Abstract
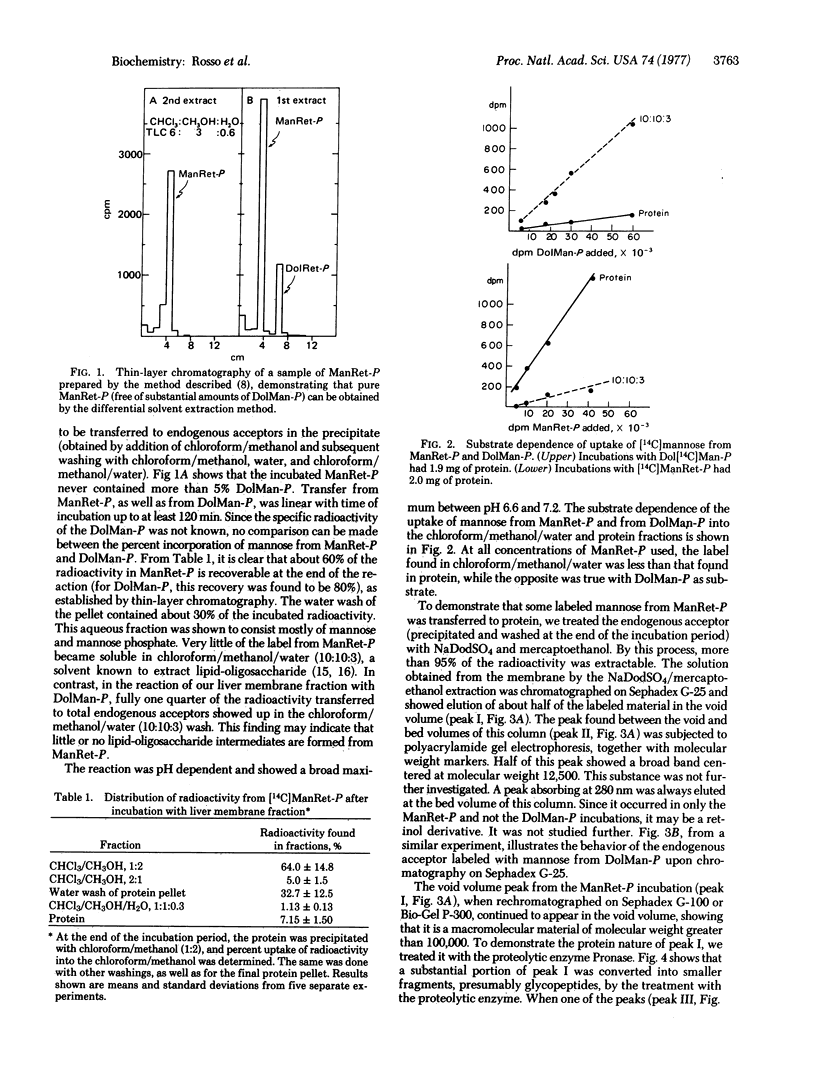
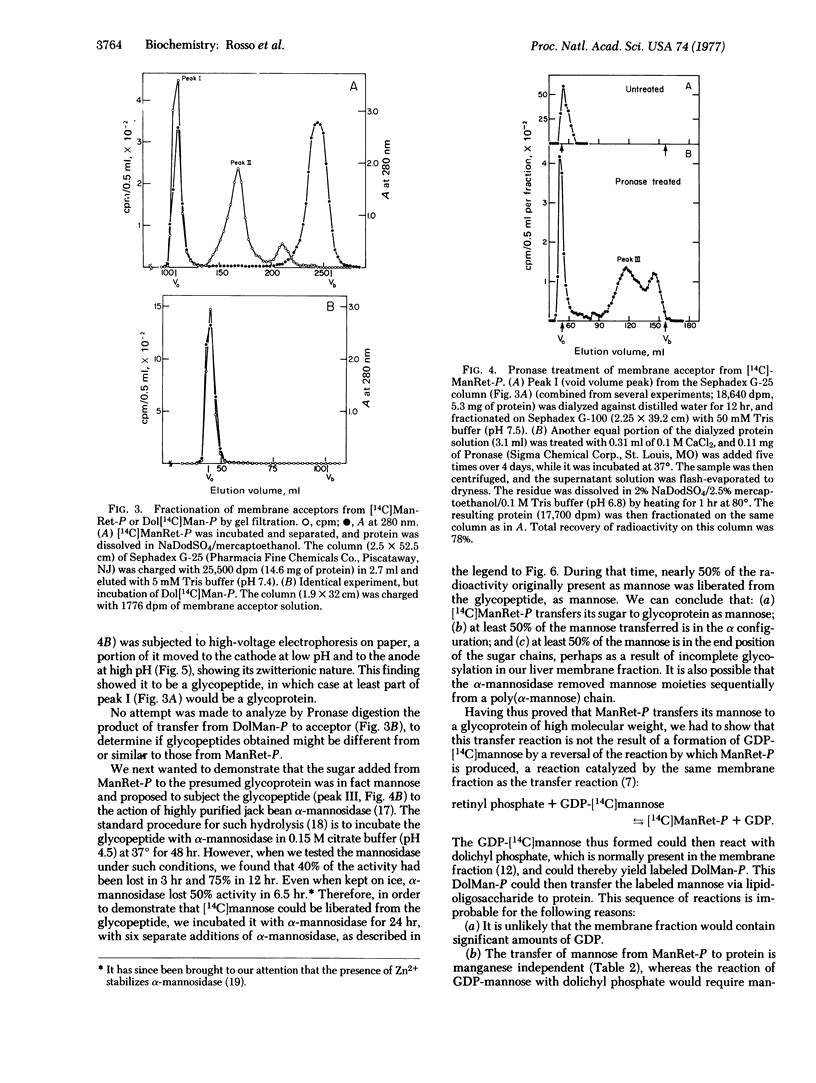
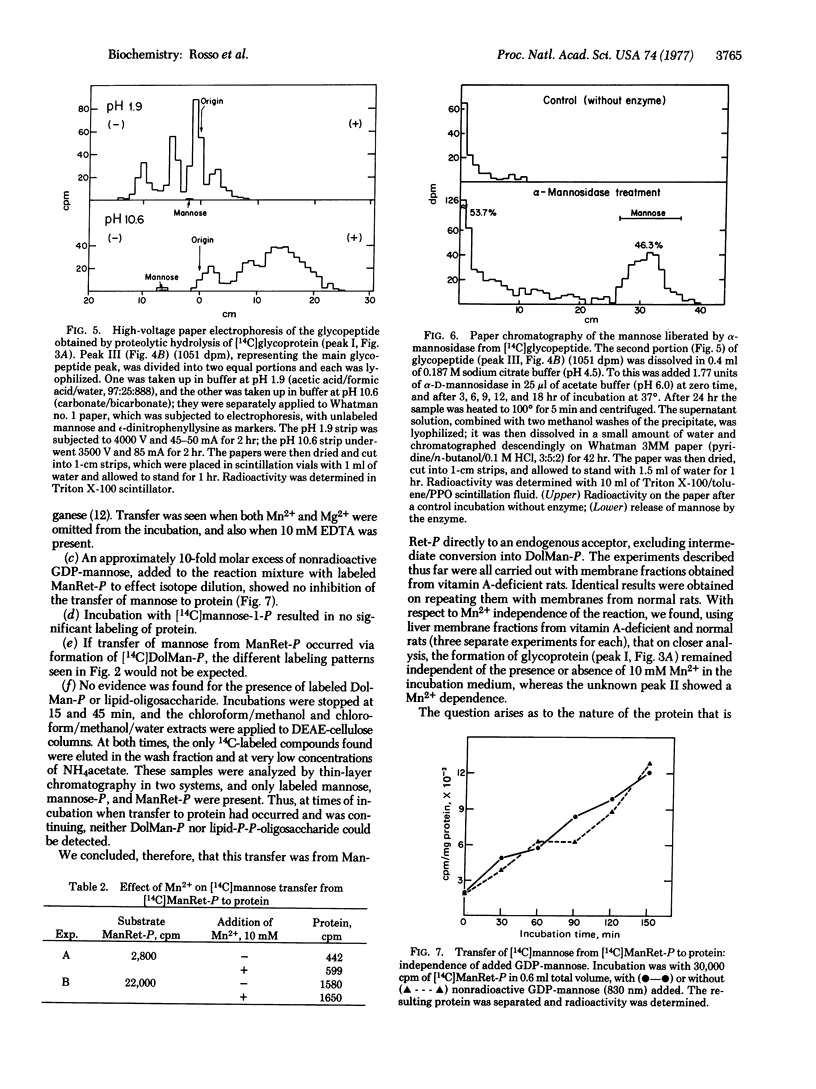
Upon incubation of [14C]mannose-labeled mannosyl retinyl phosphate with a membrane fraction from rat liver, mannose was transferred to an endogenous acceptor precipitable withchloroform/methanol to the extent of about 7%. The reaction proceeded linearly with time for 120 min at a pH optimum of about 7.0. The acceptor thus labeled with mannose could be solubilized by sodium dodecyl sulfate/mercaptoethanol. More than half of this acceptor appeared in the void volume of a Sephadex G-100 column. When it was digested with Pronase, a substantial proportion of it appeared between the void and bed volumes of a Sephadex G-100 column, thus indicating that it was a glycopeptide. In high-voltage paper electrophoresis, this glycopeptide moved to the cathode at low pH and to the anode at highpH. When digested with highly purified jack bean alpha-mannosidase, the glycopeptide released almost 50% of its radioactivity as mannose. That this transfer of mannose to glycoprotein from mannosyl retinyl phosphate does not take place via dolichyl mannosyl phosphate was shown by the fact that it is Mn2+ and Mg2+ independent, it is not inhibited by the presence of a 10-fold molar excess of nonradioactive GDP-mannose, and neither 14C-labeled dolichyl mannosyl phosphate nor 14-C labeled lipid pyrophosphoryl oligosaccharide could be detected during the incubation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arima T., Spiro R. G. Studies on the carbohydrate units of thyroglobulin. Structure of the mannose-N-acetylglucosamine unit (unit A) of the human and calf proteins. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 25;247(6):1836–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr R. M., De Luca L. M. The in vivo incorporation of mannose, retinol and mevalonic acid into phospholipids of hamster liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 9;60(1):355–363. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90212-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrens N. H., Leloir L. F. Dolichol monophosphate glucose: an intermediate in glucose transfer in liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):153–159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrens N. H., Parodi A. J., Leloir L. F. Glucose transfer from dolichol monophosphate glucose: the product formed with endogenous microsomal acceptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2857–2860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonanní F., Levinson S. S., Wolf G., De Luca L. Glycoproteins from the hamster respiratory tract and their response to vitamin A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 28;297(2):441–451. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90091-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Luca L., Maestri N., Rosso G., Wolf G. Retinol glycolipids. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):641–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Luca L., Schumacher M., Wolf G. Biosynthesis of a fucose-containing glycopeptide from rat small intestine in normal and vitamin A-deficient conditions. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4551–4558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. C., Wolf G. Vitamin A deficiency and the glycoproteins of rat corneal epithelium. J Nutr. 1974 Jun;104(6):710–718. doi: 10.1093/jn/104.6.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiorpes T. C., Molica S. J., Wolf G. A plasma glycoprotein depressed in vitamin A deficiency in the rat: alpha 1-macroglobulin. J Nutr. 1976 Nov;106(11):1659–1667. doi: 10.1093/jn/106.11.1659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennarz W. J. Lipid linked sugars in glycoprotein synthesis. Science. 1975 Jun 6;188(4192):986–991. doi: 10.1126/science.167438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. T. Studies on the glycosidases in jack bean meal. I. Isolation and properties of alpha-mannosidase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 10;242(23):5474–5480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macbeth R. A., Bekesi J. G., Sugden E., Bice S. The metabolism of plasma glycoproteins. I. Studies on the rate of incorporation of glucosamine-1-14C into protein-bound hexosamine and N-acetylneuraminic acid in the normal rat. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):3707–3713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parodi A. J., Behrens N. H., Leloir L. F., Dankert M. Glucose transfer from dolichol monophosphat glucose. The lipid moiety of the endogenous microsomal acceptor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 11;270(4):529–536. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A., Nilsson S. F., Ostberg L., Rask L., Vahlquist A. Aspects of the metabolism of retinol-binding protein and retinol. Vitam Horm. 1974;32:181–214. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A., Rask L., Helting T., Ostberg L., Fernstedt Y. Formation and properties of retinylphosphate galactose. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 25;251(16):4986–4995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosso G. C., De Luca L., Warren C. D., Wolf G. Enzymatic synthesis of mannosyl retinyl phosphate from retinyl phosphate and guanosine diphosphate mannose. J Lipid Res. 1975 May;16(3):235–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snaith S. M., Levvy G. A. Purification and properties of alpha-D-mannosidase from jack-bean meal. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(4):663–670. doi: 10.1042/bj1100663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A., Dankert M., Robbins P. W. Evidence for an intermediate stage in the biosynthesis of the Salmonella O-antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):235–241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


