Abstract
The rates of conversion of types I and III procollagens to their respective collagens were compared in seven fibroblast culture systems of murine or human origin. During 24 hr of radioactive labeling or after shorter pulses followed by chases of 20-48 hr, no evidence was obtained for conversion of radiolabeled type III procollagen to insoluble collagen. In the same cultures and under the same conditions, native collagen was generated from radiolabeled type I procollagen. There was no evidence for proteolytic degradation of type III procollagen during the chase experiments. The results are ascribed to a lack of availability of the enzymes required for processing of type III procollagen.
Full text
PDF
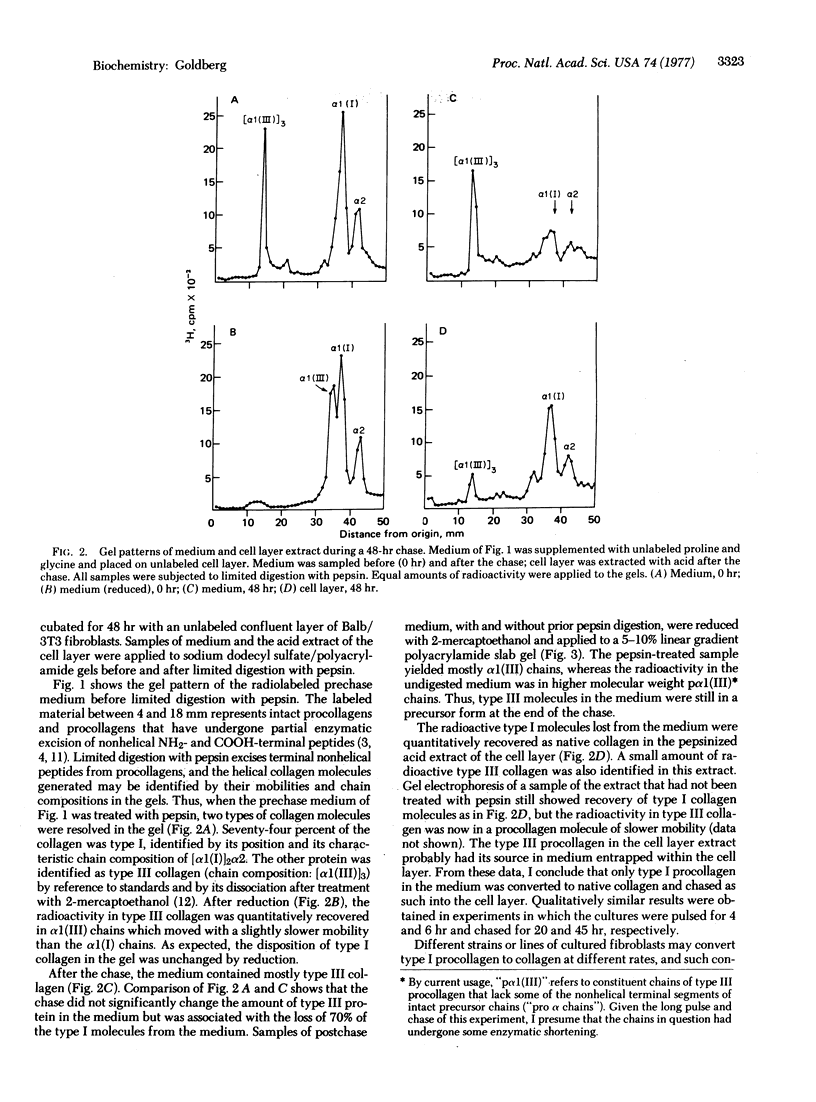
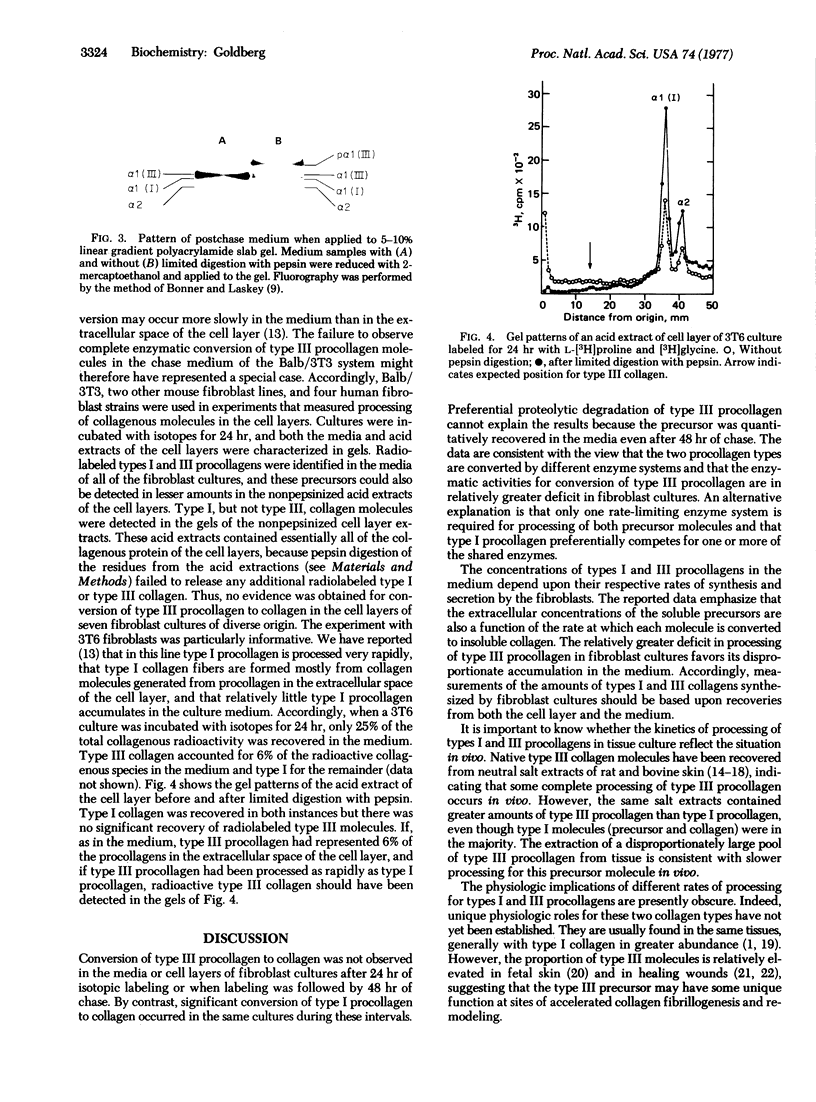

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anesey J., Scott P. G., Veis A., Chyatte D. The isolation of a soluble type III collagen precursor from rat skin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 17;62(4):946–952. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90414-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey A. J., Bazin S., Sims T. J., Le Lous M., Nicoletis C., Delaunay A. Characterization of the collagen of human hypertrophic and normal scars. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 20;405(2):412–421. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90106-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey A. J., Sims T. J., Le Lous, bazin S. Collagen polymorphism in experimental granulation tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 27;66(4):1160–1165. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90480-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., McKenney K. H., Lichtenstein J. R., Martin G. R. Preparation of type III procollagen and collagen from rat skin. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 3;13(25):5243–5248. doi: 10.1021/bi00722a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung E., Keele E. M., Miller E. J. Isolation and characterization of the cyanogen bromide peptides from the alpha 1(3) chain of human collagen. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3459–3464. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church R. L., Tanzer M. L., Lapiere C. M. Identification of two distinct species of procollagen synthesized by a clonal line of calf dermatosparactic cells. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 8;244(136):188–190. doi: 10.1038/newbio244188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. M., McEneany L. S., Bornstein P. Intermediates in the limited proteolytic conversion of procollagen to collagen. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 18;14(23):5188–5194. doi: 10.1021/bi00694a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E. H., Jr (Alpha1(3))3 human skin collagen. Release by pepsin digestion and preponderance in fetal life. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3225–3231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E. H., Jr, Munderloh N. H. Isolation and characterization of CNBr peptides of human (alpha 1 (III) )3 collagen and tissue distribution of (alpha 1 (I) )2 alpha 2 and (alpha 1 (III) )3 collagens. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 25;250(24):9304–9312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg B. Collagen synthesis as a marker for cell type in mouse 3T3 lines. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90327-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg B., Epstein E. H., Jr, Sherr C. J. Precursors of collagen secreted by cultured human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3655–3659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg B., Sherr C. J. Secretion and extracellular processing of procollagen by cultured human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):361–365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg B., Taubman M. B., Radin A. Procollagen peptidase: its mode of action on the native substrate. Cell. 1975 Jan;4(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90132-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A. Basement membranes: structural and biosynthetic considerations. J Invest Dermatol. 1975 Jul;65(1):85–92. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12598062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenaers A., Lapiere C. M. Type III procollagen and collagen in skin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 21;400(1):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90132-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein J. R., Byers P. H., Smith B. D., Martin G. R. Identification of the collagenous proteins synthesized by cultured cells from human skin. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 22;14(8):1589–1594. doi: 10.1021/bi00679a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Biochemical characteristics and biological significance of the genetically-distinct collagens. Mol Cell Biochem. 1976 Dec 10;13(3):165–192. doi: 10.1007/BF01731779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. D., McKenney K. H., Lustberg T. J. Characterization of collagen precursors found in rat skin and rat bone. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 28;16(13):2980–2985. doi: 10.1021/bi00632a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taubman M. B., Goldberg B. The processing of procollagen in cultures of human and mouse fibroblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Apr;173(2):490–494. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90286-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Glanville R. W., Nowack H., Wiedemann H., Fietzek P. P., Kühn K. Isolation, chemical and electron microscopical characterization of neutral-salt-soluble type III collagen and procollagen from fetal bovine skin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Nov;356(11):1783–1792. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.2.1783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



