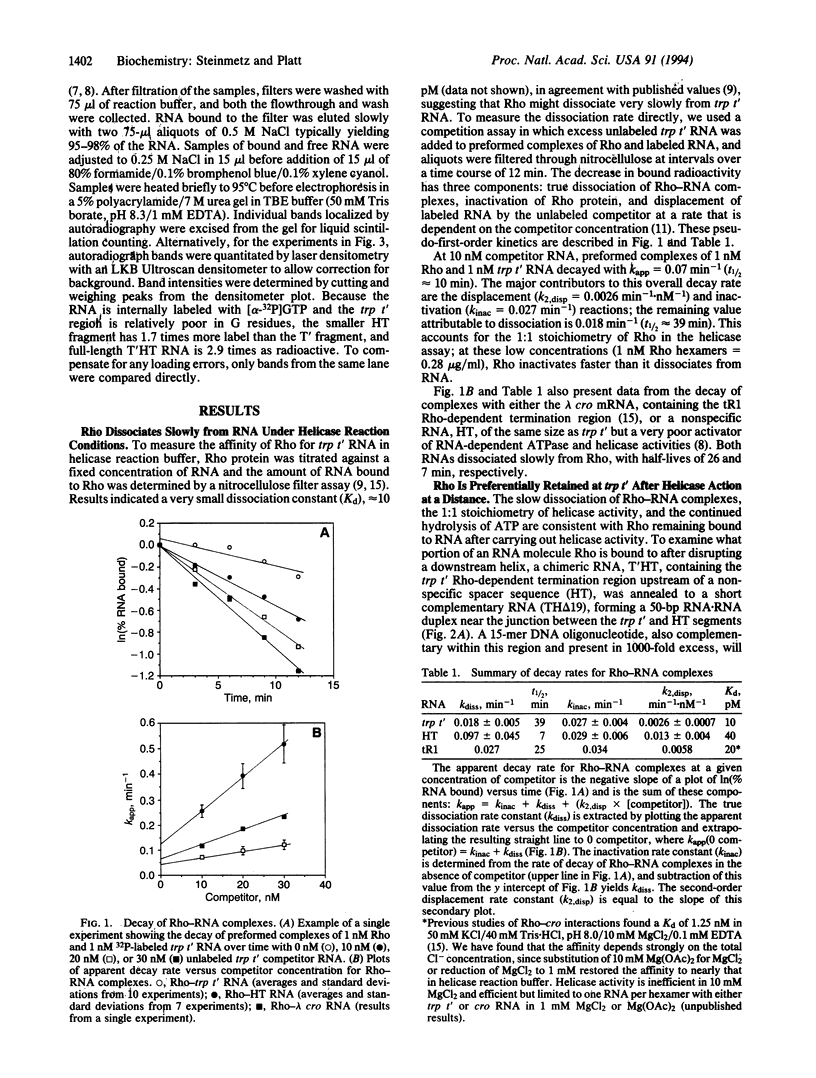
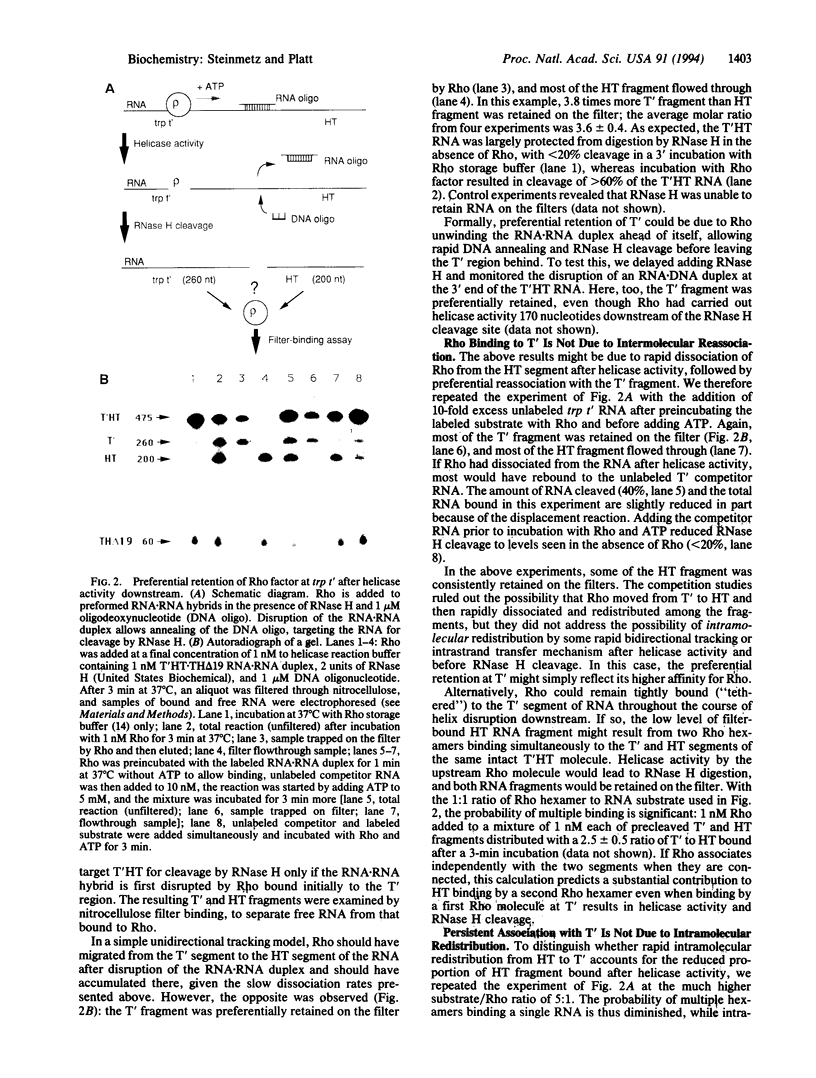
Abstract
Transcription termination factor Rho of Escherichia coli has an ATP-dependent RNA.DNA helicase activity that presumably facilitates RNA transcript release from the elongation complex. This helicase activity is unidirectional (5' to 3') and is stoichiometric, with one RNA molecule released per Rho hexamer in vitro. A simple RNA tracking model postulates that after Rho's initial binding, it translocates preferentially toward the 3' end of the RNA. Nitrocellulose filter binding studies combined with RNase H cleavage are inconsistent with this simple tracking model. Instead, they support a model in which Rho forms tight primary binding interactions with the recognition region of the RNA and remains bound there while transient secondary RNA binding interactions coupled to ATP hydrolysis serve to scan along the RNA to contact the RNA.DNA helix. This "tethered tracking" model is consistent with other properties of Rho factor, including the presence of two classes of RNA binding sites on the Rho hexamer and the 1:1 stoichiometry in the Rho helicase assay.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brennan C. A., Dombroski A. J., Platt T. Transcription termination factor rho is an RNA-DNA helicase. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):945–952. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90703-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan C. A., Platt T. Mutations in an RNP1 consensus sequence of Rho protein reduce RNA binding affinity but facilitate helicase turnover. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17296–17305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan C. A., Steinmetz E. J., Spear P., Platt T. Specificity and efficiency of rho-factor helicase activity depends on magnesium concentration and energy coupling to NTP hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5440–5447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Y., Galluppi G. R., Richardson J. P. Transcription termination at lambda tR1 is mediated by interaction of rho with specific single-stranded domains near the 3' end of cro mRNA. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1023–1028. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90701-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faus I., Richardson J. P. Structural and functional properties of the segments of lambda cro mRNA that interact with transcription termination factor Rho. J Mol Biol. 1990 Mar 5;212(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90304-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faus I., Richardson J. P. Thermodynamic and enzymological characterization of the interaction between transcription termination factor rho and lambda cro mRNA. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3510–3517. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway J. L., Platt T. Signals sufficient for rho-dependent transcription termination at trp t' span a region centered 60 base pairs upstream of the earliest 3' end point. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1761–1767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluppi G. R., Richardson J. P. ATP-induced changes in the binding of RNA synthesis termination protein Rho to RNA. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 15;138(3):513–539. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiselmann J., Seifried S. E., Yager T. D., Liang C., von Hippel P. H. Physical properties of the Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho. 2. Quaternary structure of the rho hexamer. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):121–132. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiselmann J., Wang Y., Seifried S. E., von Hippel P. H. A physical model for the translocation and helicase activities of Escherichia coli transcription termination protein Rho. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7754–7758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiselmann J., Yager T. D., Gill S. C., Calmettes P., von Hippel P. H. Physical properties of the Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho. 1. Association states and geometry of the rho hexamer. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):111–121. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiselmann J., Yager T. D., von Hippel P. H. Functional interactions of ligand cofactors with Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho. II. Binding of RNA. Protein Sci. 1992 Jul;1(7):861–873. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiselmann J., von Hippel P. H. Functional interactions of ligand cofactors with Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho. I. Binding of ATP. Protein Sci. 1992 Jul;1(7):850–860. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott J. E., Grant R. A., Ho Y. S., Platt T. Maximizing gene expression from plasmid vectors containing the lambda PL promoter: strategies for overproducing transcription termination factor rho. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):88–92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehrke K. W., Seifried S. E., Platt T. Overproduced rho factor from p39AS has lysine replacing glutamic acid at residue 155 in the linker region between its RNA and ATP binding domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 25;20(22):6107–6107. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.22.6107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P. Activation of rho protein ATPase requires simultaneous interaction at two kinds of nucleic acid-binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5760–5766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P. Rho-dependent transcription termination. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 6;1048(2-3):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D., Gold L., Platt T. Selective enrichment of RNA species for tight binding to Escherichia coli rho factor. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):201–207. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.7678562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifried S. E., Easton J. B., von Hippel P. H. ATPase activity of transcription-termination factor rho: functional dimer model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10454–10458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz E. J., Brennan C. A., Platt T. A short intervening structure can block rho factor helicase action at a distance. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18408–18413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt B. L. Escherichia coli transcription termination protein rho has three hydrolytic sites for ATP. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11130–11137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






