Abstract
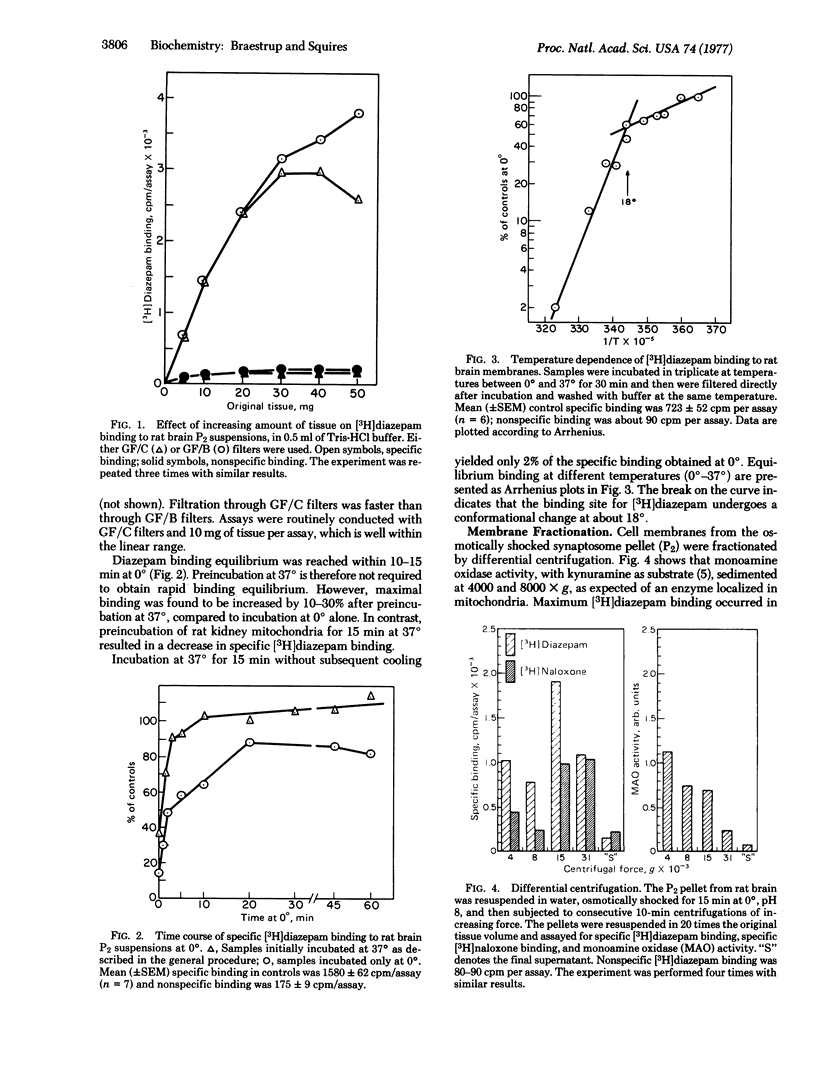
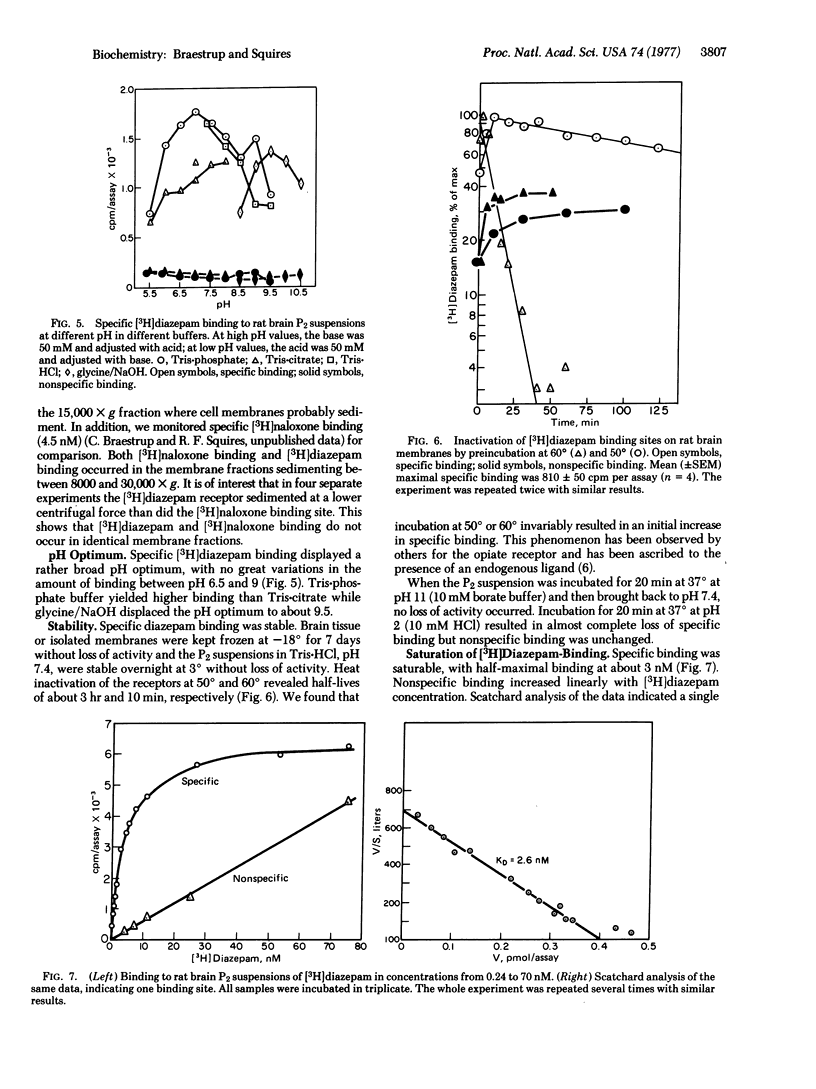
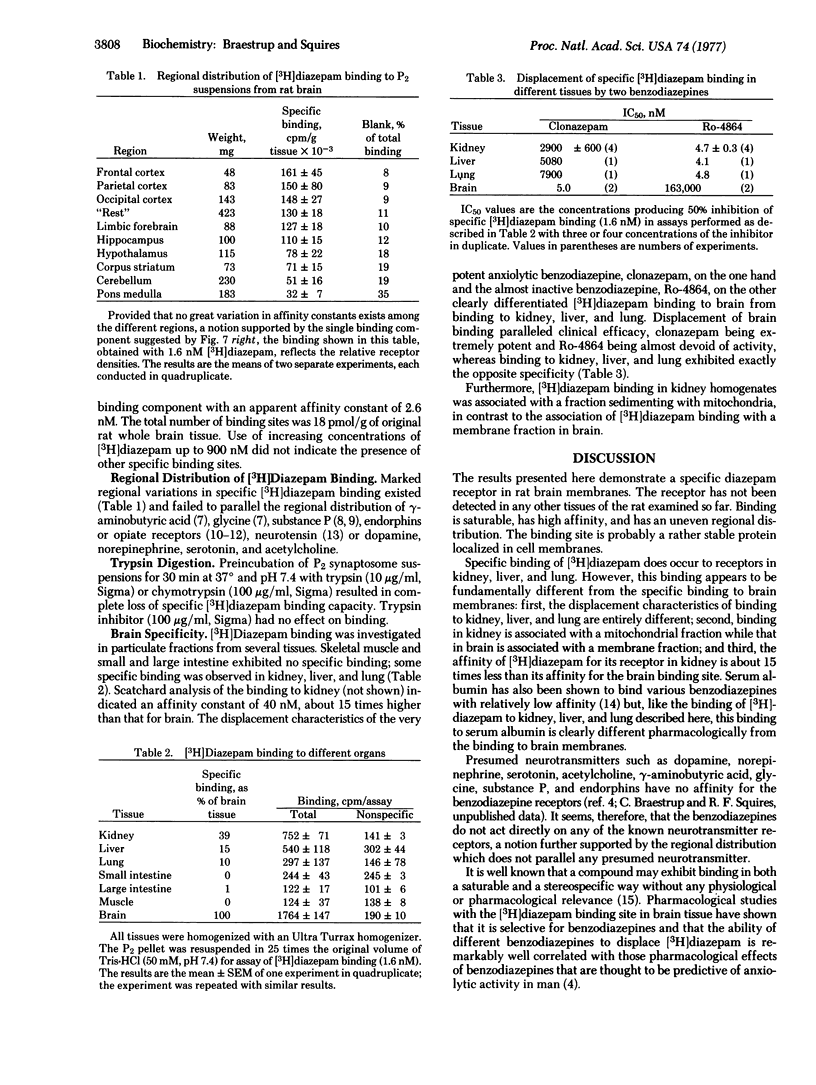
[3H]Diazepam appears to bind specifically to a single, saturable, binding site located on rat brain membranes, with an affinity constant near 3 nM at pH 7.4. Specific binding constitutes more than 90% of total binding at 0 degrees and less than 10% of total binding at 37 degrees. Arrhenius plots suggest a sharp conformational change in the diazepam receptor near 18 degrees. Mitochondrial fractions from rat kidney, liver, and lung exhibit some [3H]diazepam binding that can be displaced by nonradioactive diazepam and several other benzodiazepines. However, Ro-4864, which is almost inactive in displacing [3H]diazepam from brain membranes, is extremely potent in displacing it from kidney mitochondria. Conversely, clonazepam, the most potent inhibitor of brain binding, is an extremely weak inhibitor of kidney binding. Furthermore, diazepam binding to kidney mitochondria has an affinity constantof 40 nM, about 15 times higher than that in brain. No specific diazepam binding was detected in intestine or skeletal muscle. Thus, specific [3H]diazepam binding to membranes appears to be restricted to brain, where it is unevenly distributed: the density of diazepam receptors is about five times higher in cortex (the highest density) than in pons-meddula (lowest density). Trypsin and chymotrypsin completely abolished specific [3H]diazepambinding in brain and kidney.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Costa E., Guidotti A., Mao C. C., Suria A. New concepts on the mechanism of action of benzodiazepines. Life Sci. 1975 Jul 15;17(2):167–185. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90501-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haefely W., Kulcsár A., Möhler H., Pieri L., Polc P., Schaffner R. Possible involvement of GABA in the central actions of benzodiazepines. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1975;(14):131–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. Isolation of an endogenous compound from the brain with pharmacological properties similar to morphine. Brain Res. 1975 May 2;88(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa I., Jessell T. Post mortem changes and regional distribution of substance P in the rat and mouse nervous system. Brain Res. 1976 Nov 26;117(2):362–367. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90748-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Wollert U. Characterization of the binding of benzodiazepines to human serum albumin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1973;280(3):229–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00501348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Goodman R., Snyder S. H. An endogenous morphine-like factor in mammalian brain. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1765–1769. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90270-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor: demonstration in nervous tissue. Science. 1973 Mar 9;179(4077):1011–1014. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4077.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D., Leeman S., Tregear G. W., Niall H. D., Potts J. T., Jr Radioimmunoassay for substance P. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 21;241(112):252–254. doi: 10.1038/newbio241252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Snowman A. M., Snyder S. H. Temperature and ionic influences on opiate receptor binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;12(6):977–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires R. F. Additional evidence for the existence of several forms of mitochondrial monoamine oxidase in the mouse. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Jul;17(7):1401–1409. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90076-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires R. F., Brastrup C. Benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain. Nature. 1977 Apr 21;266(5604):732–734. doi: 10.1038/266732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl G. R., Snyder S. H. Regional and subcellular distributions of brain neurotensin. Life Sci. 1976 Dec 15;19(12):1827–1832. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90114-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A. B., Zukin S. R., Snyder S. H. Interaction of benzodiazepines with central nervous glycine receptors: possible mechanism of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2246–2250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



