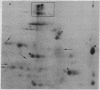
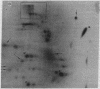
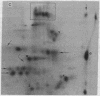
Abstract
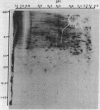
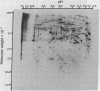
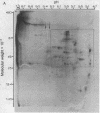
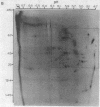
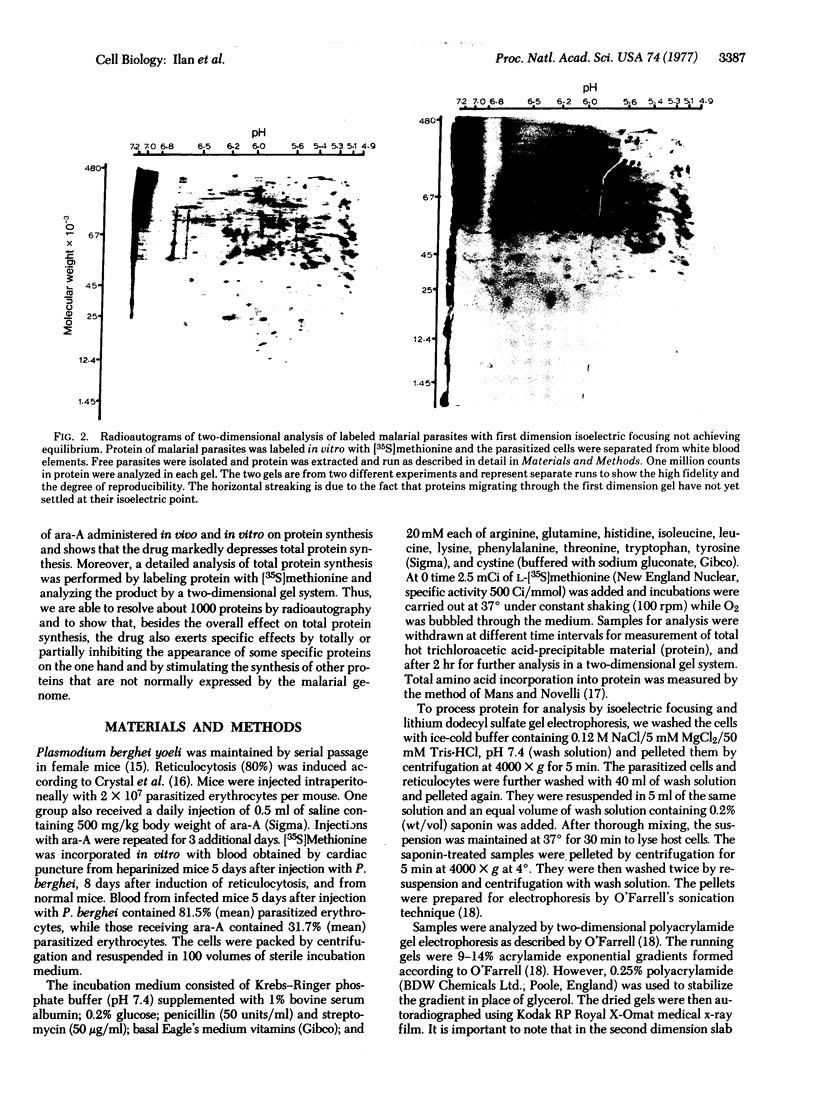
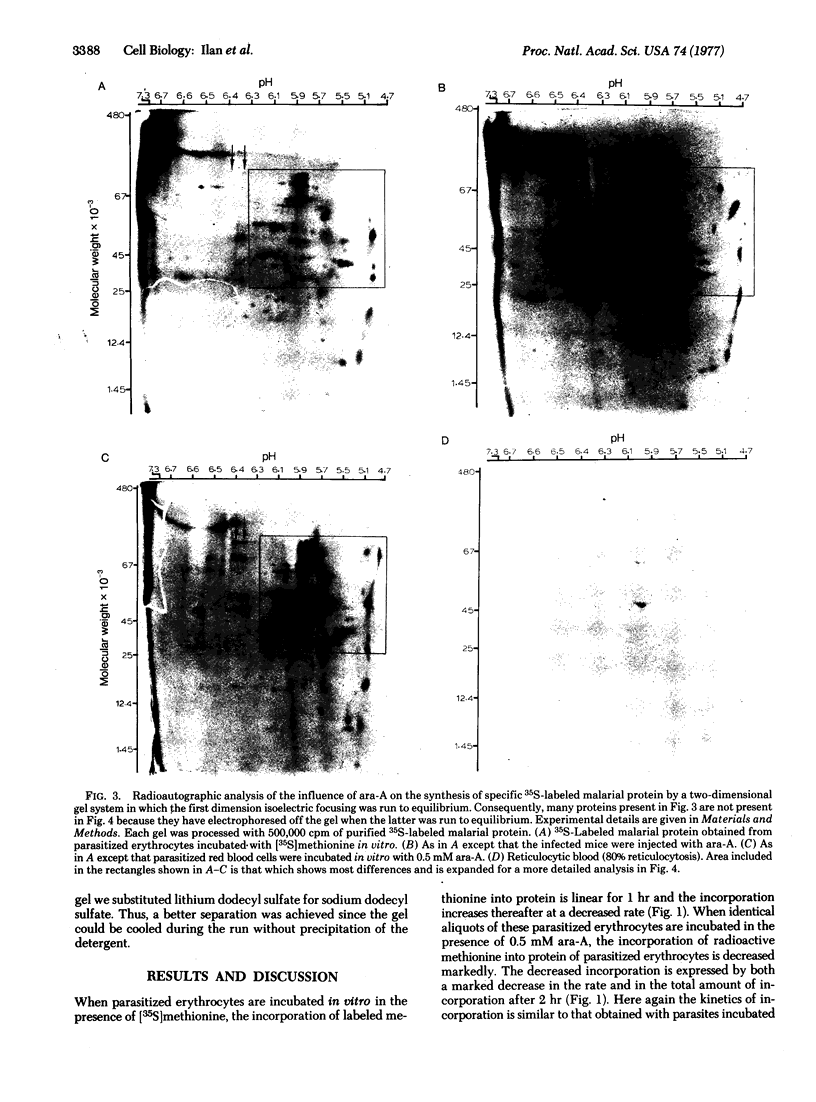
The antibiotic 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine is a drug with a broad spectrum of activity against animal viruses, with little or no effect on mammalian cells, when administered in vivo or in vitro. Here we report that the antibiotic markedly inhibited the incorporation of [35S]methionine into malarial protein. Inhibition was apparent when the parasites were either exposed to the drug in vivo during the course of infection or incubated with the drug in vitro. Moreover, the antibiotic induced pronounced changes in the spectrum of proteins synthesized. Some proteins that are prominently apparent in the control disappear from the drug-treated parasites; others specific for drug-treated parasites appear, indicating changes in the commitment for gene expression as manifested by the appearance of the final protein product. Proteins synthesized were analyzed by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gels; the first dimension used isoelectric focusing in cylinder gels and the second dimension used electrophoresis in a lithium dodecyl sulfate slab gel. Proteins were visualized by radioautography.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alger N. E., Spira D. T., Silverman P. H. Inhibition of rodent malaria in mice by rifampicin. Nature. 1970 Jul 25;227(5256):381–382. doi: 10.1038/227381b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ch'ien L. T., Cannon N. J., Charamella L. J., Dismukes W. E., Whitley R. J., Buchanan R. A., Alford C. A., Jr Effect of adenine arabinoside on severe Herpesvirus hominis infections in man. J Infect Dis. 1973 Nov;128(5):658–663. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.5.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth J. J., Cohen S. S. Inhibition of mammalian DNA polymerase by the 5'-triphosphate of 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine. Cancer Res. 1967 Sep;27(9):1528–1533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman W. L., Ilan J. Analysis by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the in vivo phosphorylation of ribosomal proteins derived from free and membrane-bound polysomes. Mol Biol Rep. 1975 Oct;2(3):219–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00356991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman W. L., Ilan J. Complete solubilization of ribosomal proteins during the fractionation of mouse liver ribosomal proteins by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Prep Biochem. 1976;6(1):13–26. doi: 10.1080/00327487608061597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilan J., Ilan J. Aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetases from cell-free extract of Plasmodium berghei. Science. 1969 May 2;164(3879):560–562. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3879.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilan J., Tokuyasu K., Ilan J. Phosphorylation of D-Arabinosyl adenine by Plasmodium berghei and its partial protection of mice against malaria. Nature. 1970 Dec 26;228(5278):1300–1301. doi: 10.1038/2281300a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahiel R. I., Vilcek J., Nussenzweig R. S. Exogenous interferon protects mice against Plasmodium berghei malaria. Nature. 1970 Sep 26;227(5265):1350–1351. doi: 10.1038/2271350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahiel R. I., Vilcek J., Nussenzweig R., Vanderberg J. Interferon inducers protect mice against plasmodium berghei malaria. Science. 1968 Aug 23;161(3843):802–804. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3843.802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz S. M., Fisken R. A., Kaump D. H., Schardn J. L. Toxicity of 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine in mice and rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1968;8:180–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LePage G. A., Lin Y. T., Orth R. E., Gottlieb J. A. 5'-Nucleotides as potential formulations for administering nucleoside analogs in man. Cancer Res. 1972 Nov;32(11):2441–2444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller F. A., Dixon G. J., Ehrlich J., Sloan B. J., McLean I. W., Jr Antiviral activity of 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine. I. Cell culture studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1968;8:136–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins R. K. Nucleosides and nucleotides: past, present, and future. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Aug 8;255:597–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schabel F. M., Jr The antiviral activity of 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine (ARA-A). Chemotherapy. 1968;13(6):321–338. doi: 10.1159/000220567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz W. W., Huang K. Y., Gordon F. B. Role of interferon in experimental mouse malaria. Nature. 1968 Nov 16;220(5168):709–710. doi: 10.1038/220709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidwell R. W., Dixon G. J., Schabel F. M., Jr, Kaump D. H. Antiviral activity of 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine. II. Activity against Herpes simplex keratitis in hamsters. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1968;8:148–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellde B. T., Briggs N. T., Sadun E. H. Susceptibility to Plasmodium berghei: parasitological biochemical and hematological studies in laboratory and wild mammals. Mil Med. 1966 Sep;131(9 Suppl):859–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]