Abstract
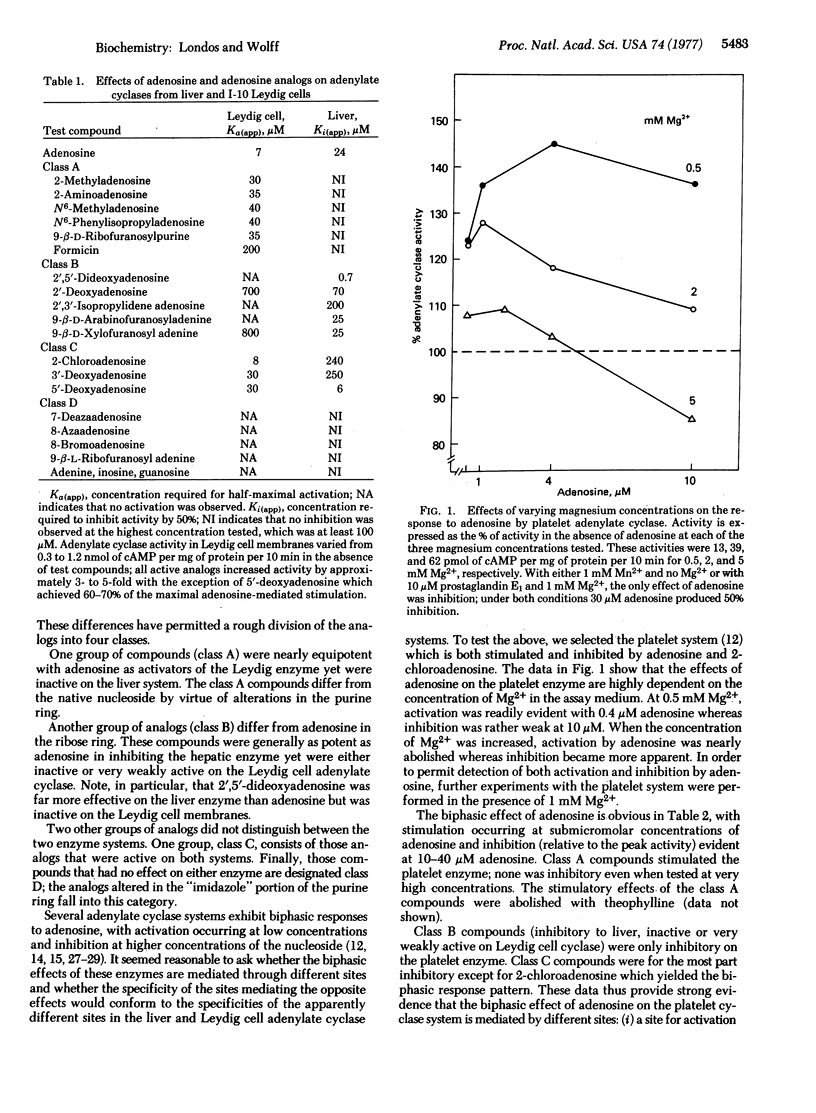
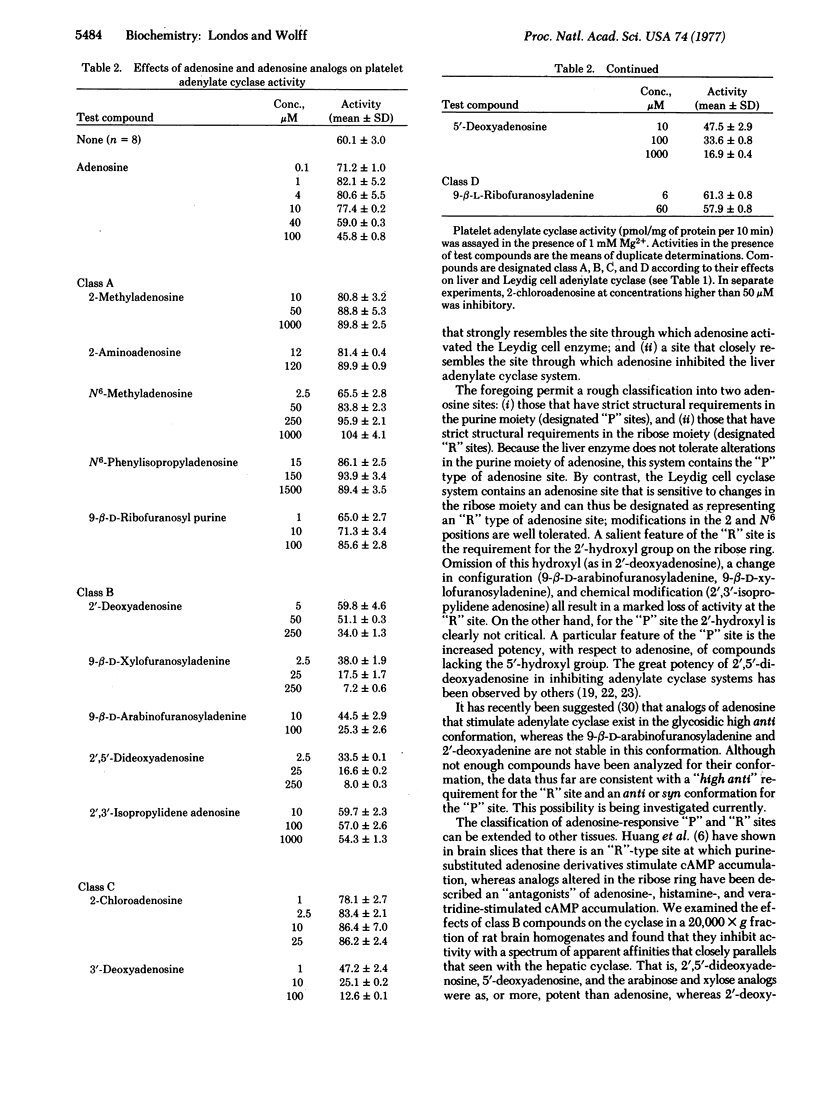
The effects of adenosine and adenosine analogs on adenylate cyclases from several tissues have been examined. Two adenosine-reactive sites have been identified: (i) the "R" site, occupancy of which usually leads to activation of cyclase and which requires integrity of the ribose ring for activity, and (ii) the "P" site, which mediates inhibition and requires integrity of the purine ring for activity. Biphasic effects of adenosine are explained by the presence of both sites on a single adenylate cyclase. Comparison of these data with those in the literature indicates that adenosine-reactive "P" and "R" sites are present generally.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnbaumer L., Nakahara T., Yang P. C. Studies on receptor-mediated activation of adenylyl cyclases. II. Nucleotide and nucleoside regulation of the activities of the beef renal medullary adenylyl cyclase and their stimulation by neurohypophyseal hormones. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7857–7866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume A. J., Dalton C., Sheppard H. Adenosine-mediated elevation of cyclic 3':5'-adenosine monophosphate concentrations in cultured mouse neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3099–3102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume A. J., Foster C. J. Mouse neuroblastoma adenylate cyclase. Adenosine and adenosine analogues as potent effectors of adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):5003–5008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume A. J., Foster C. J. Neuroblastoma adenylate cyclase. Role of 2-chloroadenosine, prostaglandin E1, and guanine nucleotides in regulation of activity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 10;251(11):3399–3404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Purinergic nerves. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Sep;24(3):509–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. B., Gross R., Su Y. F., Perkins J. P. Regulation of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate content in human astrocytoma cells by adenosine and the adenine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5296–5303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. B., Seney M. N. Regulation of adenylate cyclase from cultured human cell lines by adenosine. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4239–4246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson J. G., Jr, Rubio R., Berne R. M. Role of adenine nucleotides, adenosine, and inorganic phosphate in the regulation of skeletal muscle blood flow. Circ Res. 1971 Oct;29(4):375–384. doi: 10.1161/01.res.29.4.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., Pointer R. H., Ward W. F. Effects of adenosine nucleosides on adenylate cyclase, phosphodiesterase, cyclic adenosine monophosphate accumulation, and lipolysis in fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6866–6872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., Wieser P. B. Effects of adenosine deaminase on cyclic adenosine monophosphate accumulation, lipolysis, and glucose metabolism of fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 10;250(3):1027–1034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R. D., Stanberry L. R. Elevation of cyclic AMP in C-1300 murine neuroblastoma by adenosine and related compounds and the antagonism of this response by methylxanthines. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Jan 1;26(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Lynham J. A. Activation and inhibition of blood platelet adenylate cyclase by adenosine or by 2-chloroadenosine. Life Sci II. 1972 Dec 8;11(23):1143–1154. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(72)90269-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M., Daly J. W. Adenosine-elicited accumulation of cyclic AMP in brain slices: potentiation by agents which inhibit uptake of adenosine. Life Sci. 1974 Feb 1;14(3):489–503. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90364-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M., Shimizu H., Daly J. W. Accumulation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate in incubated slices of brain tissue. 2. Effects of depolarizing agents, membrane stabilizers, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, and adenosine analogs. J Med Chem. 1972 May;15(5):462–466. doi: 10.1021/jm00275a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londos C., Preston M. S. Regulation by glucagon and divalent cations of inhibition of hepatic adenylate cyclase by adenosine. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):5951–5956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie S. G., Bär H. P. On the mechanism of adenyl cyclase inhibition by adenosine. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1973 Mar;51(3):190–196. doi: 10.1139/y73-027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles D. L., Miles D. W., Eyring H. Conformational basis for the activation of adenylate cyclase by adenosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2194–2198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. C., Smith J. B. The influence on platelet aggregation of drugs that affect the accumulation of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in platelets. Biochem J. 1971 Jan;121(2):185–196. doi: 10.1042/bj1210185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriwaki K., Foà P. P. Inhibition of rat liver adenyl cyclase by adenosine and adenine nucleotides. Experientia. 1970 Jan 15;26(1):22–22. doi: 10.1007/BF01900365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck W. A., Carpenter J. G., Schuster R. J. Adenosine-mediated stimulation of bone cell adenylate cyclase activity. Endocrinology. 1976 Sep;99(3):901–909. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-3-901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck W. A., Carpenter J., Messinger K. Cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate in isolated bone cells. II. Responses to adenosine and parathyroid hormone. Endocrinology. 1974 Jan;94(1):148–154. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-1-148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penit J., Huot J., Jard S. Neuroblastoma cell adenylate cyclase: direct activation by adenosine and prostaglandins. J Neurochem. 1976 Feb;26(2):265–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb04475.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L., Rodbell M. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. I. Properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1849–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premont J., Perez M., Bockaert J. Adenosine-sensitive adenylate cyclase in rat striatal homogenates. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):209–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattin A., Rall T. W. The effect of adenosine and adenine nucleotides on the cyclic adenosine 3', 5'-phosphate content of guinea pig cerebral cortex slices. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Jan;6(1):13–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J., Daly J. W. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in guinea pig cerebral cortical slices. II. The role of phosphodiesterase activity in the regulation of levels of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):853–859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe U., Ebert R., Erbler H. C. Adenosine release from fat cells: effect on cyclic AMP levels and hormone actions. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:569–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberg G., Zimmerman T. P., Hiemstra K., Winston M., Chu L. C. Adenosine inhibition of lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis: possible role of cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Science. 1975 Mar 14;187(4180):957–959. doi: 10.1126/science.167434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Cook G. H. Activation of steroidogenesis and adenylate cyclase by adenosine in adrenal and Leydig tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):687–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Cook G. H. Charge effects in the activation of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6897–6903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenser T. V., Wannemacher R. W., Jr Inhibition of cholera toxin-stimulated intestinal epithelial cell adenylate cyclase by adenosine analogs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 May;152(1):126–129. doi: 10.3181/00379727-152-39342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


