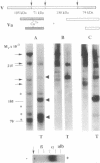
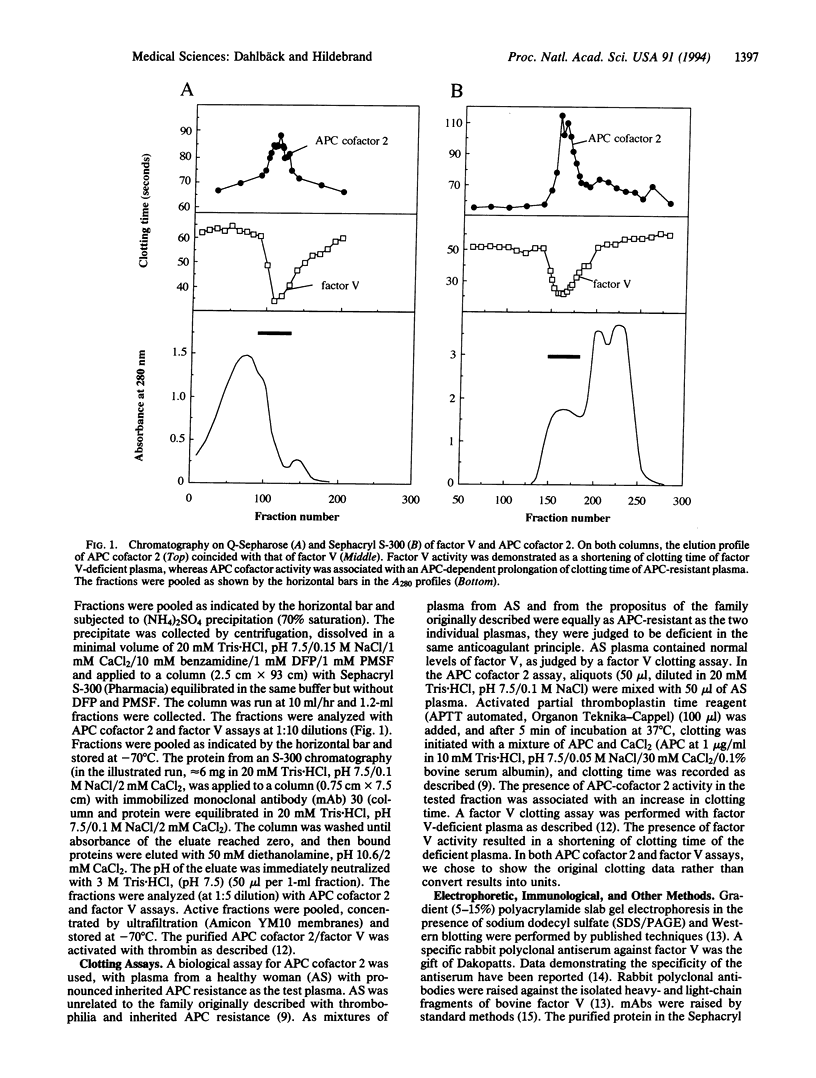
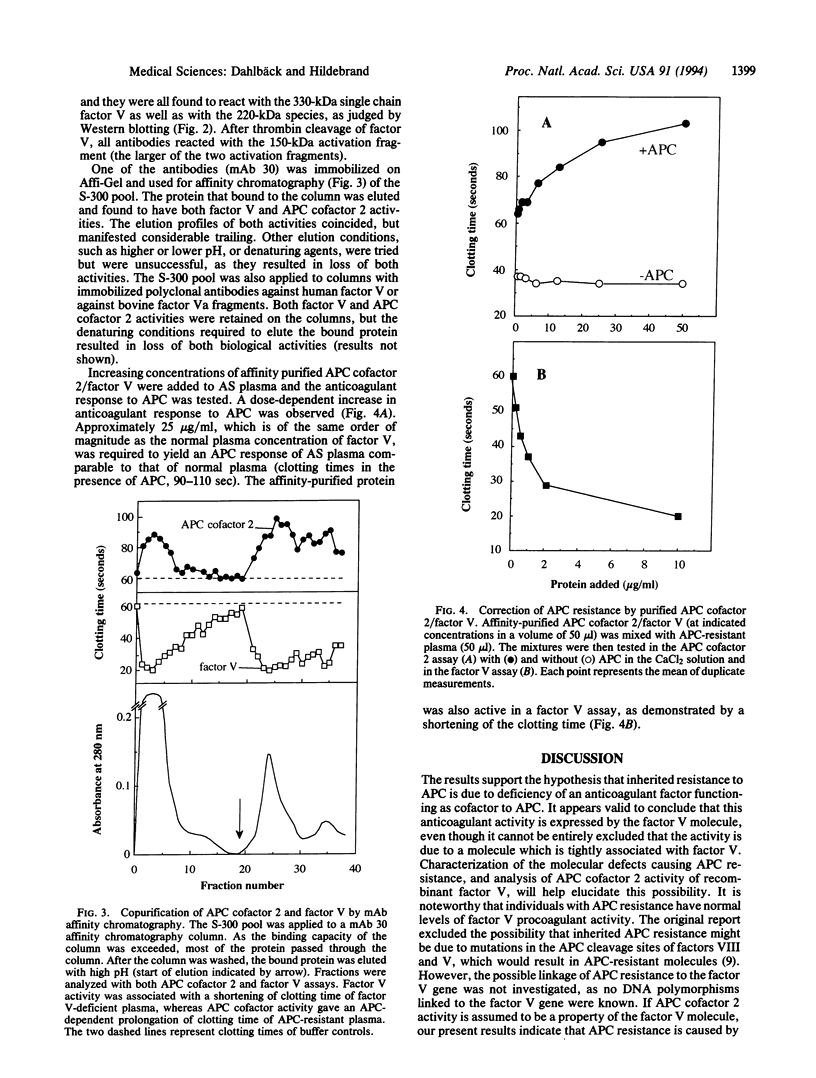
Abstract
Recently, our laboratory described a defect in anticoagulant response to activated protein C (APC). This response, APC resistance, was shown to be inherited and associated with familial thrombophilia. As other possible mechanisms were excluded, APC resistance was hypothesized to be due to deficiency of a previously unrecognized cofactor of APC. The aim of the present study was to isolate and characterize this factor. Plasma from an individual with pronounced inherited APC resistance was used as test plasma in a biological assay which monitored APC cofactor activity during its isolation from normal plasma. A purification procedure was devised that yielded a protein which was shown to be identical to coagulation factor V. It proved impossible to separate the APC cofactor activity from factor V, even by affinity chromatography using a monoclonal antibody against factor V. The affinity-purified factor V corrected the poor anticoagulant response to APC of APC-resistant plasma in a dose-dependent manner. Because the APC-resistant plasma contained normal levels of factor V procoagulant activity, the results indicated APC resistance to be due to a selective defect in the anticoagulant function of factor V. The present results show factor V not only to express procoagulant properties after its activation by thrombin but also to play an important part in the anticoagulant system as cofactor to APC.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker H. M., Tans G., Janssen-Claessen T., Thomassen M. C., Hemker H. C., Griffin J. H., Rosing J. The effect of phospholipids, calcium ions and protein S on rate constants of human factor Va inactivation by activated human protein C. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Aug 15;208(1):171–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B. Bovine coagulation factor V visualized with electron microscopy. Ultrastructure of the isolated activated forms and of the activation fragments. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9495–9501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Carlsson M., Svensson P. J. Familial thrombophilia due to a previously unrecognized mechanism characterized by poor anticoagulant response to activated protein C: prediction of a cofactor to activated protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):1004–1008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Hildebrand B., Malm J. Characterization of functionally important domains in human vitamin K-dependent protein S using monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8127–8135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B. Human coagluation factor V purification and thrombin-catalyzed activation. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):583–591. doi: 10.1172/JCI109890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B. Protein S and C4b-binding protein: components involved in the regulation of the protein C anticoagulant system. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):49–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie E. W., Fujikawa K., Kisiel W. The coagulation cascade: initiation, maintenance, and regulation. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 29;30(43):10363–10370. doi: 10.1021/bi00107a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The roles of protein C and thrombomodulin in the regulation of blood coagulation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4743–4746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie B., Furie B. C. The molecular basis of blood coagulation. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90567-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber A., Griffin J. H. Direct detection of activated protein C in blood from human subjects. Blood. 1992 May 1;79(9):2340–2348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heeb M. J., Mesters R. M., Tans G., Rosing J., Griffin J. H. Binding of protein S to factor Va associated with inhibition of prothrombinase that is independent of activated protein C. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2872–2877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane W. H., Davie E. W. Blood coagulation factors V and VIII: structural and functional similarities and their relationship to hemorrhagic and thrombotic disorders. Blood. 1988 Mar;71(3):539–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapur A., Kelsey P. R., Isaacs P. E. Factor V inhibitor in thrombosis. Am J Hematol. 1993 Apr;42(4):384–388. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830420410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaswamy S., Williams E. B., Mann K. G. The binding of activated protein C to factors V and Va. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9684–9693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. G., Jenny R. J., Krishnaswamy S. Cofactor proteins in the assembly and expression of blood clotting enzyme complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:915–956. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Dahlbäck B., Stenflo J. Thrombin-catalyzed activation of human coagulation factor V. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6556–6564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Regulation of activated protein C by a new protein. A possible function for bovine protein S. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5521–5524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wencel-Drake J. D., Dahlback B., White J. G., Ginsberg M. H. Ultrastructural localization of coagulation factor V in human platelets. Blood. 1986 Jul;68(1):244–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]