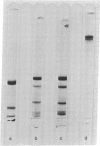
Abstract
Enzyme replacement therapy for the alleviation of Gaucher's disease has been impeded because of the difficulty in preparing large amounts of glucocerebrosidase, the enzyme that is deficient in patients with this disorder. A large-scale procedure for the purification of human placental glucocerebrosidase has been developed. The method uses cholate extraction, ammonium sulfate fractionation, acid precipitation, butanol extraction, and hydrophobic chromatography; the final enzyme preparation has a specific activity of more than 10(6) units/mg of protein with an overall recovery of 30%. In addition, the contamination of enzyme preparations, intended for human infusion, prepared by isolation procedures involving concanavalin A columns has been studied and is reported here.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almon R. R., Appel S. H. Cholinergic sites in skeletal muscle: interaction with concanavalin A. J Neurochem. 1976 Dec;27(6):1513–1519. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb02637.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADY R. O., KANFER J. N., SHAPIRO D. METABOLISM OF GLUCOCEREBROSIDES. II. EVIDENCE OF AN ENZYMATIC DEFICIENCY IN GAUCHER'S DISEASE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 18;18:221–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90743-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady R. O., Pentchev P. G., Gal A. E., Hibbert S. R., Dekaban A. S. Replacement therapy for inherited enzyme deficiency. Use of purified glucocerebrosidase in Gaucher's disease. N Engl J Med. 1974 Nov 7;291(19):989–993. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197411072911901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale G. L., Beutler E. Enzyme replacement therapy in Gaucher's disease: a rapid, high-yield method for purification of glucocerebrosidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4672–4674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale G. L., Villacorte D. G., Beutler E. Solubilization of glucocerebrosidase from human placenta and demonstration of a phospholipid requirement for its catalytic activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):1048–1053. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90760-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glew R. H., Kayman S. C., Kuhlenschmidt M. S. Studies on the binding of concanavalin A to rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3137–3145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard G. A., Schnebli H. P. Eukaryote ribosomes possess a binding site for concanavalin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):818–821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanfer J. N., Young O. M., Shapiro D., Brady R. O. The metabolism of sphingomyelin. I. Purification and properties of a sphingomyelin-cleaving enzyme from rat liver tissue. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 10;241(5):1081–1084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keenan T. W., Franke W. W., Kartenbeck J. Concanavalin A binding by isolated plasma membranes and endomembranes from liver and mammary gland. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 30;44(3):274–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81156-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H., Sheffield J. B., Nagele R. G., Jr, Kalmus G. W. The role of extracellular material in chick neurulation. I. Effects of concanavalin A. J Exp Zool. 1976 Nov;198(2):261–266. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401980216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monneron A., Segretain D. Extensive binding of concanavalin A to the nuclear membrane. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jun 1;42(2):209–213. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80787-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. The interactions of lectins with animal cell surfaces. Int Rev Cytol. 1974;39:89–190. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60939-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nopanitaya W., Hanker J., Tyan M. Concanavalin A toxicity: histological studies. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Nov;153(2):213–219. doi: 10.3181/00379727-153-39513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentchev P. G., Brady R. O., Hibbert S. R., Gal A. E., Shapiro D. Isolation and characterization of glucocerebrosidase from human placental tissue. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5256–5261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyan M. L. In vivo toxicity of concanavalin A. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Sep;146(4):1163–1165. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]