Abstract
In light of the current outbreak of Ebola virus disease, there is an urgent need to develop effective therapeutics to treat Ebola infection, and drug repurposing screening is a potentially rapid approach for identifying such therapeutics. We developed a biosafety level 2 (BSL-2) 1536-well plate assay to screen for entry inhibitors of Ebola virus-like particles (VLPs) containing the glycoprotein (GP) and the matrix VP40 protein fused to a beta-lactamase reporter protein and applied this assay for a rapid drug repurposing screen of Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drugs. We report here the identification of 53 drugs with activity of blocking Ebola VLP entry into cells. These 53 active compounds can be divided into categories including microtubule inhibitors, estrogen receptor modulators, antihistamines, antipsychotics, pump/channel antagonists, and anticancer/antibiotics. Several of these compounds, including microtubule inhibitors and estrogen receptor modulators, had previously been reported to be active in BSL-4 infectious Ebola virus replication assays and in animal model studies. Our assay represents a robust, effective and rapid high-throughput screen for the identification of lead compounds in drug development for the treatment of Ebola virus infection.
Keywords: Antipsychotics, drug repurposing screen, Ebola virus, Ebola virus glycoprotein, estrogen receptor modulator, microtubule inhibitor, virus entry, VP40
INTRODUCTION
The current outbreak of Ebola virus disease in West Africa has escalated to a scale not seen previously. As the outbreak continues, the export of virus infections to other regions in the world is occurring, accompanied in some cases by secondary infections.1 Currently, there is no proven effective treatment for Ebola virus infection. Although antibody-based therapy has been shown to be effective in a macaque model and has been used for the treatment of a few patients, the current supply of such drugs is very limited.2 The estimated mortality rate of the current Ebola outbreak is approximately 70%, which is dramatically high.3 Although a specific vaccine might eventually control Ebola virus infection, its development and deployment may take some time.4,5 Therefore, drug repurposing screens that identify approved drugs with the potential for new indications might be a good approach to rapidly discover and develop anti-Ebola virus drugs for the treatment of patients with Ebola virus infection.
We applied a previously developed Ebola virus-like particle (VLP) entry assay for a drug repurposing screen of Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drugs.6 The Ebola VLP used in this assay is comprised of two proteins: glycoprotein (GP) and the matrix protein VP40 fused to a beta-lactamase reporter enzyme, which can be used to monitor VLP entry in a regular biosafety level 2 (BSL-2) cell model. We miniaturized this assay into a 1536-well plate format for high-throughput screening (HTS). This initial drug repurposing screen led to the identification of 53 previously approved drugs with Ebola VLP entry-blocking activity. Although the activities of these drugs should be further confirmed using fully infectious Ebola viruses in vitro and in vivo in BSL-4 laboratories, we herein publish all of our data for quick access by other researchers interested in further studies. Using the assay described, we plan to conduct more comprehensive compound screening to identify additional lead compounds for drug development to treat Ebola virus infection.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Ebola VLPs containing a beta-lactamase-fused VP40 protein (EBOV BlaVP40) and GP were produced in Dr García-Sastre's lab, as previously described.6 LiveBLAzer FRET–B/G Loading Kit with CCF2-AM and Opti-MEM reduced serum medium were purchased from Life Technologies (Carlsbad, CA, USA). An adenosine triphosphate (ATP) content cell viability assay kit was purchased from Promega (Madison, WI, USA). Polystyrene plates (384-well and 1536-well black, clear bottom, sterile, tissue culture treated) were purchased from Greiner Bio-One (Monroe, NC, USA). A FDA-approved drug collection of 600 compounds was originally prepared at the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) for a personalized cancer treatment project. This collection excludes certain drugs, such as those known to be immunosuppressive, topically applied drugs, and those for approved use in animals. In a follow-up screening, we used an NCATS-approved drug collection of 2816 compounds that was previously assembled.7 All of the compounds were dissolved as a 10 mM stock solution in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and diluted in DMSO at a 1∶3 dilution to generate six concentrations in 384-well plates, followed by reformatting into three 1536-well compound source plates for HTS.
Cell culture methods
HeLa cells were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA). The cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM, Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, GE healthcare, Piscataway, NJ, USA) and 100 U/mL of penicillin and 100 µg/mL of streptomycin (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2.
Cell viability assay with the ATP content assay kit
HeLa cells were plated at 750 cells/well in 3 µL of assay medium (DMEM+10% FBS) in 1536-well assay plates and incubated for 16 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Library compounds were added to the assay plate at 23 nL/well using an NX-TR pintool station (WAKO Scientific Solutions, San Diego, CA, USA). After a 4.5 h incubation at 37 °C and 5% CO2, cytotoxicity effects were measured by adding 3 µL of ATP content assay mixture to each well and incubating the plates at room temperature for 30 min. Luminescence values were acquired using a ViewLux plate reader (PerkinElmer, Boston, MA, USA).
Ebola VLP beta-lactamase assay for HTS in 1536-well plates
This 1536-well plate assay was adapted from the original 6-well assay6 with a modification that eliminated the cell washing steps. HeLa cells were plated at 750 cells/well in 3 µL of assay medium (DMEM+10% FBS) in 1536-well assay plates and incubated for 16 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Compounds in the 1536-well drug source plates were added to the 1536-well assay plates at a volume of 23 nL/well using an NX-TR pintool station (WAKO Scientific Solutions, San Diego, CA, USA). Following a 1 h incubation at 37 °C with 5% CO2, 1 µL/well of VLP solution was added to the assay plates using a BioRapTR FRD dispenser (the VLP solution was diluted in Opti-MEM to a final concentration of 1∶16). The plates were then spinoculated by centrifugation at 1500 rpm at 4 °C for 45 min, followed by incubation at 37 °C with 5% CO2 for 4.5 h. The CCF2-AM beta-lactamase substrate was prepared at a 6× concentration following the manufacturer's instructions and added to the assay plates at 1 µL/well. Following a 2 h incubation at room temperature, dual fluorescence intensities (Ex1=405±20, Em1=460±20, and Ex2=405±20, Em2=530±20 nm) were measured using an EnVision plate reader (PerkinElmer, Boston, MA, USA). The ratio of fluorescence intensities (Em1/Em2) was calculated to represent the beta-lactamase activity that is proportional to the amount of VLP entry into the host cells.
Imaging measurement of VLP entry assay in 384-well plates
Hits identified in the primary assay were ‘cherry-picked' and serially diluted in a 1∶3 ratio in DMSO to produce 11 concentrations. The VLP entry assay was then performed in a manner similar to that described above. Briefly, HeLa cells were plated at 4000 cells/well in 40 µL assay medium (DMEM+10% FBS) and incubated for 16 h at 37 °C with 5% CO2. The compounds in DMSO solution were added at 0.5 µL/well to the assay plate; after a 1 h incubation at 37 °C with 5% CO2, 10 µL of the VLP inoculum was added to each well (final dilution of 1∶16). Following centrifugation at 4 °C for 45 min, the plates were incubated for 4.5 h at 37 °C with 5% CO2. The 6×CCF2-AM substrate solution was added to the assay plates (8.3 µL/well), and a 2 h incubation at ambient temperature was performed. The dual fluorescence intensities were measured using an EnVision plate reader as described above, and fluorescence images (both green and blue) were also processed using an InCell 2200 automated imaging system (GE Healthcare, Piscataway, NJ, USA).
Data analysis and statistics
The primary screen data and curve fitting were analyzed using software developed internally at the NIH Chemical Genomics Center (NCGC).8 Half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of compound confirmation data were calculated using Prism software (GraphPad Software, Inc. San Diego, CA). All values are expressed as the mean ± SD (n≥3).
RESULTS
Optimization of Ebola VLP entry assay for HTS
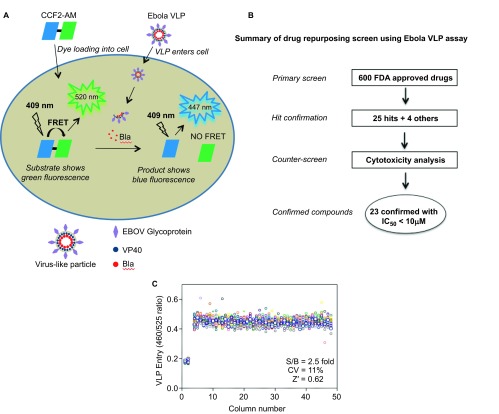
Our Ebola VLP entry assay utilizes two Ebola viral structural proteins: GP and VP40 fused to a beta-lactamase reporter. Upon expression of these two proteins in transfected 293 T cells, VLPs are produced that contain BlaVP40 packaged inside a lipid envelope in which GP is anchored. After incubation in HeLa cells, the VLPs enter the cytoplasm through the receptor binding-fusion activity of GP, thus releasing BlaVP40 into the intracellular space. VP40-beta-lactamase is delivered into the cytoplasm and can be detected by its beta-lactamase activity inside cells (Figure 1A).6 The Ebola VLPs morphologically resemble wild-type Ebola viruses.9 The original assay was developed in a 6-well plate format with multiple plate-washing steps; however, to perform compound screening with this Ebola VLP entry assay in a 1536-well plate format, we optimized the assay by miniaturization and reduction of the steps (Figure 1B). We were able to detect a robust assay signal using 750 cells at 3 µL/well in this 1536-well plate format; this greatly reduced the need for VLP solution, which is a limiting reagent for this assay. We were also able to eliminate the washing steps by using a dye-quenching solution in the beta-lactamase loading buffer. This simplified the assay procedure, reduced well-to-well variation due to intrinsic errors in the washing steps, and significantly increased the compound screening throughput. A signal-to-basal ratio of 2.5-fold with a coefficient of variation (CV) of 11% and a Z′ factor of 0.62 were obtained in a DMSO plate test in this 1536-well plate Ebola virus entry assay (Figure 1C).
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the Ebola VLP entry assay and compound screening method using this assay. (A) Ebola VLPs contain Ebola GP and the VP40 protein fused to a beta-lactamase (Bla) reporter. HeLa cells are loaded with the beta-lactamase substrate CCF2-AM, which results in green fluorescence. After VLP loading into cells, Bla hydrolyzes the substrate CCF2-AM, disrupting the fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) in the substrate and thus causing blue fluorescence. The ratio of blue/green fluorescence intensities represents the activity of Bla inside cells. (B) Flow chart of compound screening in 1536-well plates using Ebola VLP entry assay. (C) Scatter plot of the results from a DMSO plate screening. The wells in columns 1 and 2 of the 1536-well assay plates contained HeLa cells as a control (0% response); Ebola VLPs were added to all other wells (positive control, 100% response). The signal-to-basal ratio (S/B) in this plate was 2.5-fold, with a CV of 11% and a Z′ factor of 0.62.
Drug repurposing screen to identify active compounds that block Ebola VLP entry
We previously selected 600 FDA-approved drugs from our collection for a cancer project that eliminated certain compounds, including immunosuppressive drugs. This series of drugs was diluted at a 1∶3 ratio to generate six concentrations, ranging from 0.24 to 57.5 µM (final), in the assay plates. We identified 25 primary hits using a criteria of IC50<10 µM and a maximal inhibition of >70% in the Ebola VLP assay. These primary hits were then ‘cherry-picked' along with three additional microtubule inhibitors and an human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) entry inhibitor for confirmation testing. We also performed a data analysis using the green fluorescence channel to eliminate cytotoxic compounds (the green channel indicates healthy and viable cells that are loaded with the fluorescent beta-lactamase substrate).
Among the 29 ‘cherry-picked' compounds, the anti-Ebola virus entry activities of 23 were confirmed in the Ebola VLP assay (Figure 2 and Table 1). To eliminate the effect of cytotoxic compounds, we also measured compound cytotoxicity using an ATP content assay. The selectivity index (SI) for each active compound is reported as a ratio of the IC50 of blocking Ebola virus entry over that determined in the cytotoxicity assay (Tables 1 and 2). The ability of these compounds to block Ebola VLP entry was also confirmed in imaging measurements for the same assay (Figure 3). Maraviroc, an HIV entry inhibitor, was not active in this assay. These 23 confirmed compounds can be divided into six categories: microtubule inhibitors, estrogen receptor modulators, antihistamines, typical antipsychotics, ion channel/pump antagonists, and anticancer/antibiotics (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
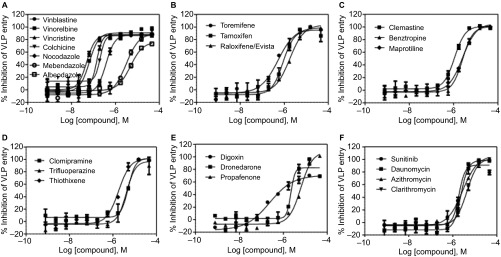
Concentration-response curves of the inhibition of Ebola VLP entry by 23 identified active compounds. These 23 compounds with confirmed anti-Ebola virus entry activity can be divided into six categories: (A) microtubule inhibitors, (B) estrogen receptor modulators, (C) antihistamines, (D) antipsychotics, (E) pump/channel antagonists, and (F) anticancer/antibiotics. The data indicate the mean±SD.
Table 1. Twenty-three active compounds that block Ebola VLP entry into HeLa cells.
| Drug Name | Block Ebola VLP entry | Cytotoxicity | Selectivity | Approved indication | MOA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (µM) | IC90 (µM) | Max. Inh. (%) | IC50 (µM) | Index (fold) | |||
| Vinblastine | 0.048 | 0.130 | 87 | >500 | >10 324 | Anticancer | Microtubule inhibitor |
| Vinorelbine/Navelbine | 0.066 | 0.190 | 90 | >500 | >7546 | Anticancer | Microtubule inhibitor |
| Vincristine | 0.141 | 0.258 | 83 | >500 | >3554 | Anticancer | Microtubule inhibitor |
| Colchicine | 0.238 | 0.354 | 73 | >500 | >2097 | Primary for gout | Microtubule inhibitor |
| Nocodazole*,† | 0.402 | 1.04 | 87 | >500 | >1242 | Anticancer | Microtubule inhibitor |
| Toremifene† | 0.566 | 3.73 | 98 | 180 | 316 | Anticancer | Estrogen receptor modulator |
| Tamoxifen† | 0.734 | 3.15 | 97 | 99.8 | 135 | Anticancer | Estrogen receptor modulator |
| Digoxin | 0.763 | 3.45 | 68 | 250 | 327 | Antiarrhythmic | Na+-K+ pump inhibitor |
| Clemastine | 1.10 | 3.76 | 98 | 95.6 | 87 | Antiallergic, hay fever, rhinitis | Histamine antagonist |
| Raloxifene/Evista† | 1.84 | 9.01 | 100 | >500 | >271 | Anticancer | Estrogen receptor modulator |
| Sunitinib | 1.91 | 3.82 | 90 | 148 | 77 | Anticancer | Kinase inhibitor |
| Thiothixene | 1.92 | 7.18 | 100 | 70.1 | 36 | Antipsychotic | Dopamine antagonist |
| Dronedarone | 2.20 | 3.51 | 81 | 48.0 | 21 | Antiarrhythmic | Multichannel blocker |
| Maprotiline | 2.44 | 12.1 | 100 | 146 | 60 | Antidepressant | Adrenergic uptake inhibitors and histamine antagonist |
| Daunomycin | 2.63 | 5.40 | 98 | >500 | >190 | Anticancer | Topoisomerase Inhibitor |
| Benztropine | 2.64 | 8.25 | 100 | 250 | 95 | Anticholinergic, antihistamine | Histamine antagonist and Cholinergic antagonist |
| Azithromycin | 2.79 | 15.8 | 100 | >500 | >179 | Antimicrobial | Protein synthesis inhibitor |
| Mebendazole | 3.44 | 14.0 | 88 | >500 | >145 | Antihelminthic | Microtubule inhibitor |
| Trifluoperazine | 4.48 | 12.0 | 97 | 97.0 | 21 | Antipsychotic, antiemetic | Dopamine antagonist |
| Clarithromycin | 4.53 | 15.1 | 100 | >500 | >110 | Antimicrobial | Protein synthesis inhibitor |
| Albendazole | 4.90 | 20.7 | 76 | >500 | >102 | Anthelmintic | Microtubule inhibitor |
| Clomipramine | 4.99 | 11.7 | 93 | 64.1 | 12 | Antidepressant | Serotonin uptake inhibitors and histamine antagonist |
| Propafenone | 6.25 | 23.8 | 100 | >500 | >80 | Antiarrhythmic | Sodium channel blocker |
Abbreviations: MOA, mechanism of action; IC90, inhibitory concentration of 90% Max. Inh., maximal inhibition.
The compound was not the original hit but was added for confirmation.
These compounds were previously reported to be active in Ebola assays.
Table 2. An additional 30 active compounds that block Ebola VLP entry in our assay at an IC50<10 µM and SI >10 plus three additional active compounds previously shown to inhibit Ebola virus infection.
| Drug Name | Block Ebola VLP entry | Cytotoxicity | Selectivity | Approved indication | MOA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (µM) | IC90 (µM) | Max. Inh. (%) | IC50 (µM) | Index (fold) | |||
| Carfilzomib | 0.432 | 1.88 | 57 | >500 | >1156 | Anticancer | Proteasome Inhibitor |
| Deslanoside | 0.485 | 11.7 | 66 | 250 | 515 | Antiarrhythmic | Na+-K+ pump inhibitor |
| Maduramicin | 0.611 | 3.94 | 104 | 24.3 | 40 | Antimicrobial | Ionophore |
| Cepharanthine† | 1.53 | 4.40 | 112 | 88.9 | 58 | Anti-inflammatory/Antineoplastic | Release of neutrophil elastase inhibitor |
| Clomiphene† (Clomifene) | 1.72 | 5.34 | 92 | 91.4 | 53 | Female infertility | Estrogen receptor modulator |
| Oxibendazole | 1.72 | 3.75 | 57 | >500 | >291 | Anthelmintic | DNA Polymerase Inhibitor |
| Daunorubicin | 2.43 | 4.45 | 96 | 250 | 103 | Antimicrobial/anticancer | DNA Topoisomerase II inhibitor |
| Niclosamide | 2.66 | 6.60 | 81 | >500 | >188 | Antihelmintic | STAT-3 Inhibitor |
| Zoloft† (sertraline) | 2.73 | 9.08 | 79 | 73.2 | 27 | Antidepressant | Serotonin reuptake inhibitor |
| Mefloquine | 2.73 | 13.0 | 94 | 43.2 | 16 | Antimalarial | Hemozoin formation inhibitor |
| Tilorone | 3.43 | 19.0 | 100 | >500 | >146 | Antiviral | DNA Polymerase Inhibitor |
| Bazedoxifene | 3.43 | 2.63 | 89 | 43.2 | 13 | Postmenopausal osteoporosis | Estrogen receptor modulator |
| Topotecan | 3.85 | 10.8 | 107 | >500 | >130 | Anticancer | DNA Topoisomerase I Inhibitor |
| Bosutinib | 3.85 | 21.3 | 101 | 43.2 | 11 | Anticancer | Bcr-Abl inhibitor |
| Thioproperazine | 4.32 | 12.5 | 103 | >500 | >116 | Antipsychotic | Postsynaptic receptors modulator |
| Spiramycin | 4.32 | 11.7 | 92 | >500 | >116 | Antimicrobial | Protein synthesis inhibitor |
| Mibefradil | 4.32 | 7.34 | 96 | 43.2 | 10 | Antihypertensive | Calcium channel blocker |
| Amodiaquine† | 4.43 | 27.3 | 106 | >500 | >113 | Antimalarial | Histamine N-methyltransferase inhibitor |
| Nitrovin | 4.85 | 7.14 | 95 | >500 | >103 | Antimicrobial | Ionophore |
| Bifemelane | 4.85 | 18.1 | 99 | 250 | 52 | Antidepressant | Cholinergic system modulator |
| Bitolterol | 6.11 | 22.6 | 85 | 250 | 41 | Bronchodilator | Beta-adrenergic receptor agonist |
| Proglumetacin | 6.85 | 17.3 | 93 | >500 | >73 | Anti-inflammatory | Cyclooxygenase-1 inhibitor |
| Aprindine | 7.69 | 26.6 | 93 | >500 | >65 | Antiarrhythmic | Na+-K+ pump inhibitor |
| Cyclomethycaine | 7.69 | 19.6 | 86 | >500 | >65 | Anesthetic | Na+-K+ pump inhibitor |
| Posaconazole | 7.69 | 8.33 | 77 | >500 | >65 | Antifungal | Membrane-bound enzyme inhibitor |
| Alverine Citrate | 8.63 | 21.8 | 90 | >500 | >58 | Antispasmodic | Parasympathetic nervous system modulator |
| Azaclorzine | 9.43 | 37.1 | 88 | >500 | >53 | Antianginal | Beta-adrenergic receptor agonist |
| Salmeterol | 9.68 | 13.0 | 90 | >500 | >52 | Antiasthma | Beta-adrenergic receptor agonist |
| Piperacetazine | 9.68 | 18.1 | 90 | >500 | >52 | Antipsychotic | Dopamine antagonist |
| Gefitinib | 9.68 | 17.9 | 93 | >500 | >52 | Anticancer | EGFR inhibitor |
| Imipramine† | 13.7 | 52.2 | 102 | >500 | >36 | Antidepressant | Serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor |
| Chloroquine† | 15.3 | 133 | 98 | >500 | >32 | Antimalarial | Hemozoin formation inhibitor |
| Nilotinib† | 24.3 | 104 | 100 | 50.1 | 2 | Anticancer | Tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
Abbreviation: EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor.
These compounds were previously reported to be active in Ebola virus infection assays or animal models.
Figure 3.
Images of the inhibition of Ebola VLP entry into HeLa cells by representative compounds that block Ebola VLP entry into host cells using a high content assay. Vinorelbine, Vincristine, Vinblastine, and Colchicine concentration-dependently blocked the blue fluorescence representing VLP entry into cells. Maraviroc, an HIV entry blocker, did not show any effect in this assay and served as a negative control. A 20× objective was used to capture the images.
During the submission and revision of this manuscript, we completed the screening of an additional 2216 drugs in the NCATS-approved and investigational drug collection.7 The 30 additional active compounds first listed in Table 2 were selected as having an IC50<10 µM with a maximal inhibition of >50% and an SI>10 in the Ebola VLP assay. The last three compounds in Table 2, Imipramine, Chloroquine, and Nilotinib, have IC50 values between 10 and 30 µM but have previously been reported to inhibit Ebola virus infection.10,11,12 The 95 remaining active compounds with an IC50 value of 10 to 30 µM, an SI<10-fold, or are not FDA approved for human use are listed in Supplementary Table S1.
DISCUSSION
We quickly applied a BSL-2 Ebola virus entry assay for a repurposing screen of 600 selected drugs. This assay identifies compounds that block Ebola VLP entry into host cells mediated by Ebola virus surface GP. Although the active compounds found to block Ebola VLP entry need to be further tested in wild-type Ebola virus infection assays and in animal models to confirm their antiviral activity, our results represent a proof-of-principle investigation supporting the suitability of this assay for rapid screening of Ebola antiviral compounds that inhibit viral entry. Based on our screen of 600 FDA-approved drugs, we quickly identified 23 compounds that block Ebola VLP entry, with the most potent compound being the microtubule inhibitor Vinblastine (IC50=48 nM). We also found an additional 30 active FDA-approved compounds with an IC50<10 µM and SI>10 in the extended screening of 2216 additional approved or investigational drugs in our collection. We decided to publish all our data from this drug repurposing screen so that other researchers may quickly access all the accumulated data in this ongoing emergency situation caused by the current unprecedented Ebola virus outbreak. Although our laboratories do not have direct access to BSL-4 facilities for the further confirmation of the activity of these compounds in Ebola virus infection assays and animal models, we hope that our data will be used by other researchers who do possess the capability of performing these experiments.
The 23 drugs identified with inhibitory effects on Ebola VLP entry can be grouped into six categories based on their approved indications. The group with the most potent anti-Ebola virus entry activity consists of microtubule inhibitors, including Vinblastine (IC50=48 nM), Vinorelbine (IC50=66 nM), Vincristine (IC50=140 nM), Colchicine (IC50=238 nM), Nocodazole (IC50=402 nM), Mebendazole (IC50=3.4 µM), and Albendazole (IC50=4.8 µM). Microtubules have previously been implicated in Ebola virus VP40 and GP functions.13,14,15 Nocodazole's activity in blocking Ebola virus entry has been described, and the mechanism of action is believed to be related to microtubule depolymerization, leading to the inhibition of viral entry.13
A second group comprises the estrogen receptor modulators Toremifene (IC50=0.56 µM), Tamoxifen (IC50=0.73 µM), and Raloxifene (IC50=1.8 µM). A 2013 report indicated that Toremifene and another estrogen receptor modulator, Clomiphene, effectively block Ebola virus infection independent of the estrogen receptor and were effective in a mouse infection model.16 As previously reported, HeLa cells are estrogen receptor-negative,17,18,19 and the effect of estrogen receptor modulators in blocking Ebola virus entry is believed to be unrelated to the classical estrogen receptors.16 The identification of estrogen receptor modulators and microtubule inhibitors in our screen validates the BSL-2 Ebola virus entry assay for the identification of virus entry inhibitors.
A third group of compounds has antihistamine and anticholinergic activities and includes Clemastine (IC50=1.1 µM), Maprotiline (IC50=2.4 µM), and Benztropine (IC50=2.6 µM). A fourth group contains the antipsychotic/antidepressant drugs Clomipramine (IC50=4.9 µM), Thiothixene (IC50=1.9 µM), and Trifluoperazine (IC50=4.4 µM). The possible mechanism of action of these drugs in inhibiting Ebola VLP entry remains unknown.
A fifth group includes pump/channel blockers such as Digoxin (IC50=0.76 µM), Dronedarone (IC50=2.2 µM), and Propafenone (IC50=6.2 µM). The activity of Digoxin has been found in multiple drug repurposing screens against many targets, including cancer and HIV.20,21,22 Digoxin was reported to suppress HIV-1 structural protein synthesis by altering viral RNA processing23 and to inhibit HIV-1 gene expression via α-1 subunit of the Na+/K+-ATPase inhibition.20 However, Digoxin shows cytotoxicity at a compound concentration similar to that effective in blocking Ebola VLP entry. Dronedarone, a multichannel inhibitor indicated for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmia, inhibits class I sodium (at rapid pacing rates) and class IV calcium channels and exhibits non-competitive anti-adrenergic activity.10 Propafenone is also an orally active antiarrhythmic drug that blocks sodium channels and has beta-adrenoreceptor antagonist and weak calcium antagonist activities.24 The potencies of this group of compounds against Ebola virus entry are relatively weak.
The last four drugs are anticancer drugs and antibiotics. Sunitinib is a multi-kinase inhibitor.25 Daunomycin, similar to Doxorubicin, intercalates DNA, inhibiting DNA biosynthesis. DNA intercalators have also been previously found to induce the production of the antiviral cytokine interferon.11 Azithromycin and Clarithromycin are macrolide antibiotics that block bacterial protein synthesis. It remains to be determined how these drugs affect Ebola VLP entry.
During the manuscript submission and review process, we screened an additional 2216 approved drugs from our NCGC pharmaceutical collection,7 which also contains experimental and animal drugs. We identified and confirmed 30 additional active compounds selected using criteria of an IC50<10 µM with a maximal inhibition >50% and an SI>10-fold in the Ebola virus entry assay (Table 2). Table 2 also shows three additional active compounds previously shown to inhibit Ebola virus infection.10,11,12 In addition, we identified 95 active compounds with IC50 values of 10 to 30 µM or an SI<10-fold or without FDA approval for human use (Supplementary Table S1). At present, we cannot exclude that a few of our reported drugs inhibit reporter beta-lactamase activity instead of inhibiting Ebola VLP-entry. Anti-Ebola virus activities of 16 approved drugs that were tested in the Ebola virus infection assays and/or animal models have been previously reported in the literature.12,15,16,26,27,28,29,30,31 We found that 11 of these 16 compounds are active in our Ebola VLP entry assay (Tables 1 and 2): Nocodazole (IC50=0.4 µM), Toremifene (0.55 µM), Tamoxifen (0.76 µM), Raloxifene 1.84 (1.53 µM), Cepharanthine (1.53 µM), Clomiphene (1.72 µM), Dronedarone (2.2 µM), Amodiaquine (4.43 µM), Imipramine (13.7 µM), Chloroquine (15.3 µM), and Nilotinib (15.3 µM).
Although more experiments will be needed to fully understand the possible use of any of these compounds against Ebola virus infection, here we describe a surrogate Ebola virus entry assay that can be used for HTS in a BSL-2 facility for the rapid screening of extensive compound collections. The identification of several drugs previously known to inhibit Ebola virus entry in our repurposing screen further supports the usefulness of our approach. All the screening data obtained in this Ebola VLP entry assay are deposited in the PubChem database for open access. Using the Ebola VLP entry assay described here, we will continue to screen additional experimental drugs in our collection that are currently in clinical trials, and we will also expand this compound screening using the entire NCATS diverse collection of approximately 400 000 compounds. We hope that our screening efforts will result in the identification of novel lead compounds for the development of drugs to treat Ebola virus infections.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the compound management group at NCATS, National Institutes of Health (NIH), for their professional support, as well as Richard Cadagan and Osman Lizardo for excellent technical support at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, USA. This work was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the NCATS, and the NIH. Antiviral screen assays in Adolfo García-Sastre's lab are supported by NIH grants R01AI079110 and R01AI089539.
Footnotes
Note: Supplementary Information for this article can be found on Emerging Microbes & Infections's website (http://www.nature.com/emi/).
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Table S1
References
- Kreuels B, Wichmann D, Emmerich P, et al. A Case of Severe Ebola Virus Infection Complicated by Gram-Negative Septicemia N Engl J Med 2014 Oct 22. Doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1411677 [DOI] [PubMed]
- Qiu X, Wong G, Audet J, et al. Reversion of advanced Ebola virus disease in nonhuman primates with ZMapp. Nature. 2014;514:47–53. doi: 10.1038/nature13777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHO Ebola Response Team Ebola virus disease in West Africa–the first 9 months of the epidemic and forward projections. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1481–1495. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1411100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanapathipillai R, Restrepo AM, Fast P, et al. Ebola Vaccine - An Urgent International Priority N Engl J Med 2014 Oct 7. Doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1412166 [DOI] [PubMed]
- Cohen J. Infectious disease. Ebola vaccine: little and late. Science. 2014;345:1441–1442. doi: 10.1126/science.345.6203.1441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tscherne DM, Manicassamy B, Garcia-Sastre A. An enzymatic virus-like particle assay for sensitive detection of virus entry. J Virol Methods. 2010;163:336–343. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2009.10.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang R, Southall N, Wang Y, et al. The NCGC pharmaceutical collection: a comprehensive resource of clinically approved drugs enabling repurposing and chemical genomics. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3:80ps16. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3001862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y, Jadhav A, Southal N, Huang R, Nguyen DT. A grid algorithm for high throughput fitting of dose-response curve data. Curr Chem Genomics. 2010;4:57–66. doi: 10.2174/1875397301004010057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez O, Johnson J, Manicassamy B, et al. Zaire Ebola virus entry into human dendritic cells is insensitive to cathepsin L inhibition. Cell Microbiol. 2010;12:148–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2009.01385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoy SM, Keam SJ. Dronedarone. Drugs. 2009;69:1647–1663. doi: 10.2165/11200820-000000000-00000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Gil L, Ayllon J, Ortigoza MB, et al. Identification of small molecules with type I interferon inducing properties by high-throughput screening. PloS One. 2012;7:e49049. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wool-Lewis RJ, Bates P. Characterization of Ebola virus entry by using pseudotyped viruses: identification of receptor-deficient cell lines. J Virol. 1998;72:3155–3160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.72.4.3155-3160.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dube D, Schornberg KL, Shoemaker CJ, et al. Cell adhesion-dependent membrane trafficking of a binding partner for the ebolavirus glycoprotein is a determinant of viral entry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:16637–16642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008509107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruthel G, Demmin GL, Kallstrom G, et al. Association of ebola virus matrix protein VP40 with microtubules. J Virol. 2005;79:4709–4719. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.8.4709-4719.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonezawa A, Cavrois M, Greene WC. Studies of ebola virus glycoprotein-mediated entry and fusion by using pseudotyped human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virions: involvement of cytoskeletal proteins and enhancement by tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Virol. 2005;79:918–926. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.2.918-926.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen LM, Brannan JM, Delos SE, et al. FDA-approved selective estrogen receptor modulators inhibit Ebola virus infection. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5:190ra79. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3005471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang ER, Lim SJ, Lee ES, et al. The histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A sensitizes estrogen receptor alpha-negative breast cancer cells to tamoxifen. Oncogene. 2004;23:1724–1736. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levenson AS, Jordan VC. Transfection of human estrogen receptor (ER) cDNA into ER-negative mammalian cell lines. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1994;51:229–239. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(94)90035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touitou I, Mathieu M, Rochefort H. Stable transfection of the estrogen receptor cDNA into Hela cells induces estrogen responsiveness of endogenous cathepsin D gene but not of cell growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990;169:109–115. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird GM, Eisele EE, Rabi SA, Nikolaeva D, Siliciano RF. A novel cell-based high-throughput screen for inhibitors of HIV-1 gene expression and budding identifies the cardiac glycosides. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014;69:988–994. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkt471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia M, Huang R, Sakamuru S, et al. Identification of repurposed small molecule drugs for chordoma therapy. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013;14:638–647. doi: 10.4161/cbt.24596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z, Zheng M, Li Z, et al. Cardiac glycosides inhibit p53 synthesis by a mechanism relieved by Src or MAPK inhibition. Cancer Res. 2009;69:6556–6564. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong RW, Balachandran A, Ostrowski MA, Cochrane A. Digoxin suppresses HIV-1 replication by altering viral RNA processing. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9:e1003241. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryson HM, Palmer KJ, Langtry HD, Fitton A. Propafenone. A reappraisal of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and therapeutic use in cardiac arrhythmias. Drugs. 1993;45:85–130. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199345010-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leone Roberti Maggiore U, Valenzano Menada M, Venturini PL, Ferrero S. The potential of sunitinib as a therapy in ovarian cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2013;22:1671–1686. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2013.841138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya S, Warfield KL, Ruthel G, Bavari S, Aman MJ, Hope TJ. Ebola virus uses clathrin-mediated endocytosis as an entry pathway. Virology. 2010;401:18–28. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.02.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García M, Cooper A, Shi W, et al. Productive replication of Ebola virus is regulated by the c-Abl1 tyrosine kinase. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:123ra124. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring G, Rohrmann K, Atenchong N, et al. The clinically approved drugs amiodarone, dronedarone and verapamil inhibit filovirus cell entry. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014;69:2123–2131. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oestereich L, Lüdtke A, Wurr S, Rieger T, Muñoz-Fontela C, Günther S. Successful treatment of advanced Ebola virus infection with T-705 (favipiravir) in a small animal model. Antiviral Res. 2014;105:17–21. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.02.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madrid PB, Chopra S, Manger ID, et al. A systematic screen of FDA-approved drugs for inhibitors of biological threat agents. PloS One. 2013;8:e60579. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker CJ, Schornberg KL, Delos SE, et al. Multiple cationic amphiphiles induce a Niemann-Pick C phenotype and inhibit Ebola virus entry and infection. PloS One. 2013;8:e56265. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Table S1