Abstract
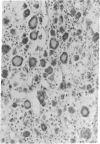
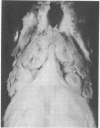
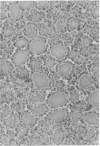
The Amazon molly, Poecilia formosa, is a small fish that grows in clones. Hence, cells from one animal may be transplanted to another without danger of rejection. Cells from thyroid and adjacent tissue were irradiated with UV light in vitro and injected into the abdominal cavity of isogeneic recipients. At appropriate UV doses and numbers of cells injected, all recipients showed exuberant thyroid proliferation. We give arguments and data indicating that the proliferation is a tumor, not a goitrogenic response. If the UV irradiation is followed, but not preceded, by photoreactivating illumination, the yield of thyroid growths is markedly decreased. Because other investigations have shown that photoreactivation monomerizes UV-induced cyclobutylpyrimidine dimers in DNA and does not affect other photoproducts, our data indicate that pyrimidine dimers in DNA can give rise to tumors.
Full text
PDF
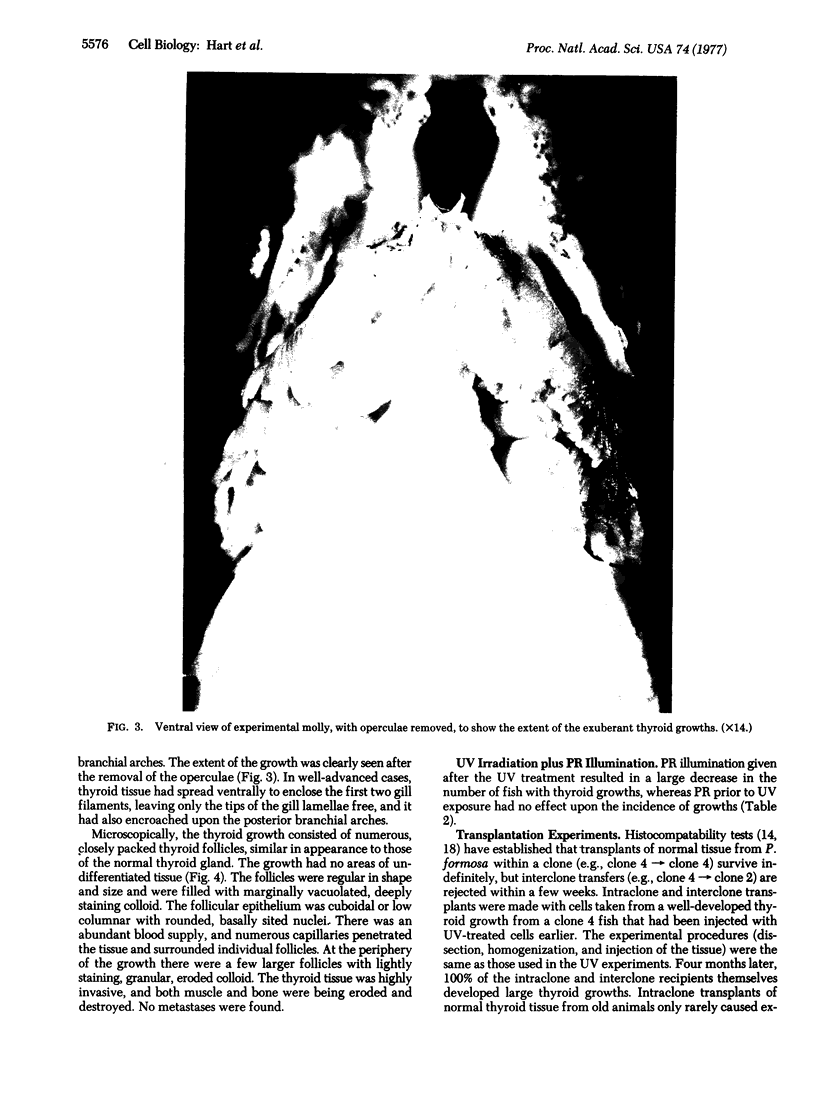
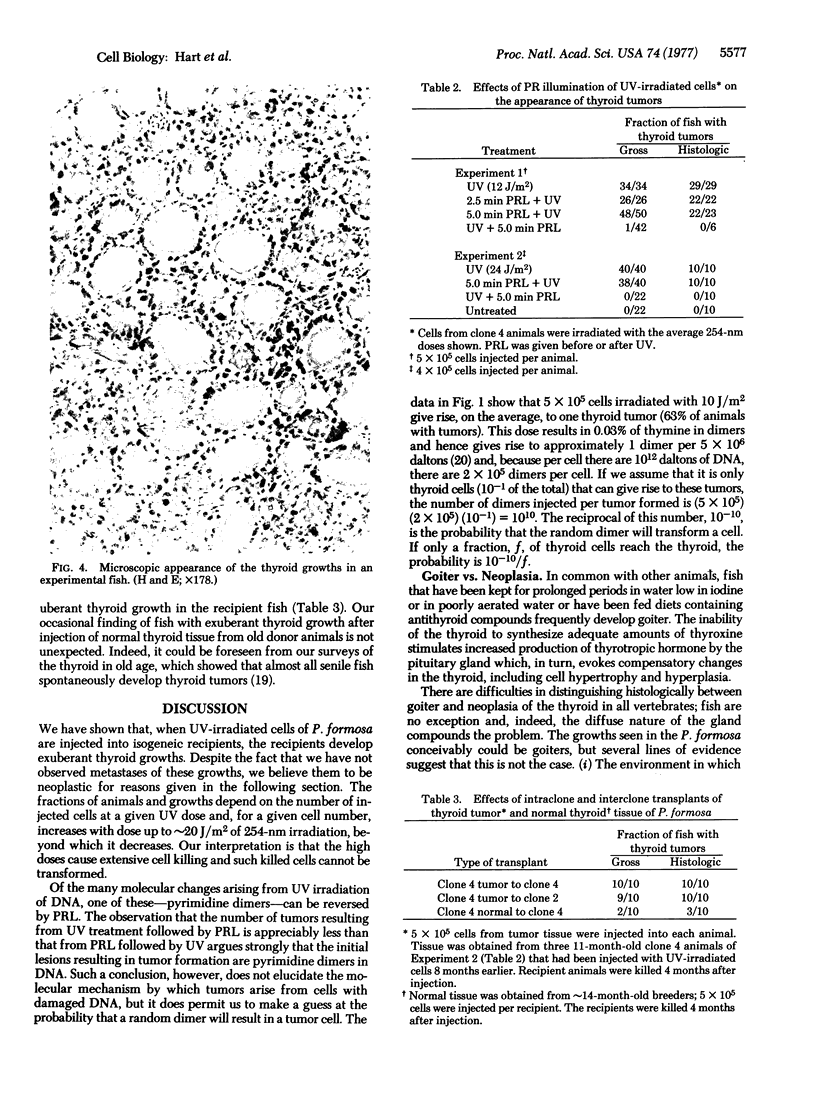

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bridges B. A. Short term screening tests for carcinogens. Nature. 1976 May 20;261(5557):195–200. doi: 10.1038/261195a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidelberger C. Chemical carcinogenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:79–121. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAGGER J. A small and inexpensive ultraviolet dose-rate meter useful in biological experiements. Radiat Res. 1961 Apr;14:394–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagger J., Fossum T., McCaul S. Ultraviolet irradiation of suspensions of micro-organisms: possible errors involved in the estimation of average fluence per cell. Photochem Photobiol. 1975 May;21(5):379–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1975.tb06690.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOROWITZ H. J. Absorption effects in volume irradiation of microorganisms. Science. 1950 Mar 3;111(2879):229–229. doi: 10.1126/science.111.2879.229-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann J., Ames B. N. Detection of carcinogens as mutagens in the Salmonella/microsome test: assay of 300 chemicals: discussion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):950–954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann J., Choi E., Yamasaki E., Ames B. N. Detection of carcinogens as mutagens in the Salmonella/microsome test: assay of 300 chemicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5135–5139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS S. The in vitro initiation of pulmonary adenomas in fetal mouse lung by a single exposure to ultraviolet irradiation of wavelength 2,537 A. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1955 Feb;15(4):1001–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow R. B., Regan J. D., German J., Carrier W. L. Evidence that xeroderma pigmentosum cells do not perform the first step in the repair of ultraviolet damage to their DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):1035–1041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow R. B., Setlow J. K. Effects of radiation on polynucleotides. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1972;1:293–346. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.01.060172.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow R. B. The wavelengths in sunlight effective in producing skin cancer: a theoretical analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3363–3366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhead A. D., Scully P. M. A comparative study of the pretumorous thyroid gland of the gynogenetic teleost, Poecilia formosa, and that of other poeciliid fishes. Cancer Res. 1977 Oct;37(10):3751–3755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]