Abstract
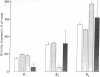
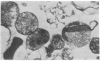
The vasoactive intestinal polypeptide was present in synaptosomal (nerve ending) preparations from cerebral cortex, hypothalamus, and striatum of rat brain in higher concentrations than in these tissues as a whole. The total content and relative specific activity of the peptide increased with progressive purification of the synaptosomal fractions and generally followed the distribution of known synaptosomal constituents--dopamine, norepinephrine, and lactate dehydrogenase (L-lactate:NAD+ oxidoreductase, EC 1.1.1.27). The peptide was also released from synaptosomal pellets with increased K+ concentration, and this release was Ca2+-dependent. The findings suggest a role for vasoactive intestinal polypeptide as a transmitter or modulator of synaptic function.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaustein M. P., Johnson E. M., Jr, Needleman P. Calcium-dependent norepinephrine release from presynaptic nerve endings in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2237–2240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. G., Polak M. M., Modlin I., Bloom S. R., Albuquerque R. H., Pearse A. G. Possible dual role for vasoactive intestinal peptide as gastrointestinal hormone and neurotransmitter substance. Lancet. 1976 May 8;1(7967):991–993. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91863-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG C. C. A SENSITIVE METHOD FOR SPECTROPHOTOFLUOROMETRIC ASSAY OF CATECHOLAMINES. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1964 Dec;3:643–649. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(64)90089-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6854–6861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockray G. J. Immunochemical evidence of cholecystokinin-like peptides in brain. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):568–570. doi: 10.1038/264568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giachetti A., Rosenberg R. N., Said S. I. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in brain synaptosomes. Lancet. 1976 Oct 2;2(7988):741–742. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glowinski J., Iversen L. L. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of [3H]norepinephrine, [3H]dopamine and [3H]dopa in various regions of the brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Aug;13(8):655–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Efendić S., Hellerström C., Johansson O., Luft R., Arimura A. Cellular localization of somatostatin in endocrine-like cells and neurons of the rat with special references to the A1-cells of the pancreatic islets and to the hypothalamus. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1975;200:5–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON M. K., WHITTAKER V. P. LACTATE DEHYDROGENASE AS A CYTOPLASMIC MARKER IN BRAIN. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:404–409. doi: 10.1042/bj0880404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Edvinsson L., Fahrenkrug J., Håkanson R., Owman C., Schaffalitzky de Muckadell O., Sundler F. Immunohistochemical localization of a vasodilatory polypeptide (VIP) in cerebrovascular nerves. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 27;113(2):400–404. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90951-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Fahrenkrug J., Schaffalitzky De Muckadell O., Sundler F., Håkanson R., Rehfeld J. R. Localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) to central and peripheral neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3197–3200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeman S. E., Mroz E. A. Substance P. Life Sci. 1974 Dec 15;15(12):2033–2044. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Baetens O., Rufener C., Brown M., Vale W., Guillemin R. Evidence for immunoreactive neurotensin in dog intestinal mucosa. Life Sci. 1976 Aug 15;19(4):559–561. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENNINGTON R. J. Biochemistry of dystrophic muscle. Mitochondrial succinate-tetrazolium reductase and adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80:649–654. doi: 10.1042/bj0800649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said S. I., Faloona G. R. Elevated plasma and tissue levels of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the watery-diarrhea syndrome due to pancreatic, bronchogenic and other tumors. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jul 24;293(4):155–160. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197507242930401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said S. I., Mutt V. Isolation from porcine-intestinal wall of a vasoactive octacosapeptide related to secretin and to glucagon. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):199–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said S. I., Mutt V. Polypeptide with broad biological activity: isolation from small intestine. Science. 1970 Sep 18;169(3951):1217–1218. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3951.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said S. I., Rosenberg R. N. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide: abundant immunoreactivity in neural cell lines and normal nervous tissue. Science. 1976 May 28;192(4242):907–908. doi: 10.1126/science.1273576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenker C., Mroz E. A., Leeman S. E. Release of substance P from isolated nerve endings. Nature. 1976 Dec 23;264(5588):790–792. doi: 10.1038/264790a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl G. R., Snyder S. H. Regional and subcellular distributions of brain neurotensin. Life Sci. 1976 Dec 15;19(12):1827–1832. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90114-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderhaeghen J. J., Signeau J. C., Gepts W. New peptide in the vertebrate CNS reacting with antigastrin antibodies. Nature. 1975 Oct 16;257(5527):604–605. doi: 10.1038/257604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAKER V. P. The isolation and characterization of acetylcholine-containing particles from brain. Biochem J. 1959 Aug;72:694–706. doi: 10.1042/bj0720694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warberg J., Eskay R. L., Barnea A., Reynolds R. C., Porter J. C. Release of luteinizing hormone releasing hormone and thyrotropin releasing hormone from a synaptosome-enriched fraction of hypothalamic homogenates. Endocrinology. 1977 Mar;100(3):814–825. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-3-814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]