Abstract
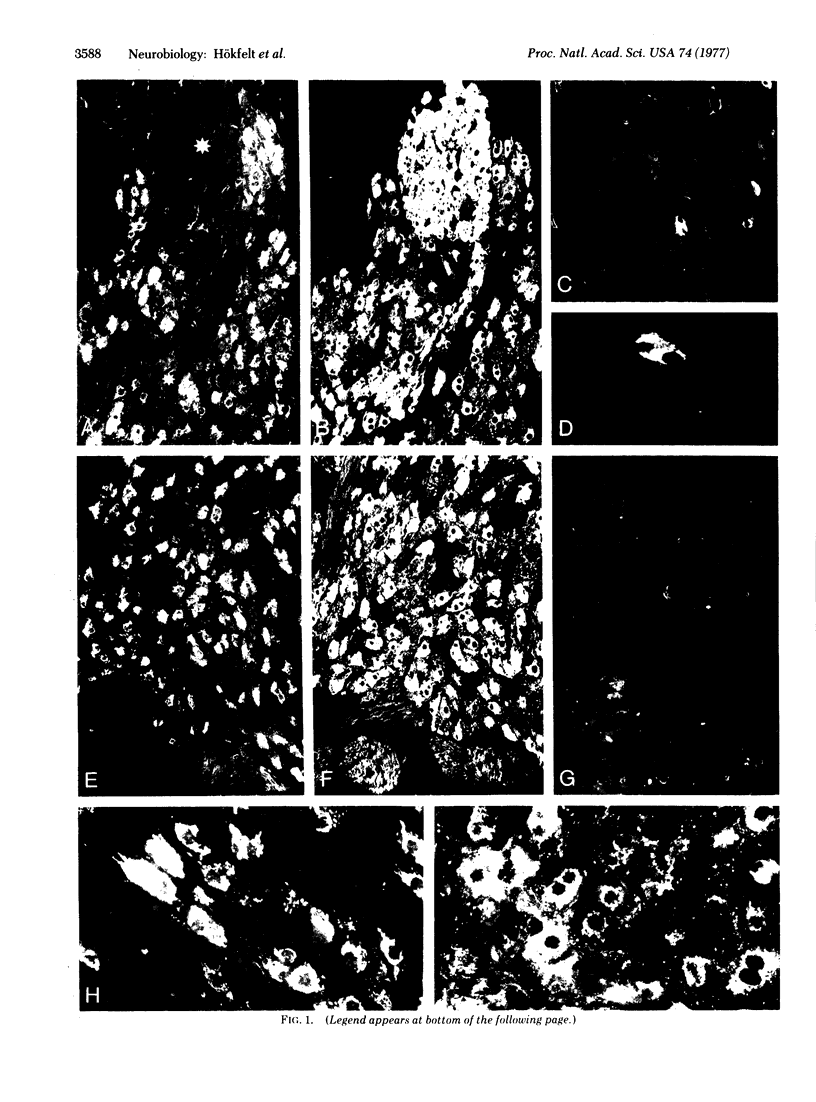
By means of the indirect immunofluorescence technique of Coons and collaborators, somatostatin-like immunoreactivity has been demonstrated in principal ganglion cells of some sympathetic ganglia. The noradrenergic nature of these cells was established by “staining” of the same or consecutive sections with antiserum to dopamine β-hydroxylase [dopamine β-monooxygenase; 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethylamine, ascorbate:oxygen oxidoreductase (β-hydroxylating), EC 1.14.17.1], the enzyme converting dopamine to noradrenaline (norepinephrine). In guinea pigs the somatostatin immunoreactive material was found in almost two-thirds of all principal ganglion cells of the coeliac-superior mesenteric ganglion complex (anterior inferior part) and of the inferior mesenteric ganglion, but only in a few cells of the superior cervical ganglion. It appeared to be localized close to the Golgi complex. The present findings may represent a concomitant storage of a biogenic amine and a small peptide in a neuron. Because both noradrenaline and somatostatin may fulfill a role as a neurotransmitter or modulator, the sympathetic neurons described in this study may represent an example of mammalian nerve cells not conforming to Dale's hypothesis, i.e., the one neuronone transmitter concept.
Keywords: amine precursor uptake and decarboxylation (APUD) concept, Dale's principle, peripheral peptide neurons
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brazeau P., Vale W., Burgus R., Ling N., Butcher M., Rivier J., Guillemin R. Hypothalamic polypeptide that inhibits the secretion of immunoreactive pituitary growth hormone. Science. 1973 Jan 5;179(4068):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4068.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownstein M. J., Saavedra J. M., Axelrod J., Zeman G. H., Carpenter D. O. Coexistence of several putative neurotransmitters in single identified neurons of Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4662–4665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. G., Polak M. M., Modlin I., Bloom S. R., Albuquerque R. H., Pearse A. G. Possible dual role for vasoactive intestinal peptide as gastrointestinal hormone and neurotransmitter substance. Lancet. 1976 May 8;1(7967):991–993. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91863-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Do some nerve cells release more than one transmitter? Neuroscience. 1976 Aug;1(4):239–248. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90054-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H. Fluorescent antibody methods. Gen Cytochem Methods. 1958;1:399–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubé D., Leclerc R., Pelletier G., Arimura Aschally A. V. Immunohistochemical detection of growth hormone-release inhibiting hormone (somatostatin) in the guinea-pig brain. Cell Tissue Res. 1975 Aug 25;161(3):385–392. doi: 10.1007/BF00220006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer R. G., Dyball R. E. Evidence for a direct effect of LRF and TRF on single unit activity in the rostral hypothalamus. Nature. 1974 Dec 6;252(5483):486–488. doi: 10.1038/252486a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elde R., Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Terenius L. Immunohistochemical studies using antibodies to leucine-enkephalin: initial observations on the nervous system of the rat. Neuroscience. 1976 Aug;1(4):349–351. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elfvin L. G., Hökfelt T., Goldstein M. Fluorescence microscopical, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies on sympathetic ganglia of the guinea pig, with special reference to the sif cells and their catecholamine content. J Ultrastruct Res. 1975 Jun;51(3):377–396. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(75)80101-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geffen L. B., Livett B. G., Rush R. A. Immunohistochemical localizatio of protein components of catecholamine storage vesicles. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(3):593–605. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B. K., Zide D., Udenfriend S. The use of dopamine -hydroxylase as a marker for the central noradrenergic nervous system in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2722–2726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Efendić S., Hellerström C., Johansson O., Luft R., Arimura A. Cellular localization of somatostatin in endocrine-like cells and neurons of the rat with special references to the A1-cells of the pancreatic islets and to the hypothalamus. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1975;200:5–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Elde R., Johansson O., Luft R., Nilsson G., Arimura A. Immunohistochemical evidence for separate populations of somatostatin-containing and substance P-containing primary afferent neurons in the rat. Neuroscience. 1976;1(2):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Fuxe K., Goldstein M. Applications of immunohistochemistry to studies on monoamine cell systems with special reference to nervous tissues. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;254:407–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobowitz D. Catecholamine fluorescence studies of adrenergic neurons and chromaffin cells in sympathetic ganglia. Fed Proc. 1970 Nov-Dec;29(6):1929–1944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerkut G. A., Sedden C. B., Walker R. J. Uptake of DOPA and 5-hydroxytryptophan by monoamine-forming neurones in the brain of Helix aspersa. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1967 Oct;23(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(67)90483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi S., Otsuka M. The effects of substance P and other peptides on spinal neurons of the frog. Brain Res. 1974 Jan 18;65(3):397–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90231-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulich L., Dhariwal A. P., McCann S. M. Stimulatory and inhibitory effects of purified hypothalamic extracts on growth hormone release from rat pituitary in vitro. Endocrinology. 1968 Oct;83(4):783–790. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-4-783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Fahrenkrug J., Schaffalitzky De Muckadell O., Sundler F., Håkanson R., Rehfeld J. R. Localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) to central and peripheral neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3197–3200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Barker J. L. Excitation of supraoptic neurosecretory cells by angiotensin II. Nat New Biol. 1971 Oct 6;233(40):172–174. doi: 10.1038/newbio233172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson G., Larsson L. I., Håkanson R., Brodin E., Pernow B., Sundler F. Localization of substance P-like immunoreactivity in mouse gut. Histochemistry. 1975;43(1):97–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00490158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWMAN C., SJOESTRAND N. O. SHORT ADRENERGIC NEURONS AND CATECHOLAMINE-CONTAINING CELLS IN VAS DEFERENS AND ACCESSORY MALE GENITAL GLANDS OF DIFFERENT MAMMALS. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1965 Apr 8;66(2):300–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00344342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owman C., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Occurrence and function of amines in endocrine cells producing polypeptide hormones. Fed Proc. 1973 Jul;32(7):1785–1791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. A., Erlandsen S. L., Hegre O. D., McEvoy R. C., Elde R. P. Central and peripheral localization of somatostatin. Immunoenzyme immunocytochemical studies. J Histochem Cytochem. 1976 Jul;24(7):872–882. doi: 10.1177/24.7.60436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse A. G., Polak J. M. Immunocytochemical localization of substance P in mammalian intestine. Histochemistry. 1975;41(4):373–375. doi: 10.1007/BF00490081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse A. G. The cytochemistry and ultrastructure of polypeptide hormone-producing cells of the APUD series and the embryologic, physiologic and pathologic implications of the concept. J Histochem Cytochem. 1969 May;17(5):303–313. doi: 10.1177/17.5.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier G., Leclerc R., Dube D., Labrie F., Puviani R., Arimura A., Schally A. V. Localization of growth hormone-release-inhibiting hormone (somatostatin) in the rat brain. Am J Anat. 1975 Mar;142(3):397–401. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001420309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier G., Leclerc R., Dubé D. Immunohistochemical localization of hypothalamic hormones. J Histochem Cytochem. 1976 Jul;24(7):864–871. doi: 10.1177/24.7.784871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickel V. M., Joh T. H., Reis D. J. Monoamine-synthesizing enzymes in central dopaminergic, noradrenergic and serotonergic neurons. Immunocytochemical localization by light and electron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1976 Jul;24(7):792–306. doi: 10.1177/24.7.8567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud L. P., Martin J. B., Brazeau P. Depressant action of TRH, LH-RH and somatostatin on activity of central neurones. Nature. 1975 May 15;255(5505):233–235. doi: 10.1038/255233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shantha T. R., Bourne G. H. The thiamine pyrophosphatase technique as an indicator of the morphology of the Golgi apparatus in the neurons. V. Studies on sympathetic ganglion cells. Cytologia (Tokyo) 1966 Jun;31(2):132–143. doi: 10.1508/cytologia.31.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Otsuka M. Regional distribution of substance P in the spinal cord and nerve roots of the cat and the effect of dorsal root section. Brain Res. 1975 Apr 4;87(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90774-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan A. T., Tsang D., Renaud L. P., Martin J. B. Effect of somatostatin on calcium transport in guinea pig cortex synaptosomes. Brain Res. 1977 Mar 4;123(1):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90656-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale W., Brazeau P., Rivier C., Brown M., Boss B., Rivier J., Burgus R., Ling N., Guillemin R. Somatostatin. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1975;31:365–397. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571131-9.50014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



