Abstract
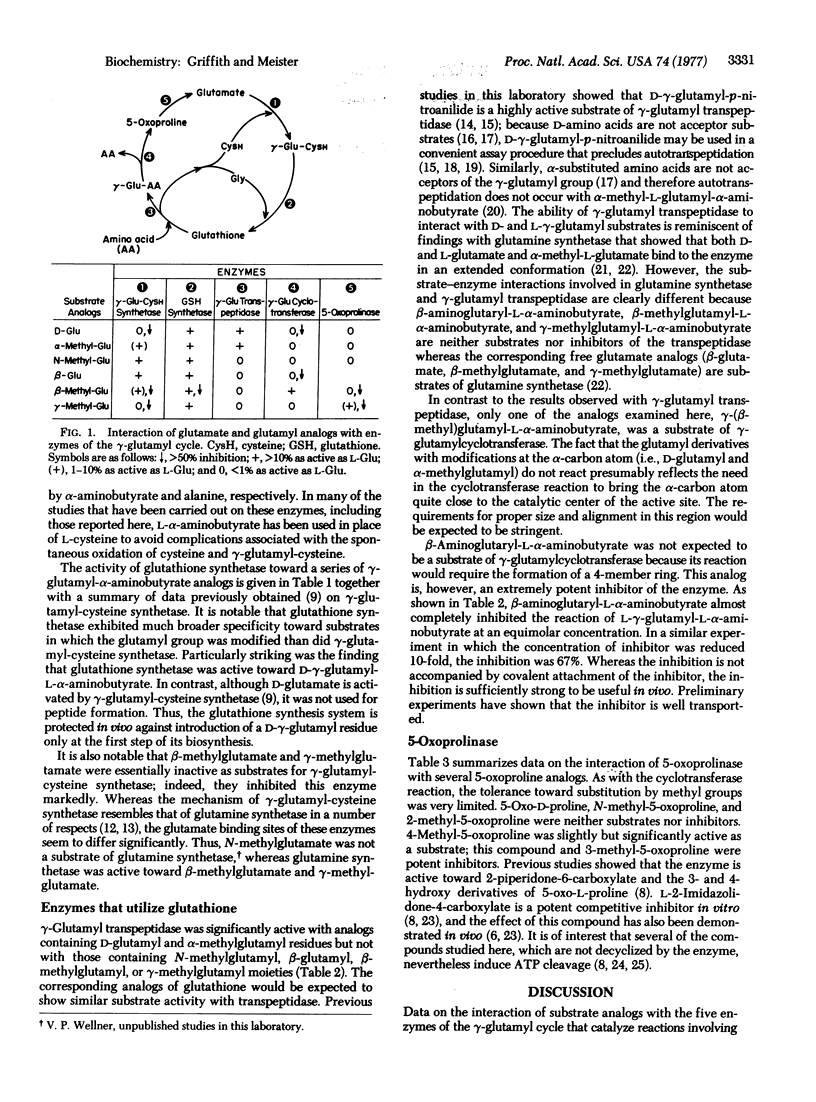
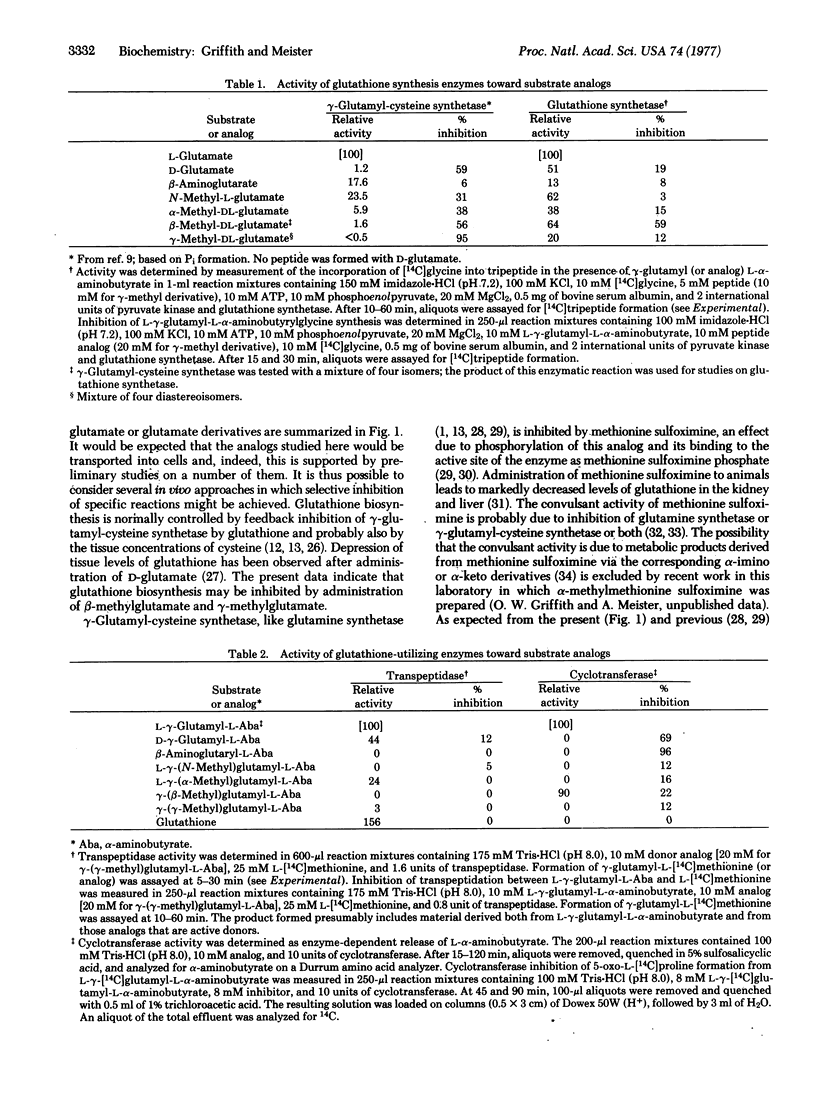
Substrate analogs have been obtained that selectively inhibit the reactions of the gamma-glutamyl cycle or that are susceptible to only limited metabolism by the cycle. Thus, glutathione synthesis may be inhibited and analogs of glutathione may be synthesized that do not participate in transpeptidation. Specific inhibitors of gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase and 5-oxoprolinase have been obtained. The findings offer new approaches to the in vivo study of the cycle and also to the design of more specifically directed analogs of inhibitors such as methionine sulfoximine and 6-diazo-5-oxonorleucine.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper A. J., Stephani R. A., Meister A. Enzymatic reactions of methionine sulfoximine. Conversion to the corresponding alpha-imino and alpha-keto acids and to alpha-ketobutyrate and methane sulfinimide. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6674–6682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONE J., FOWDEN L. A new amino acid amide in the groundnut plant (Arachis hypogaea); evidence of the occurrence of gamma-methyleneglutamine and gamma-methyleneglutamic acid. Biochem J. 1952 Jul;51(4):451–458. doi: 10.1042/bj0510451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FODOR P. J., MILLER A., WAELSCH H. Quantitative aspects of enzymatic cleavage of glutathione. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jun;202(2):551–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W., Meister A. Dependence of energy coupling on nucleotide base structure in the reaction catalyzed by 5-oxo-L-prolinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jun 7;70(3):759–765. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90657-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Horiuchi S., Morino Y. Affinity labeling of rat-kidney gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Mar 1;73(2):335–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan H. M., Manning L. R., Meister A. Stereospecific synthesis of alpha-methyl-L-glutamine by glutamine synthetase. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1063–1068. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkowsky A. M., Bergamini M. V., Orlowski M. Kinetic studies of sheep kidney gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4736–4743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning J. M., Moore S., Rowe W. B., Meister A. Identification of L-methionine S-sulfoximine as the diastereoisomer of L-methionine SR-sulfoximine that inhibits glutamine synthetase. Biochemistry. 1969 Jun;8(6):2681–2685. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A., Tate S. S. Glutathione and related gamma-glutamyl compounds: biosynthesis and utilization. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:559–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A. The specificity of glutamine synthetase and its relationship to substrate conformation at the active site. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1968;31:183–218. doi: 10.1002/9780470122761.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLOWSKI M., MEISTER A. GAMMA-GLUTAMYL-P-NITROANILIDE: A NEW CONVENIENT SUBSTRATE FOR DETERMINATION AND STUDY OF L- AND D-GAMMA-GLUTAMYLTRANSPEPTIDASE ACTIVITIES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 6;73:679–681. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Meister A. -Glutamyl cyclotransferase. Distribution, isozymic forms, and specificity. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2836–2844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palekar A. G., Tate S. S., Meister A. Decrease in glutathione levels of kidney and liver after injection of methionine sulfoximine into rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 3;62(3):651–657. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90448-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman P. G., Meister A. Regulation of gamma-glutamyl-cysteine synthetase by nonallosteric feedback inhibition by glutathione. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1422–1426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman P. G., Orlowski M., Meister A. Inhibition of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase by L-methionine-S-sulfoximine. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6684–6690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronzio R. A., Rowe W. B., Meister A. Studies on the mechanism of inhibition of glutamine synthetase by methionine sulfoximine. Biochemistry. 1969 Mar;8(3):1066–1075. doi: 10.1021/bi00831a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. B., Meister A. Identification of L-methionine-S-sulfoximine as the convulsant isomer of methionine sulfoximine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):500–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekura R., Meister A. gamma-Glutamylcysteine synthetase. Further purification, "half of the sites" reactivity, subunits, and specificity. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2599–2605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekura R., Van Der Werf P., Meister A. Mechanism and significance of the mammalian pathway for elimination of D-glutamate; inhibition of glutathione synthesis by D-glutamate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 12;71(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Affinity labeling of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and location of the gamma-glutamyl binding site on the light subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):931–935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Interaction of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase with amino acids, dipeptides, and derivatives and analogs of glutathione. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7593–7602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. A., Meister A. Hydrolysis and transfer reactions catalyzed by gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase; evidence for separate substrate sites and for high affinity of L-cystine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 12;71(1):32–36. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90245-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Werf P., Griffith O. W., Meister A. 5-Oxo-L-prolinase (L-pyroglutamate hydrolase). Purification and catalytic properties. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6686–6692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Werf P., Stephani R. A., Meister A. Accumulation of 5-oxoproline in mouse tissues after inhibition of 5-oxoprolinase and administration of amino acids: evidence for function of the gamma-glutamyl cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1026–1029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Werf P., Stephani R. A., Orlowski M., Meister A. Inhibition of 5-oxoprolinase by 2-imidazolidone-4-carboxylic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):759–761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALEY S. G. Acidic peptides of the lens. 3. The structure of ophthalmic acid. Biochem J. 1958 Jan;68(1):189–192. doi: 10.1042/bj0680189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALEY S. G. Acidic peptides of the lens. Biochem J. 1956 Dec;64(4):715–726. doi: 10.1042/bj0640715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


