Abstract
Complement depletion mediated by high molecular weight (IgM) rabbit antibodies specifically bound to spin-label lipid haptens dispersed in model membranes is controlled by various physical attributes of those membranes other than the total number of exposed determinants that they provide. Carrier lipids used at 32° were (i) a “fluid” phosphatidylcholine (PC), (ii) a “solid” PC, and (iii) a cholesterol/PC mixture. The concentration of hapten in the plane of the membranes (two-dimensional concentration) was varied while the overall hapten molarity (three-dimensional concentration) was kept constant.
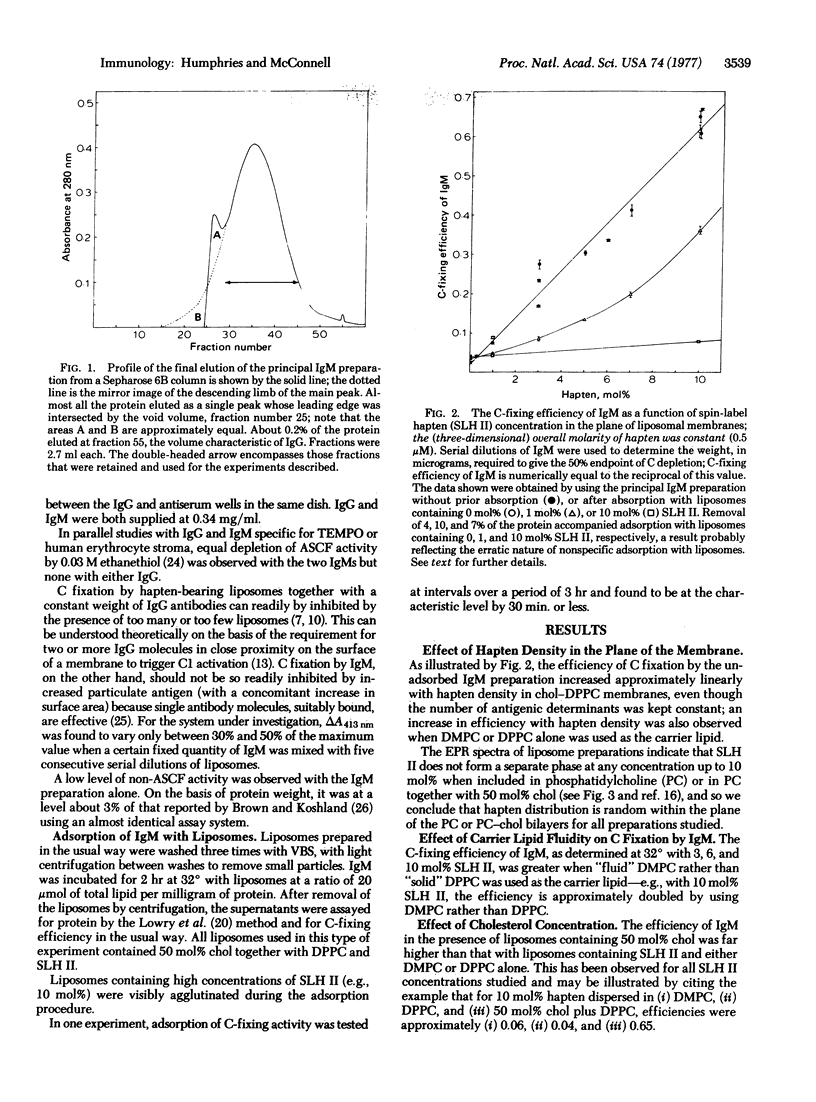
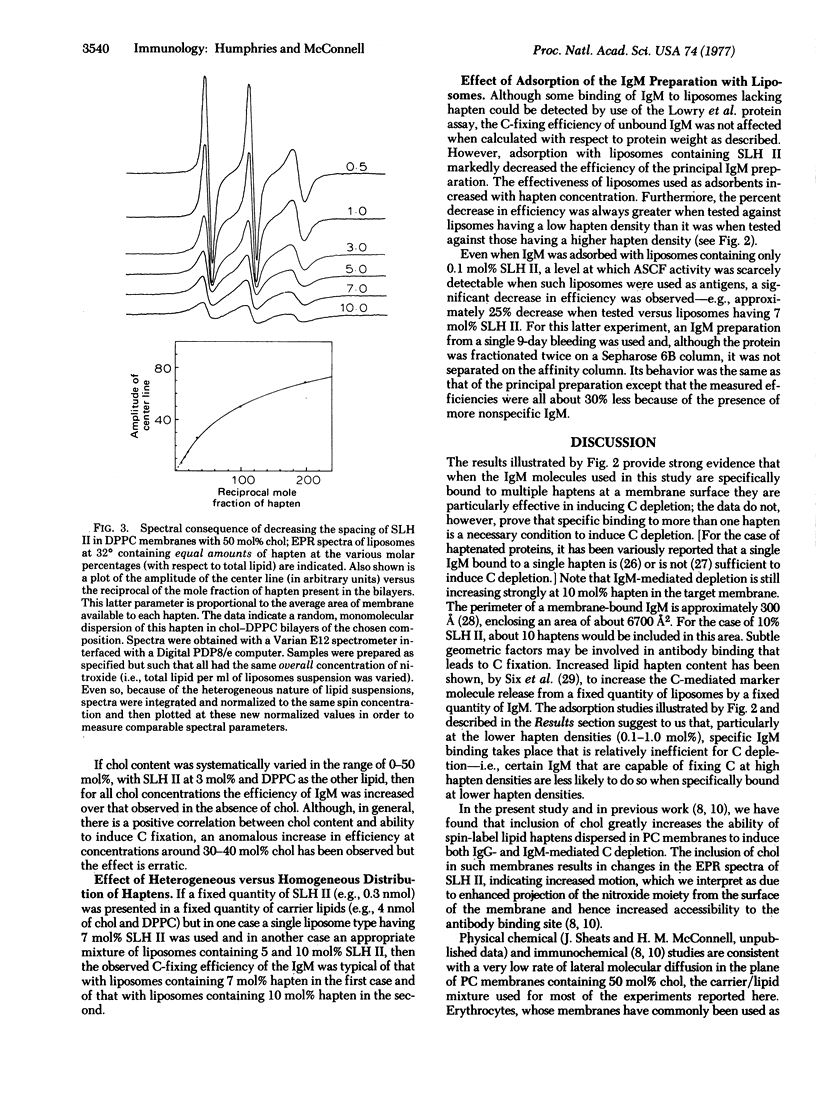
Both specific binding and the efficiency of depletion by IgM are markedly enhanced by systematically decreasing the average distance between haptens (∞ → 26 A). Heterogeneous distribution was found to be more favorable than a random homogeneous distribution of the same number of haptens in the same total quantity of lipids. IgM efficiency is also markedly increased by the inclusion of cholesterol in PC membranes, an effect thought to result from enhanced projection of the determinant from the surface of the membrane and hence increased accessibility to the antibody-binding site. Furthermore, the efficiency of IgM was increased by using haptens dispersed in fluid rather than in solid PC membranes.
The results are consistent with the hypothesis that IgM molecules must be bound to a critical multiple of antigenic determinants at a membrane surface in order to induce complement-mediated attack and that subtle variation of the physical state of membrane antigens can be the crucial factor in determining the outcome of this type of efferent immune response.
Keywords: hapten specing, cholesterol, membrane fluidity, electron paramagnetic resonance
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADA G. L., NOSSAL G. J., PYE J., ABBOT A. ANTIGENS IN IMMUNITY. I. PREPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF FLAGELLAR ANTIGENS FROM SALMONELLA ADELAIDE. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1964 Jun;42:267–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alving C. R., Joseph K. C., Wistar R. Influence of membrane composition on the interaction of a human monoclonal "anti-Forssman" immunoglobulin with liposomes. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 5;13(23):4818–4824. doi: 10.1021/bi00720a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Complement fixation on cell surfaces by 19S and 7S antibodies. Science. 1965 Oct 22;150(3695):505–506. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3695.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Hemolysin titration based on fixation of the activated first component of complement: evidence that one molecule of hemolysin suffices to sensitize an erythrocyte. J Immunol. 1965 Sep;95(3):559–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. C., Koshland M. E. Activation of antibody Fc function by antigen-induced conformational changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5111–5115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brûlet P., McConnell H. M. Lateral hapten mobility and immunochemistry of model membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):2977–2981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.2977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brûlet P., McConnell H. M. Structural and dynamical aspects of membrane immunochemistry using model membranes. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 22;16(6):1209–1217. doi: 10.1021/bi00625a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. The requirement for the association of two adjacent rabbit gamma-G-antibody molecules in the fixation of complement by immune complexes. J Immunol. 1968 Feb;100(2):407–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunniff R. V., Stollar B. D. Properties of 19 S antibodies in complement fixation. I. Temperature dependence and role of antigen structure. J Immunol. 1968 Jan;100(1):7–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Saussure V. A., Dandliker W. B. Ultracentrifuge studies on the effects of thiocyanate ion on antigen--antibody systems. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90180-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein A., Munn E. A. Conformation of the free and antigen-bound IgM antibody molecules. Nature. 1969 Dec 27;224(5226):1307–1309. doi: 10.1038/2241307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M. Induction of immunity and tolerance to the dinitrophenyl determinant in vitro. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 5;231(18):21–23. doi: 10.1038/newbio231021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., Borsos T., Rapp H. J., Vannier W. E. Heterogeneity of rabbit IgM antibody as detected by C'1a fixation. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):589–603. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphires G. M., McConnell H. M. Antigen mobility in membranes and complement-medical immune attack. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2483–2487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries G. M., McConnell H. M. Antibodies against nitroxide spin labels. Biophys J. 1976 Mar;16(3):275–277. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85687-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyslop N. E., Jr, Dourmashkin R. R., Green N. M., Porter R. R. The fixation of complement and the activated first component (C1) of complement by complexes formed between antibody and divalent hapten. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):783–802. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Tada T., Ishizaka K. Fixation of C' and C'la by rabbit gamma-G- and gamma-M-antibodies with particulate and soluble antigens. J Immunol. 1968 Jun;100(6):1145–1153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C. Antibody-complement interaction with lipid model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 14;265(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linscott W. D., Hansen S. S. Non-complement-fixing IgM antibodies in the guinea pig. J Immunol. 1969 Sep;103(3):423–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R., Peters J., Tews K. H., Bähr W. A microfluorimetric study of translational diffusion in erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 15;367(3):282–294. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90085-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Nakoinz I., Cohn M. Antibody dependent cellular immunity in newborn mice. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 3;245(144):157–158. doi: 10.1038/newbio245157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Prichard J., Cohn M. Reticulum cell sarcoma: an effector cell in antibody-dependent cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):898–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey P., McConnell H. M. Binding of antibodies to nitroxide spin labels and to the corresponding hydroxylamines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Nov 22;73(2):248–254. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90700-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. M., Russell P. K. Complement fixation blocking activity of anti-dengue IgM antibody. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):875–877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Six H. R., Uemura K. I., Kinsky S. C. Effect of immunoglobulin class and affinity on the initiation of complement-dependent damage to liposomal model membranes sensitized with dinitrophenylated phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1973 Sep 25;12(20):4003–4011. doi: 10.1021/bi00744a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WASSERMAN E., LEVINE L. Quantitative micro-complement fixation and its use in the study of antigenic structure by specific antigen-antibody inhibition. J Immunol. 1961 Sep;87:290–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


