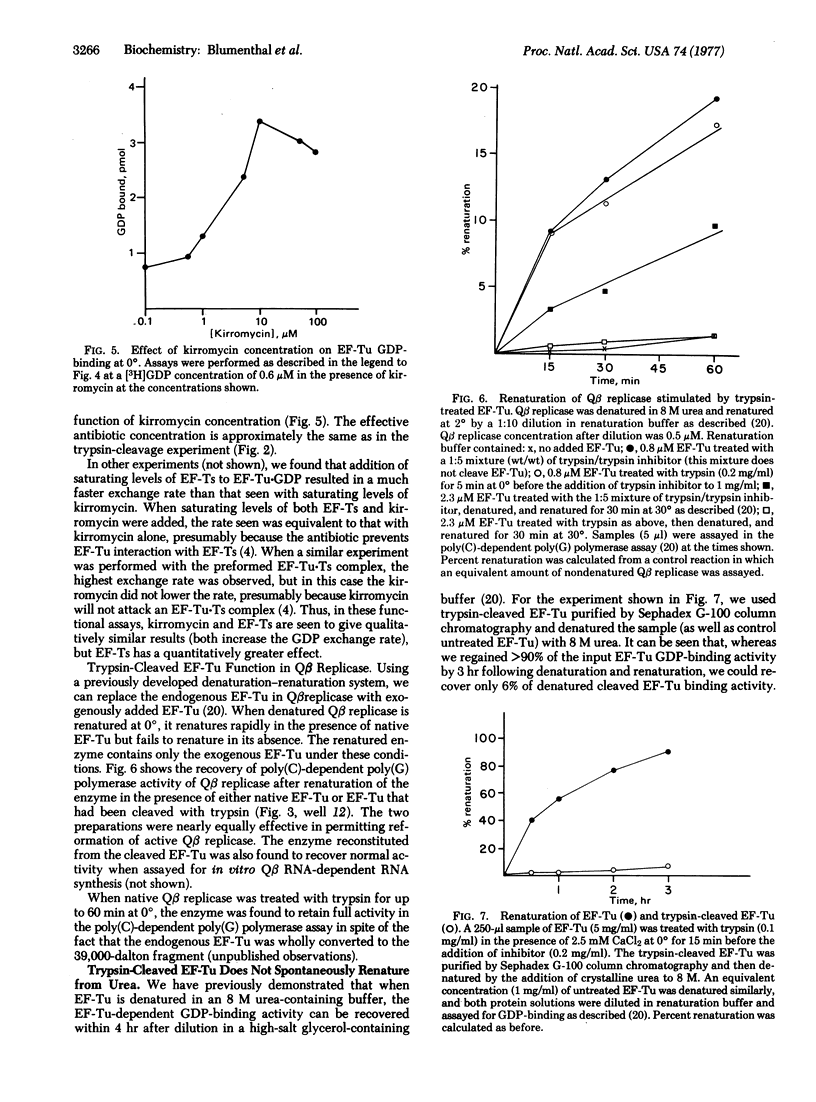
Alterations of the structure of EF-Tu have been investigated by using the rate of EF-Tu cleavage by trypsin as a conformational probe. The presence of EF-Ts bound to EF-Tu results in a 10-fold increase in the cleavage rate. The antibiotic kirromycin, which inhibits protein synthesis by virtue of its interaction with EF-Tu, mimics this effect of EF-Ts. Both kirromycin and EF-Ts also facilitate the exchange of free GDP with GDP bound to EF-Tu. The results suggest that EF-Ts and kirromycin induce a similar conformational change in EF-Tu, thereby "opening" the guanine nucleotide binding site. The trypsin-cleaved EF-Tu still can bind GDP and EF-Ts and can function in Qbeta replicase, but it no longer spontaneously renatures following denaturation in urea.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai K. I., Kawakita M., Kaziro Y., Maeda T., Onishi S. I. Conformational transition in polypeptide elongation factor Tu as revealed by electron spin resonance. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3311–3313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K. I., Kawakita M., Kaziro Y. Studies on polypeptide elongation factors from Escherichia coli. II. Purification of factors Tu-guanosine diphosphate, Ts, and Tu-Ts, and crystallization of Tu-guanosine diphosphate and Tu-Ts. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):7029–7037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K., Arai T., Kawakita M., Kaziro Y. Conformational transitions of polypeptide chain elongation factor Tu. I. Studies with hydrophobic probes. J Biochem. 1975 May;77(5):1095–1106. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K., Maeda T., Kawakita M., Ohnishi S., Kaziro Y. Conformational transitioons of polypeptide chain elongation factor Tu. II. Further studies by electron spin resonance. J Biochem. 1976 Nov;80(5):1047–1055. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K., Nakamura S., Arai T., Kawakita M., Kaziro Y. Limited hydrolysis of the polypeptide chain elongation factor Tu by trypsin. Isolation and characterization of the polypeptide fragments. J Biochem. 1976 Jan;79(1):69–83. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal T., Landers T. A. Renaturation of a multisubunit multiactivity enzyme complex: recovery of phage Qbeta RNA replicase, EF-Tu, and EF-Ts activities after denaturation in urea. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 27;15(2):422–425. doi: 10.1021/bi00647a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal T., Landers T. A., Weber K. Bacteriophage Q replicase contains the protein biosynthesis elongation factors EF Tu and EF Ts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1313–1317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S., Blumenthal T. Function and structure in ribonucleic acid phage Qbeta ribonucleic acid replicase. Effect of inhibitors of EF-Tu on ribonucleic acid synthesis and renaturation of active enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2749–2753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S., Blumenthal T. Reconstitution of Qbeta RNA replicase from a covalently bonded elongation factor Tu-Ts complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1131–1135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane L. J., Miller D. L. Guanosine triphosphate and guanosine diphosphate as conformation-determining molecules. Differential interaction of a fluorescent probe with the guanosine nucleotide complexes of bacterial elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 26;13(5):933–938. doi: 10.1021/bi00702a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gast W. H., Leberman R., Schulz G. E., Wittinghofer A. Crystals of partially trypsin-digested elongation factor Tu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Oct 5;106(4):943–950. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90344-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Rosenbusch J. P. A functionally active tryptic fragment of Escherichia coli elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 16;15(23):5105–5110. doi: 10.1021/bi00668a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Rosenbusch J. P. Abundance and membrane association of elongation factor Tu in E. coli. Nature. 1976 May 6;261(5555):23–26. doi: 10.1038/261023a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landers T. A., Blumenthal T., Weber K. Function and structure in ribonucleic acid phage Q beta ribonucleic acid replicase. The roles of the different subunits in transcription of synthetic templates. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5801–5808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J. Protein biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:409–448. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Printz M. P., Miller D. L. Evidence for conformational changes in elongation factor Tu induced by GTP and GDP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jul 2;53(1):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91413-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbusch J. P., Jacobson G. R., Jaton J. C. Does a bacterial elongation factor share a common evolutionary ancestor with actin? J Supramol Struct. 1976;5(3):391–396. doi: 10.1002/jss.400050311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach H., Miller D. L., Hachmann J. Studies on the role of factor Ts in polypeptide synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Mar;137(1):262–269. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. E., Jr, Cohn M. Magnetic resonance studies of the manganese guanosine di- and triphosphate complexes with elongation factor Tu. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2004–2009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Chinali G., Parmeggiani A. Kirromycin, an inhibitor of protein biosynthesis that acts on elongation factor Tu. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4910–4914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





