Abstract
Lymphocytes isolated from normal human peripheral blood can be induced to form colonies in vitro by incubation with the appropriate inducer. Phytohemagglutinin can induce colonies with T (thymus-derived) lymphocytes. Optimun colony formation with about two colonies per 10(2) peripheral blood lymphocytes was obtained by adding, in addition to phytohemagglutinin, autologous plasma, autoologous red blood cells, and fresh L-glutamine or L-cystine. In the absence of these fresh amino acids, no colonies were formed at seeding levels below 10(5) cells per 35 mm petri dish. The addition of either of these amino acids gave a 10-fold decrease in the minimum number of cells that had to be seeded for colony formation. Lipopolysaccharide did not induce the formation of colonies, but enhanced the formation of T cell colonies by phytohemagglutinin. The mixing of lymphocytes from persons with and deficient in glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase (EC 1-1-1-49) has shown that phytohemagglutinin-induced colonies can be derived from single cells and are, therefore, clones. No colonies were formed by lethally irradiated cells. Incubation with pokeweed mitogen also induced the formation of colonies. With autologous plasma and autologous red blood cells, pokeweek mitogen induced about one colony per 5 X 10(3) cells seeded and no colonies at seeding levels below 10(5) cells per petri dish. The minimum number of cells needed for colony formation by pokeweed mitogen was not decreased by fresh L-glutamine or L-cystine. The results indicate that normal human lymphocytes can be cloned in vitro and that induction of these lymphocyte colonies can be regulated by lectins and other specific factors.
Full text
PDF

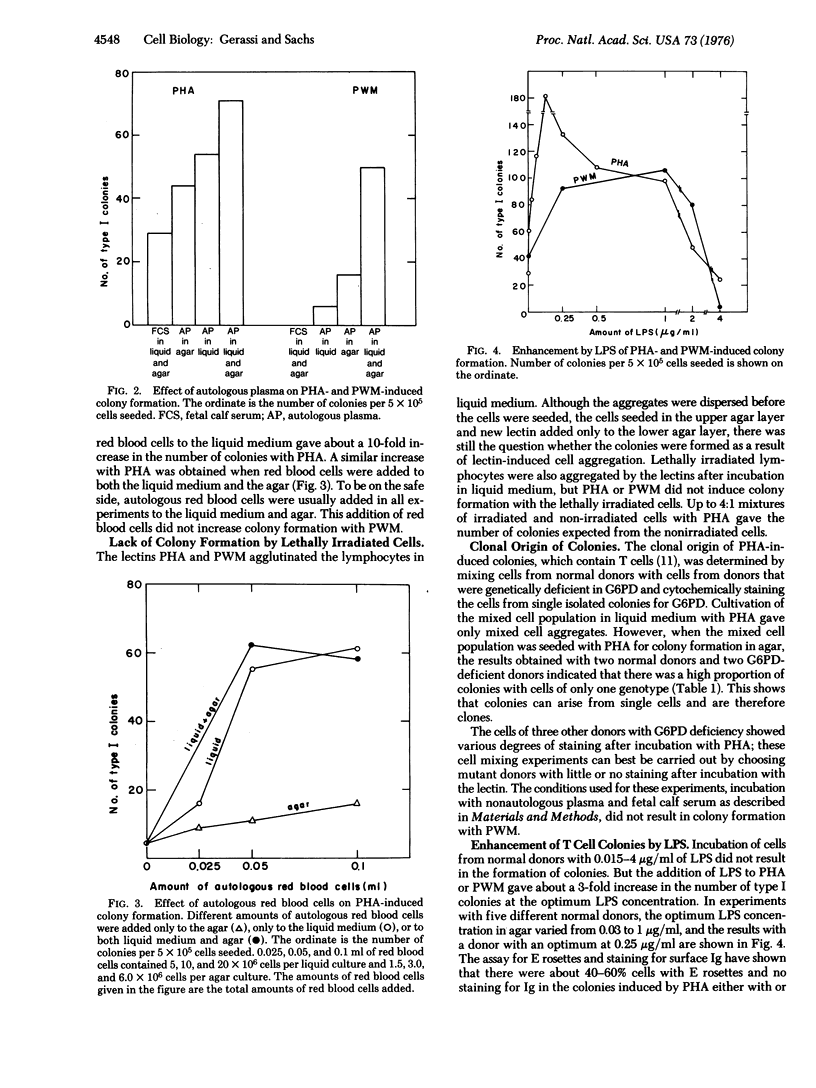
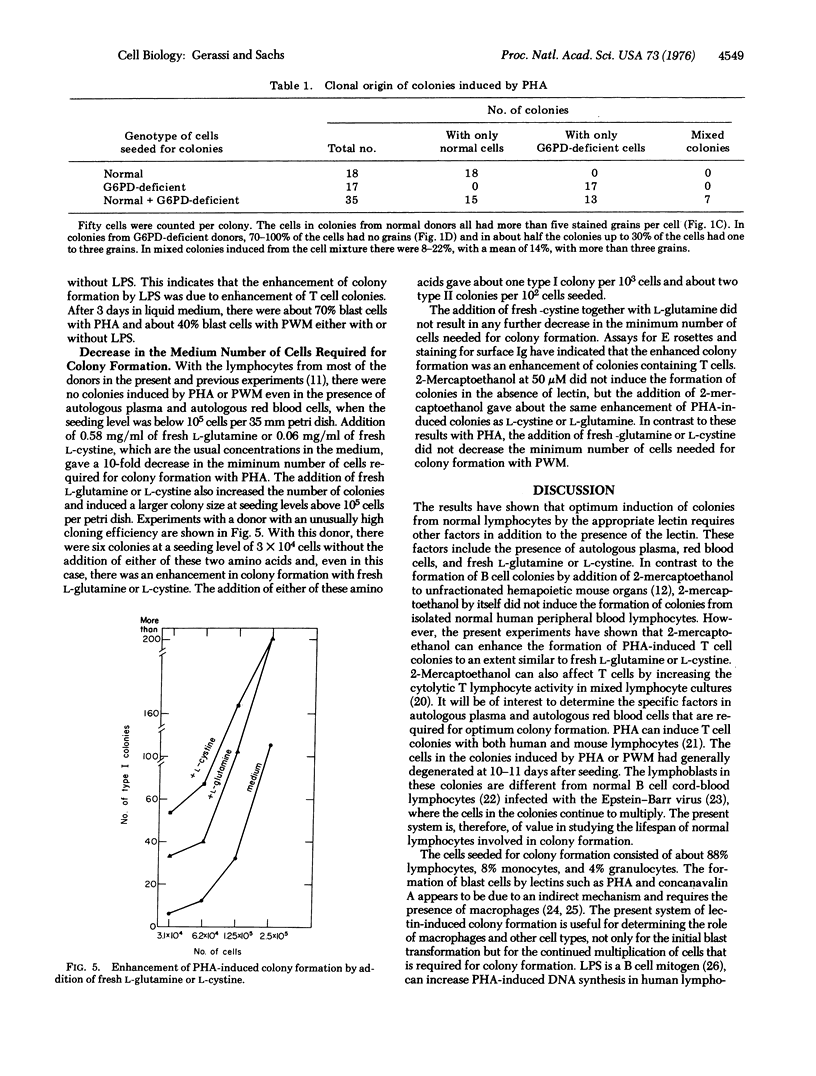

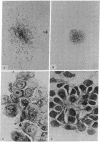
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armerding D., Katz D. H. Activation of T and B lymphocytes in vitro. I. Regulatory influence of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on specific T-cell helper function. J Exp Med. 1974 Jan 1;139(1):24–43. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer C. F., Bowers W. E. Periodate and concanavalin A induce blast transformation of rat lymphocytes by an indirect mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3590–3593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley T. R., Metcalf D. The growth of mouse bone marrow cells in vitro. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1966 Jun;44(3):287–299. doi: 10.1038/icb.1966.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J., Klein E., Klein G., Clifford P., Singh S. Immunoglobulin and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase as markers of cellular origin in Burkitt lymphoma. J Exp Med. 1973 Jul 1;138(1):89–102. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibach E., Gerassi E., Sachs L. Induction of colony formation in vitro by human lymphocytes. Nature. 1976 Jan 15;259(5539):127–129. doi: 10.1038/259127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg H., Sachs L. Destruction of mouse and rat embryo cells in tissue culture by lymph node cells from unsensitized rats. J Cell Physiol. 1965 Oct;66(2):199–219. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030660207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. W., MacDonald H. R., Engers H. D., Fitch F. W., Cerottini J. Increased cytolytic T lymphocyte activity induced by 2-mercaptoethanol in mixed leukocyte cultures: kinetics and possible mechanisms of action. J Immunol. 1976 Apr;116(4):1071–1077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa Y., Pluznik D. H., Sachs L. In vitro control of the development of macrophage and granulocyte colonies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):488–495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Greaves M. Functional analysis of murine and human B lymphocyte subsets. Transplant Rev. 1975;24:177–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Wigzell H., Aiuti F. Human lymphocyte subpopulations: classification according to surface markers and-or functional characteristics. Transplant Rev. 1973;16:163–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1973.tb00120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. The Epstein-Barr virus and neoplasia. N Engl J Med. 1975 Dec 25;293(26):1353–1357. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197512252932607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Control of Fc and C3 receptors on myeloid leukemic cells. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):580–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Different blocks in the differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3507–3511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKS P. A., GROSS R. T. Erythrocyte glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency: evidence of differences between Negroes and Caucasians with respect to this genetically determined trait. J Clin Invest. 1959 Dec;38:2253–2262. doi: 10.1172/JCI104006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Nossal G. J., Warner N. L., Miller J. F., Mandel T. E., Layton J. E., Gutman G. A. Growth of B-lymphocyte colonies in vitro. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1534–1549. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz U., Sachs L. Membrane difference in peripheral blood lymphocytes from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Hodgkin's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2428–2432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishell R. I., Dutton R. W. Immunization of dissociated spleen cell cultures from normal mice. J Exp Med. 1967 Sep 1;126(3):423–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paran M., Sachs L., Barak Y., Resnitzky P. In vitro induction of granulocyte differentiation in hematopoietic cells from leukemic and non-leukemic patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1542–1549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluznik D. H., Sachs L. The cloning of normal "mast" cells in tissue culture. J Cell Physiol. 1965 Dec;66(3):319–324. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030660309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluznik D. H., Sachs L. The induction of clones of normal mast cells by a substance from conditioned medium. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Oct;43(3):553–563. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMOT B., FISHER S., SZEINBERG A., ADAM A., SHEBA C., GAFNI D. A study of subjects with erythrocyte glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. II. Investigation of leukocyte enzymes. J Clin Invest. 1959 Dec;38:2234–2237. doi: 10.1172/JCI104004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstraus M., Chasin L. A. Isolation of mammalian cell mutants deficient in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity: linkage to hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):493–497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstreich D. L., Farrar J. J., Dougherty S. Absolute macrophage dependency of T lymphocyte activation by mitogens. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):131–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenszajn L., Shoham D. The demonstration of dehydrogenases and diaphorases in cells of peripheral blood and bone marrow. Blood. 1967 May;29(5):737–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs L. Regulation of membrane changes, differentiation, and malignancy in carcinogenesis. Harvey Lect. 1974;68:1–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidtke J. R., Najarian J. S. Synergistic effects on DNA synthesis of phytohemagglutinin or concanavalin A and lipopolysaccharide in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):742–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sredni B., Kalechman Y., Michlin H., Rozenszajn L. A. Development of colonies in vitro of mitogen-stimulated mouse T lymphocytes. Nature. 1976 Jan 15;259(5539):130–132. doi: 10.1038/259130a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wajntal A., DeMars R. A tetrazolium method for distinguishing between cultured human fibroblasts having eiter normal or deficient levels of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochem Genet. 1967 Jun;1(1):61–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00487737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto N., Hinuma Y. Clonal transformation of human leukocytes by Epstein-Barr virus in soft agar. Int J Cancer. 1976 Feb 15;17(2):191–196. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]