Abstract
Transcriptional regulators play important roles in the control of key developmental events. We have identified sw3-3, a likely candidate for such a function, in tissues of the eye and other neural organs. It encodes a basic-leucine zipper-like protein, in which two leucine zipper motifs flank a basic domain. The latter contains helix-disturbing amino acids such as glycine and proline, at positions occupied by conserved asparagine and alanine residues (respectively) in "conventional" basic-leucine zipper proteins. sw3-3 is widely expressed at early embryonic stages in the lens, retina, and other neural tissues and is down-regulated thereafter with a spatial and temporal pattern that correlates with the cessation of mitotic activity and the onset of cell migration and differentiation.
Full text
PDF

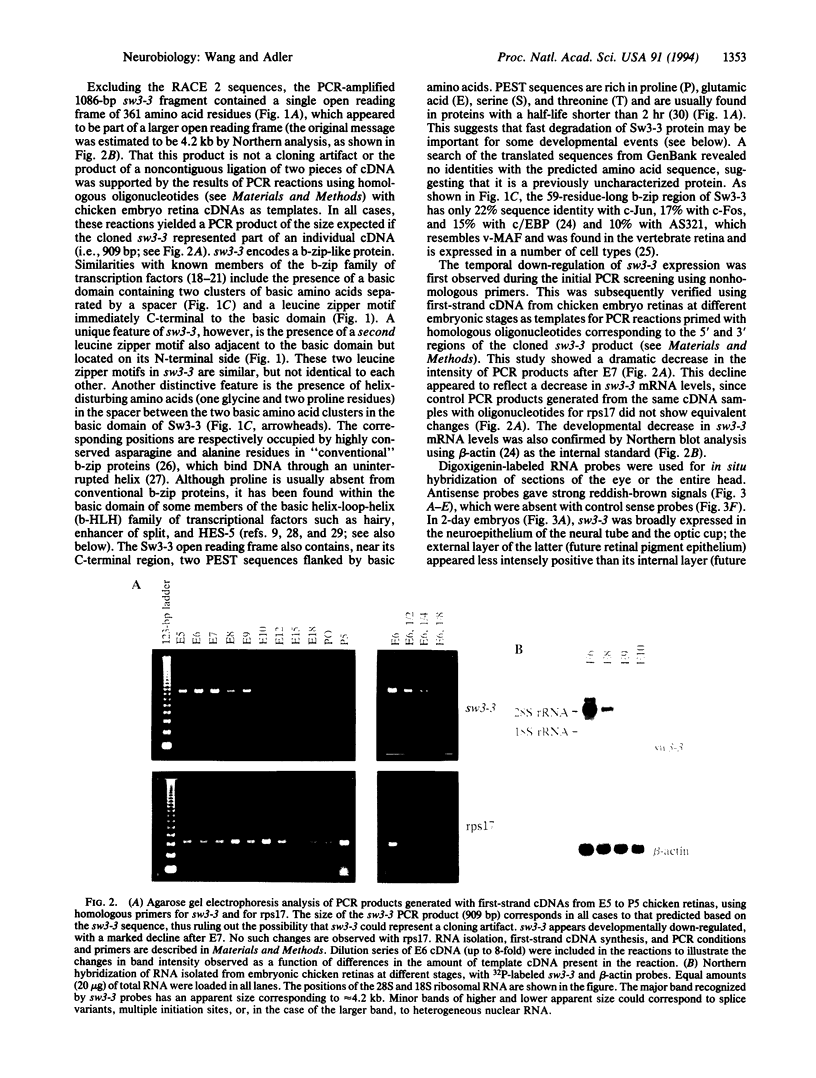
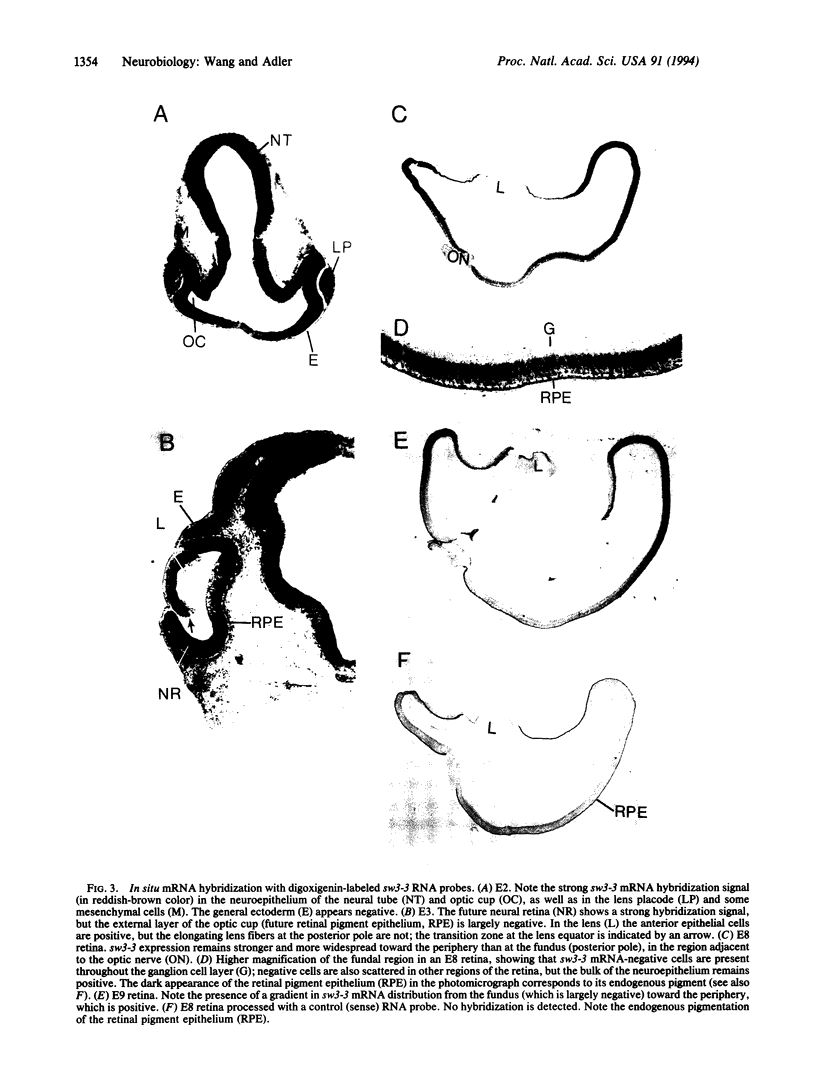

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler R. Determination of cellular types in the retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1993 Apr;34(5):1677–1682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler R. Plasticity and differentiation of retinal precursor cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;146:145–190. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60382-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akazawa C., Sasai Y., Nakanishi S., Kageyama R. Molecular characterization of a rat negative regulator with a basic helix-loop-helix structure predominantly expressed in the developing nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21879–21885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begley C. G., Lipkowitz S., Göbel V., Mahon K. A., Bertness V., Green A. R., Gough N. M., Kirsch I. R. Molecular characterization of NSCL, a gene encoding a helix-loop-helix protein expressed in the developing nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):38–42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Ortega J. A. Mechanisms of a cellular decision during embryonic development of Drosophila melanogaster: epidermogenesis or neurogenesis. Adv Genet. 1990;27:403–453. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan M., DiCicco-Bloom E. M., Xiang X., Benezra R., Chada K. The gene for the helix-loop-helix protein, Id, is specifically expressed in neural precursors. Dev Biol. 1992 Nov;154(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90042-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger T. E., Brandl C. J., Struhl K., Harrison S. C. The GCN4 basic region leucine zipper binds DNA as a dimer of uninterrupted alpha helices: crystal structure of the protein-DNA complex. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1223–1237. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Abate C., Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2494702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grün G. The development of the vertebrate retina: a comparative survey. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1982;78:1–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Rosenfeld M. G. Mechanisms of complex transcriptional regulation: implications for brain development. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):183–196. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90257-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt C. E., Bertsch T. W., Ellis H. M., Harris W. A. Cellular determination in the Xenopus retina is independent of lineage and birth date. Neuron. 1988 Mar;1(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A. J. An autoradiographic analysis of the time of appearance of neurons in the developing chick neural retina. Dev Biol. 1974 May;38(1):30–40. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90256-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. The role of the leucine zipper in the fos-jun interaction. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):646–651. doi: 10.1038/336646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine E. M., Schechter N. Homeobox genes are expressed in the retina and brain of adult goldfish. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2729–2733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo L. C., Johnson J. E., Wuenschell C. W., Saito T., Anderson D. J. Mammalian achaete-scute homolog 1 is transiently expressed by spatially restricted subsets of early neuroepithelial and neural crest cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1524–1537. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P., Carriere C., Dozier C., Quatannens B., Mirabel M. A., Vandenbunder B., Stehelin D., Saule S. Characterization of a paired box- and homeobox-containing quail gene (Pax-QNR) expressed in the neuroretina. Oncogene. 1992 Sep;7(9):1721–1728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan A. P., Davidson D. R., Sime C., Graham E., Baldock R., Bhattacharya S. S., Hill R. E. The Msh-like homeobox genes define domains in the developing vertebrate eye. Development. 1991 Aug;112(4):1053–1061. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.4.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscona A. A., Linser P. Developmental and experimental changes in retinal glia cells: cell interactions and control of phenotype expression and stability. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1983;18:155–188. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60582-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuman T., Keen A., Knapik E., Shain D., Ross M., Nornes H. O., Zuber M. X. ME1 and GE1: basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors expressed at high levels in the developing nervous system and in morphogenetically active regions. Eur J Neurosci. 1993 Apr 1;5(4):311–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1993.tb00498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N. MyoD family: a paradigm for development? Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1454–1461. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papaconstantinou J. Molecular aspects of lens cell differentiation. Science. 1967 Apr 21;156(3773):338–346. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3773.338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persons B. J., Modak S. P. The pattern of DNA synthesis in the lens epithelium and the annular pad during development and growth of the chick lens. Exp Eye Res. 1970 Jan;9(1):144–151. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(70)80069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatigorsky J. Lens differentiation in vertebrates. A review of cellular and molecular features. Differentiation. 1981;19(3):134–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1981.tb01141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J., Turner D., Cepko C. Lineage analysis in the vertebrate nervous system by retrovirus-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):156–160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redemann-Fibi B., Schuermann M., Müller R. Stage and tissue-specific expression of fosB during mouse development. Differentiation. 1991 Feb;46(1):43–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1991.tb00864.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Wells R., Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):364–368. doi: 10.1126/science.2876518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C. A., Hogan A., Pinchin S. M., Howe K. M., Lardelli M., Ish-Horowicz D. The Drosophila hairy protein acts in both segmentation and bristle patterning and shows homology to N-myc. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3095–3103. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08461.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence S. G., Robson J. A. An autoradiographic analysis of neurogenesis in the chick retina in vitro and in vivo. Neuroscience. 1989;32(3):801–812. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90300-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Mechanisms for diversity in gene expression patterns. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90256-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaroop A., Xu J. Z., Pawar H., Jackson A., Skolnick C., Agarwal N. A conserved retina-specific gene encodes a basic motif/leucine zipper domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):266–270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. L., Cepko C. L. A common progenitor for neurons and glia persists in rat retina late in development. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):131–136. doi: 10.1038/328131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R., Tjian R. Leucine repeats and an adjacent DNA binding domain mediate the formation of functional cFos-cJun heterodimers. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.2494701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetts R., Fraser S. E. Multipotent precursors can give rise to all major cell types of the frog retina. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1142–1145. doi: 10.1126/science.2449732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y., Baldassare M., Fisher P., Rathbun G., Oltz E. M., Yancopoulos G. D., Jessell T. M., Alt F. W. LH-2: a LIM/homeodomain gene expressed in developing lymphocytes and neural cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):227–231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]