Abstract
Transformation of chick embryo fibroblasts by Rous sarcoma virus results in decreased amounts of a major cell surface protein and of collagen. To determine the mechanism accounting for the decreased production of these proteins, we have measured the relative amounts of functional mRNAs for these and other transformation-sensitive proteins. Total cellular RNAs extracted from normal cells and from cells transformed by the Schmidt-Ruppin strain of Rous sarcoma virus were translated in a cell-free system derived from wheat germ. Analysis of the in vitro translation products of RNAs from normal and transformed chick embryo fibroblasts shows a 5-fold reduction in the translatable mRNA for cell surface protein and a 10-fold reduction in translatable mRNA for two collagen precursors. In addition, increases in functional mRNA are observed for myosin and for two membrane polypeptides with molecular weights of 95,000 and 78,000; the latter two proteins increase on transformation, but the increases are in large part secondary to the depletion of glucose from the medium of transformed cells. Our data suggest that some of the major cellular changes induced by oncogenic viruses are due to changes in the activity of specific cellular genes.
Full text
PDF

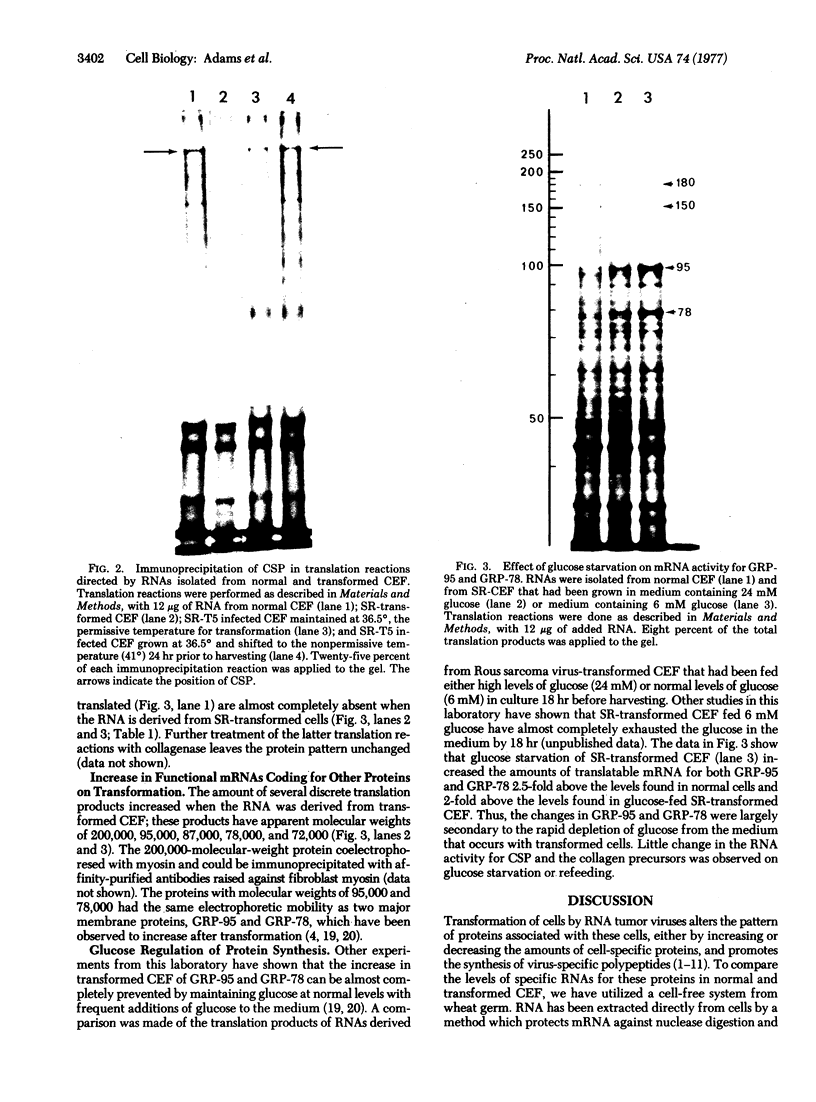

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axén R., Porath J., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of peptides and proteins to polysaccharides by means of cyanogen halides. Nature. 1967 Jun 24;214(5095):1302–1304. doi: 10.1038/2141302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. B., Gallimore P. H., McDougall J. K. Correlation between tumor induction and the large external transformation sensitive protein on the cell surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3570–3574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg C. G., Kiehn D., Hakomori S. Changes in a surface-labelled galactoprotein and in glycolipid concentrations in cells transformed by a temperature-sensitive polyoma virus mutant. Nature. 1974 Mar 29;248(447):413–415. doi: 10.1038/248413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Goldberg B., Todaro G. J. Differentiated cell types and the regulation of collagen synthesis. Nature. 1966 Nov 5;212(5062):631–633. doi: 10.1038/212631b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N. M. A comparison of membrane proteins of normal and transformed cells by lactoperoxidase labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):489–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Alteration of cell-surface proteins by viral transformation and by proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3170–3174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Cell surface proteins and malignant transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 30;458(1):73–107. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(76)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Wyke J. A. Alterations in surface proteins in chicken cells transformed by temperature-sensitive mutants of Rous sarcoma virus. Virology. 1975 Apr;64(2):492–504. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaka T., Yoshida M., Owada M., Toyoshima K. Alterations in membrane polypeptides of chick embryo fibroblasts induced by transformation with avian sarcoma viruses. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):226–237. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson W., Bhatnagar R. S., Liu T. Z. Loss of ability to synthesize collagen in fibroblasts transformed by rous sarcoma virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Oct;55(4):807–810. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.4.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlstein E. Plasma membrane glycoprotein which mediates adhesion of fibroblasts to collagen. Nature. 1976 Aug 5;262(5568):497–500. doi: 10.1038/262497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins P. W., Wickus G. G., Branton P. E., Gaffney B. J., Hirschberg C. B., Fuchs P., Blumberg P. The chick fibroblast cell surface after transformation by Rous sarcoma virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):1173–1180. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Taylor J. M., McKnight G. S., Palacios R., Gonzalez C., Kiely M. L., Schimke R. T. Isolation of hen oviduct ovalbumin and rat live albumin polysomes by indirect immunoprecipitation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3665–3671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shizuta Y., Davies P. J., Olden K., Pastan I. Diminished content of plasma membrane-associated myosin in transformed fibroblasts. Nature. 1976 Jun 3;261(5559):414–415. doi: 10.1038/261414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone K. R., Smith R. E., Joklik W. K. Changes in membrane polypeptides that occur when chick embryo fibroblasts and NRK cells are transformed with avian sarcoma viruses. Virology. 1974 Mar;58(1):86–100. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohman R. C., Moss P. S., Micou-Eastwood J., Spector D., Przybyla A., Paterson B. Messenger RNA for myosin polypeptides: isolation from single myogenic cell cultures. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Ruoslahti E. Disappearance of a major cell-type specific surface glycoprotein antigen (SF) after transformation of fibroblasts by Rous sarcoma virus. Int J Cancer. 1974 May 15;13(5):579–586. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910130502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Ruoslahti E. Fibroblast surface antigen produced but not retained by virus-transformed human cells. J Exp Med. 1975 Aug 1;142(2):530–535. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.2.530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Yamada K. M., Yamada S. S., Pouysségur J., Pastan I. Microfilament bundles and cell shape are related to adhesiveness to substratum and are dissociable from growth control in cultured fibroblasts. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):375–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Ohanian S. H., Pastan I. Cell surface protein decreases microvilli and ruffles on transformed mouse and chick cells. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Yamada S. S., Pastan I. Cell surface protein partially restores morphology, adhesiveness, and contact inhibition of movement to transformed fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1217–1221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Yamada S. S., Pastan I. The major cell surface glycoprotein of chick embryo fibroblasts is an agglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3158–3162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]