Abstract
Ortho-hydroxy-anilides are part of natural products like the new antibiotics platencin (A) and platensimycin (B). An important step in the total synthesis of these antibiotics or their derivatives is the preparation of the o-hydroxy-anilide partial structure. The presented method allows the preparation of o-hydroxy-anilides and o-dihydroxy-anilides from 2-nitrophenol esters in a one-step synthesis without protecting the hydroxy group. Aryl- and alkyl-anilides were prepared following this method as simple analogues of platensimycin (A). The resulting compounds were tested in an agar diffusion assay for their antibiotic potency.
Keywords: Anilides, Hydrogenation, Antibiotic activity, Aminolysis
Introduction
The 3-amino-2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid core is an essential part of the new antibiotic drugs platencin (A) and platensimycin (B) [Figure 1], which show a high activity against Gram-positive bacteria, especially methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) or vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE). Platencin (A) shows MIC values against MRSA of about 0.1 μg/mL and platensimycin (B) 0.2–0.4 μg/mL against MRSA and 0.4–0.8 μg/mL against VRE. Furthermore, platensimycin (B) shows low toxicity against mammalian cells (IC50 > 1000 μg/mL in HeLa cells).
Fig. 1.
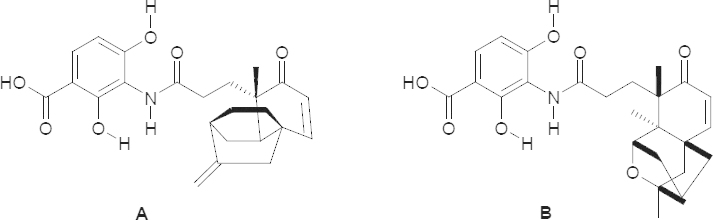
Structure of platencin (A) and platensimycin (B)
Platencin and platensimycin show a new mechanism of action by inhibiting the bacterial fatty acid synthesis. Bacterial fatty acid synthesis is carried out by fatty acid synthase (FAS II). Each step in this synthesis is encoded by separate proteins. A key step in the pathway is the condensation of the acyl-enzyme intermediate and malonyl-acyl carrier protein by catalysis of the FabF–enzyme towards the ß-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein (elongation of the fatty acid chain). Both natural products inhibit the FabF-enzyme (Fig. 2) [1–4].
Fig. 2.
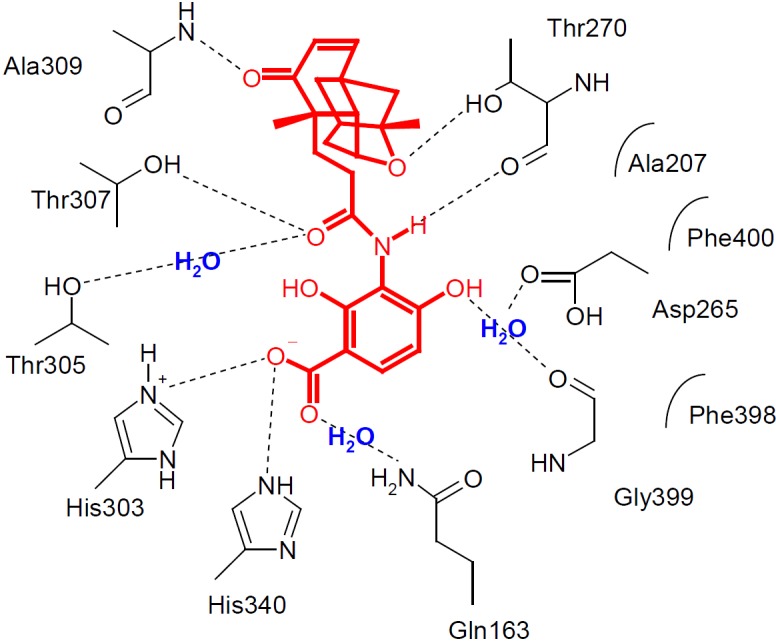
Schematic diagram showing the key interactions between platensimycin and the FabF enzyme [4]
The total synthesis of both natural products is long and expensive. In the last few years, a lot of total syntheses of platencin (A) and platensimycin (B) were published. Even the synthesis of the 3-amino-2,4-dihydroxy benzoic acid partial structure, which is essential for binding to the enzyme FabF (Figure 2), takes several steps in these total syntheses [5–13]. In continuation of our work on simple platensimycin analogues [14, 15], we hereby present the short and effective preparation of the o-hydroxy-anilide partial structure without the requirement of a protecting group.
Results and Discussion
In the first series, commercially available 4-hydroxy-3-nitrobenzoic acid (1) was esterified with methanol / H2SO4 following a standard protocol to give the methyl ester 2 [14]. The phenol group of the methyl ester 2 was esterified with several aromatic or aliphatic carboxylic acid chlorides to give the phenol esters 3a–h. The following hydrogenation of the nitro group with Pd/C (5%) in methanol led to the amino group which reacted in the same procedure under aminolysis of the phenol ester to the resulting anilides 4a–g [14–18]. The olefin partial structures of 3a and 3f were hydrogenated under these conditions but the halogen substituent of 3b was stable. Reaction of 3h led only to a mixture of the products that couldn´t be separated by flash column chromatography.
Sch. 1.
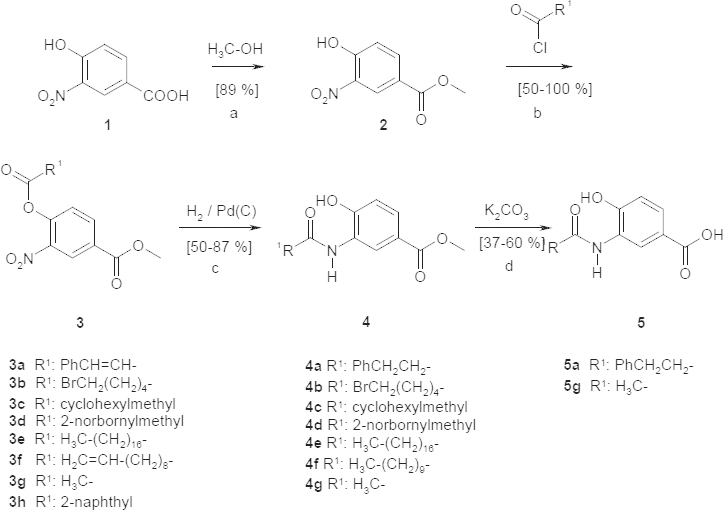
Synthesis of benzoic acid derivatives, a: methanol; b: toluene; c: methanol; d: methanol
Exemplarily, two of the methyl esters were hydrolyzed to give the benzoic acid derivatives 5a and 5g as found in the natural products platencin (A) and platensimycin (B).
In the second series, 2-nitroresorcinol (6) was esterified with a half equivalent of acyl chloride to give the monoesters 7a–h. As a byproduct, a remarkable amount of the diesters was observed even when using an excess of 2-nitroresorcinol (6), but the diesters could be separated clearly by preparative flash column chromatography. The resulting esters 7a–h were hydrogenated in the way described above to give the anilides 8a–h in high yields (80–90%).
Sch. 2.
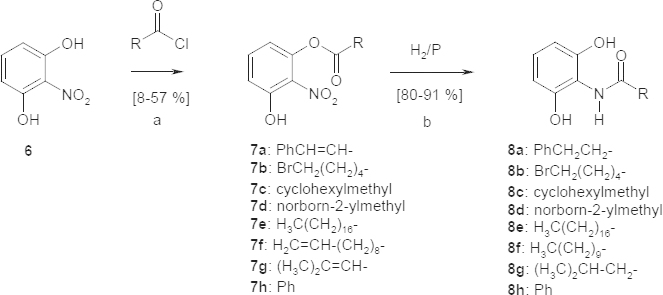
Synthesis of resorcinol derivatives, a: toluene; b: methanol
The mechanism of the aminolysis of the phenol esters is an intramolecular rearrangement as shown by the hydrogenation of an equimolar mixture of 3c and 7h and a subsequent GC-MS analysis. The gas chromatogram showed only two peaks of the products 4c and 8h and no peak of 8c or methyl 3-benzamido-4-hydroxybenzoate.
The resulting compounds were tested in an agar diffusion assay [21] against several bacteria (Gram-positive and Gram-negative) and fungi, but showed only weak or no antibiotic activities in this assay as shown exemplarily for some compounds in Table 1. Only the precursor 2 showed an interesting activity against bacteria and fungi.
Tab. 1.
Agar diffusion assay 100 μg / disc, (te: tetracycline, cl: clotrimazol 30 μg/disc); GI (growth inhibition), nt: not tested, zone of inhibition [mm]
| 2 | 3e | 4c | 4d | 4e | 4g | 5a | 8e | 8f | te | cl | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | 25 | 10 (GI) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 0 |
| Pseudomonas antimicrobia | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 23 | 0 |
| Staphylococcus equorum | 32 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 23 | 9 |
| Streptococcus entericus | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 12 | 11 |
| Candida glabrata | 25 (GI) | 10 (GI) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | nt | 15 |
| Aspergillus niger | 22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | nt | 15 |
| Yarrowia lipolytica | 12 (GI) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 (GI) | 0 | 0 | nt | 20 |
| Hypopichi burtonii | 23 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | nt | 17 |
Conclusion
The presented synthesis describes a simple and efficient method to prepare o-hydroxy-anilides directly from o-nitrophenol esters under mild conditions and without affording any protecting group. Thus it is a helpful tool in preparing platensimycin analogues or other natural products containing this partial structure.
The tested compounds themselves showed no or only weak antibiotic activity as shown exemplarily for some compounds (Table 1). This indicates that the o-hydroxy-anilide partial structure is not the determining factor alone for the interaction with the FabF enzyme of platencin or platensimycin. The complex cyclic part is also essential for the high antibiotic activity of these natural products.
Experimental
General Methods
All solvents used were of HPLC grade or p.a. grade and/or purified according to standard procedures. Chemical reagents were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (Schnelldorf, Germany) and Acros (Geel, Belgium).
IR-spectra: Perkin-Elmer FT-IR Paragon 1000; MS: Hewlett Packard MS-Engine, electron ionisation (EI) 70eV, chemical ionisation (CI) with CH4 (300 eV); GC-MS: Shimadzu GC17A, carrier gas: He, column: fused silica capillary column 30 m, detector: EI (70eV). NMR (400 MHz): Jeol GSX 400 (1H: 400 MHz, 13C: 125 MHz); melting points: Büchi Melting Point B-540 (not corrected); flash column chromatography (FCC): silica gel 60 (230–400 mesh, E. Merck, Darmstadt).
General Procedure 1 (Preparation of Phenol Esters)
One mmol to 2.0 mmol of the acid were dissolved in 20 mL dry toluene or dry 1,2-dimethoxyethane and 1.0 mL to 2.0 mL (11.5 mmol to 27.5 mmol) SOCl2 were added. The solution was refluxed for 1 h, the solvent was evaporated, and the residue was dissolved in 25 mL toluene or 1,2-dimethoxyethane. Alternatively, 0.5 to 1.5 mmol of the commercially available acid chlorides were used. One mmol of the phenol or 1 mmol of the 2-nitroresorcinol and 5 mL N-ethyl-N-methyl-ethanamine or 5 mL pyridine were added and the solution was stirred for 12 h at room temperature. The solvent was evaporated and the residue was taken up in 30 mL water (for the methyl esters in 30 mL 10% aqueous NaOH) and 30 mL ethyl acetate or diethyl ether. The organic layer was separated and the aqueous layer was again extracted with 30 mL ethyl acetate or diethyl ether, the combined organic layers were dried over Na2SO4, the solvent was evaporated and the residue was purified by flash column chromatography (isohexane/ethyl acetate 8–10:1).
Alternatively, the reaction could be carried out in a microwave reactor at 80°C for 15 minutes and 235 W, but in most cases with lower yields.
General Procedure 2 (Hydrogenation)
One mmol of the phenol ester was dissolved in 30 mL methanol and 50 mg 5% Pd on charcoal were added. The suspension was stirred for 14 h under H2 atmosphere at room temperature, the catalyst was filtered off (over silica gel 60), and the solvent was evaporated. If necessary, the residue was purified by flash column chromatography.
General Procedure 3 (Ester Hydrolysis)
An amount of 0.5 mmol of the ester were dissolved in 30 mL methanolic K2CO3 solution (5%) and refluxed for 24 h. The solvent was evaporated, the residue dissolved in aqueous HCl (10%), and extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 30 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over Na2SO4 and the solvent was evaporated. If necessary, the residue was purified by flash column chromatography.
Methyl (E)-4-[(clnnamoyl)oxy]-3-nltrobenzoate (3a)
The compound was prepared from 230 mg (1.55 mmol) cinnamic acid and 200 mg of 2 (1.01 mmol) according to “General Procedure 1” to give 155 mg (47%) as a pale yellow oil. IR (NaCl, film), v, cm-1: 3063, 2951, 2359, 2329, 1724, 1633, 1615, 1537, 1315, 1288, 1188, 1111, 981, 763, 702. MS (CI, m/z, %): 328 (M++1, 2), 131 (100). MS (EI, m/z, %): 131 (100), 103 (36), 77 (18). HR-MS: Calcd. for C17H13NO6: 327.0743 g/mol. Found: 327.0731 g/mol. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 3.97 (s, 3 H, OCH3), 6.55 (m, 2 H, aromat. CH, -CH=), 7.43 (m, 3 H, 2 aromat. CH), 7.60 (m, 3 H, 3 aromat. CH), 7.87 (m, 1 H, -CH=), 8.32 (dd, J = 2.1 Hz, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H, 6-H), 8.73 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1 H, 2-H). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 52.9 (OCH3), 115.4 (-CH=), 125.6 (aromat. CH), 127.1 (aromat. CH), 128.6 (2 aromat. CH), 129.1 (2 aromat. CH), 131.3 (aromat. CH), 133.7 (quat. C), 135.3 (aromat. CH), 141.9 (quat. C), 147.4 (quat. C), 148.9 (=CH-), 162.5 (quat. C), 163.8 (CO), 164.7 (CO).
Methyl 4-[(6-bromohexanoyl)oxy]-3-nltrobenzoate (3b)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 1” from 276 mg (1.5 mmol) 6-bromohexanoic acid and 197 mg (1.0 mmol) of 2 to give 306 mg (82%) of 3g as a pale yellow solid. IR (NaCl, film), v, cm-1: 2952, 2867, 1775, 1731, 1616, 1540, 1351, 1288, 1254, 1102. HR-MS: Calcd. for C14H16BrNO6: 373.0161 g/mol. Found: 373.0155 g/mol. MS (CI, m/z, %): 179 (C6H11BrO, 42), 177 (C6H11BrO, 40), 115 (100). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 1.60 (m, 2 H, CH2), 1.82 (tt, J = 7.4 Hz, J = 7.4 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 1.94 (tt, J = 6.8 Hz, J = 6.9 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 2.70 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.45 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.98 (s, 3 H, OCH3), 7.34 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1 H, 5-H), 8.32 (dd, J = 2.1 Hz, J = 8.5 Hz, 1 H, 6-H), 8.75 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1 H, 2-H). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 23.6 (CH2), 27.4 (CH2), 32.2 (CH2), 33.4 (CH2), 33.7 (CH2), 52.9 (OCH3), 125.5 (aromat. CH), 127.2 (aromat. CH), 128.8 (quat. C), 135.4 (aromat. CH), 141.6 (quat. C), 147.3 (quat. C), 164.4 (CO), 170.5 (CO).
Methyl 4-[(cyclohexylacetyl)oxy]-3-nltrobenzoate (3c)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 1” from 628 mg (4.42 mmol) cyclohexyl ethanoic acid and 800 mg (4.42 mmol) of 2 to give 1.215 g (86%) of 3c as a pale yellow solid of mp 40°C. IR (NaCl, film), v, cm-1: 2926, 2853, 1775, 1732, 1617, 1541, 1448, 1437, 1352, 1288, 1253, 1097, 924, 823, 769. HR-MS: Calcd. for C16H19NO6: 321.1212 g/mol. Found: 321.1213 g/mol. MS (El, m/z, %): 321 (M+, 0.18), 290 (0.24), 197 (3.6), 181 (4), 166 (13), 125 (100). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 1.00–1.89 (m, 10 H, 5 CH2), 1.94 (m, 1 H, CH), 2.54 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.98 (s, 3 H, CH3), 7.32 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 8.30 (dd, J = 2.0 Hz, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 8.72 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH). 13C-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 25.9 (2 CH2), 26.0 (CH2), 33.0 (2 CH2), 34.4 (CH), 41.6 (CH2), 52.9 (OCH3), 125.60 (aromat. CH), 127.1 (aromat. CH), 128.7 (quat. C), 135.29 (aromat. CH), 141.8 (quat. C), 147.4 (quat. C), 164.4 (CO), 170.1 (CO).
Methyl 4-[(bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-ylacetyl)oxy]-3-nitrobenzoate (3d)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 1” from 230 mg (1.5 mmol) 2-norbornylethanoic acid and 197 mg (1 mmol) of 2 to give 270 mg (81%) of 3d as a pale yellow solid. IR (NaCl, film), v, cm-1: 2952, 2871, 1777, 1731, 1616, 1540, 1437, 1540, 1437, 1351, 1288, 1254, 1091, 918. HR-MS: Calcd. for C17H19NO6: 333.1212 g/mol. Found: 333.1213 g/mol. MS (El, m/z, %): 333 (M+, 0.2), 181 (3), 166 (12), 137 (89), 109 (100). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 1.26–1.54 (m, 8 H, 4 CH2), 2.04 (m, 1 H, CH), 2.11 (m, 1 H, CH), 2.28 (m, 1 H, CH), 2.49 (dd, J = 7.8 Hz, J = 16.1 Hz, 1 H, CH2), 2.64 (dd, J = 7.7 Hz, J = 16.1 Hz, 1 H, CH2), 3.98 (s, 3 H, OCH3), 7.32 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H, 5-H), 8.31 (ddd, J = 0.9 Hz, J = 2.0 Hz, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H, 6-H), 8.74 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1 H, 2-H). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 28.6 (CH2), 29.8 (CH2), 35.4 (CH2), 36.9 (CH), 37.9 (CH2), 38.0 (CH), 41.0 (CH2); 41.3 (CH), 53.0 (CH3), 125.7 (aromat. CH), 127.3 (aromat. CH), 128.7 (quat. C), 135.4 (aromat. CH), 141.7 (quat. C), 147.4 (quat. C), 164.4 (CO), 170.2 (CO).
Methyl 3-nltro-4-(octadecanoyloxy)benzoate (3e)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 1” from 620 mg (2.0 mmol) octadecanoyl chloride and 300 mg (1.5 mmol) of 2 to give 730 mg (100%) of 3e as a white solid of mp 70°C. HR-MS: Calcd. for C26H41NO6: 463.293389 g/mol. Found: 463.2932 g/mol. MS (El, m/z, %): 463 (M+, 0,12), 284 (8), 267 (100), 181 (48), 166 (32). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 0.88 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3 H, CH3), 1.26 (m, 26 H, 13 CH2), 1.42 (m, 2 H, CH2), 1.65 (m, 2 H, CH2), 1.77 (m, 2 H, CH2), 2.66 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.98 (s, 3 H, OCH3), 7.33 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 8.31 (dd, J = 2.1 Hz, J = 8.5 Hz, 1 H, 2-H), 8.74 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 14.2 (CH3), 22.7 (CH2), 24.4 (CH2), 29.2 (CH2), 29.4 (CH2), 29.4 (CH2), 29.6 (CH2), 29.7 (CH2), 29.7 (CH2), 29.7 (CH2), 29.7 (5 CH2), 31.9 (CH2), 34.0 (CH2), 52.9 (CH3O), 125.6 (aromat. CH), 127.2 (aromat. CH), 128.8 (quat. C), 135.4 (aromat. CH), 135.4 (quat. C), 147.5 (quat. C), 164.4 (CO), 171.0 (CO).
Methyl 3-nltro-4-(undec-10-enoyloxy)benzoate (3f)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 1” from 500 mg (2.7 mmol) undec-10-enoic acid and 355 mg (1.8 mmol) of 2 to give 425 mg (65%) of 3f as a pale yellow solid. MS (CI, m/z, %): 364 (M++1, 2), 167 (100). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 1.29 (m, 10 H, 5 CH2), 1.63 (m, 2 H, CH2), 2.04 (m, 2 H, CH2), 2.35 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.95 (s, 3 H, OCH3), 4.96 (m, 2 H, =CH2), 5.81 (ddt, J = 6.7 Hz, J = 10.4 Hz, J = 17.0 Hz, 1 H, =CH-), 7.23 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 8.24 (dd, J = 2.1 Hz, J = 8.8 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 8.83 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 24.6 (CH2), 28.8 (CH2), 29.0 (CH2), 29.0 (2 CH2), 29.2 (CH2), 29.2 (CH2), 33.8 (CH2), 33.9 (CH2), 52.6 (OCH3), 114.1 (=CH2), 120.2 (aromat. CH), 127.3 (aromat. CH), 137.9 (aromat. CH), 139.2 (-CH=), 158.1 (quat. C), 164.8 (CO), 179.5 (CO).
Methyl 4-(acetyloxy)-3-nitrobenzoate (3g)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 1” from 478 mg (2.0 mmol) of 2 and 234 mg (3.0 mmol) acetyl chloride to give 185 mg (41%) of 3g as a pale yellow oil. IR (KBr), v, cm-1:3269, 2955, 1724, 1626, 1583, 1540, 1435, 1329, 1288, 1182, 1143, 760. HR-MS: Calcd. for C10H9NO6: 239.0430 g/mol. Found: 239.0428 g/mol. MS (CI, m/z, %): 240 (M++1, 30), 198 (100). MS (El, m/z, %): 239 (M+, 2), 197 (70), 166 (100), 120 (26), 63 (28). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 2.41 (s, 3 H, CH3), 3.98 (s, 3 H, OCH3), 7.34 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 8.32 (dd, J = 2.2 Hz, J = 8.5 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 8.75 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 20.76 (CH3), 52.84 (OCH3), 125.55 (aromat. CH), 127.2 (aromat. CH), 128.9 (quat. C), 135.4 (aromat. CH), 147.3 (quat. C), 164.3 (CO), 168.0 (CO).
4-(Methoxycarbonyl)-2-nitrophenyl naphthalene-2-carboxylate (3h)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 1” from 300 mg (1.57 mmol) 2-naphthoyl chloride and 210 mg (1.06 mmol) 2 to give 506 mg (92%) of 3h as colourless crystals of mp 144°C. IR (KBr), v, cm-1: 1737, 1612, 1537, 1280, 1255, 1222, 1193, 1046, 757. MS (CI, m/z, %): = 352 (M++1, 2), 173 (14), 155 (100). MS (El, m/z, %): 351 (M+, 4), 326 (8), 155 (100), 127 (52). HR-MS: Calcd for C19H13NO6: 351.0743 g/mol. Found: 351.0757 g/mol. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 4.00 (s, 3 H, CH3), 7.55 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1 H, CH), 7.60 (dd, J = 8.2 Hz, J = 8.2 Hz, 1 H, CH), 7.66 (dd, J = 8.2 Hz, J = 8.2 Hz, 1 H, CH), 7.93 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1 H, CH), 7.97 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1 H, CH), 8.02 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1 H, CH), 8.16 (dd, J = 1.8 Hz, J = 8.2 Hz, 1 H, CH), 8.38 (dd, J = 1.8 Hz, J = 8.2 Hz, 1 H, CH), 8.48 (m, 2 H, 2 aromat. CH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 52.87 (CH3), 125.3 (aromat. CH), 125.7 (aromat. CH), 125.7 (quat. C), 127.0 (aromat. CH), 127.3 (aromat. CH) 127.9 (aromat. CH), 128.7 (CH), 128.7 (quat. arom. C), 129.1 (CH), 129.6 (CH), 132.4 (quat. arom. C), 132.9 (aromat. CH), 135.4 (aromat. CH), 136.2 (quat. C), 140.0 (quat. C), 147.7 (quat. C), 164.1 (CO), 164.4 (CO).
Methyl 4-hydroxy-3-[(3-phenylpropanoyl)amlno]benzoate (4a)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 2” from 150 mg (0.46 mmol) 3a to give 120 mg (87%) of 4a as colourless crystals of mp 152°C. IR (NaCl, film), v, cm-1: 3412, 3026, 2958, 2720, 1899, 1708, 1654, 1595, 1543, 1450, 1437, 1293, 1275, 1126, 766, 697, 631. HR-MS: Calcd. for C17H17NO4: 299.1158. Found: 299.1162. MS (CI, m/z, %): 300 (M++1, 100), 167 (12). MS (El, m/z, %): 299 (M+, 10), 167 (100), 136 (22), 105 (24), 91 (46). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 2.78 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.07 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.83 (s, 3 H, OCH3), 6.99 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 7.24 (m, 3 H, 3 aromat. CH), 7.31 (m, 2 H, 2 aromat. CH), 7.76 (m, 2 H, 2 aromat. CH), 8.16 (s, 1 H, NH), 10.02 (s, 1 H, OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 31.7 (CH2), 38.7 (CH2), 52.1 (OCH3), 119.9 (aromat. CH), 122.0 (quat. C), 124.2 (aromat. CH), 125.5 (quat. C), 126.8 (aromat. CH), 128.3 (2 aromat. CH), 128.9 (aromat. CH), 128.9 (2 aromat. CH), 139.8 (quat. C), 153.4 (quat. C), 166.6 (CO), 173.3 (CO).
Methyl 3-[(6-bromohexanoyl)amlno]-4-hydroxybenzoate (4b)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 2” from 330 mg (0.88 mmol) 3b to give 150 mg (50%) of 4b as a pale brown solid of mp 132°C. IR (KBr), v, cm-1: 3406, 3066, 2954, 2856, 1703, 1667, 1610, 1593, 1433, 1447, 1433, 1273, 1125, 997, 908, 770, 642, 631. HR-MS: Calcd. for C14H18BrNO4: 343.0419. Found: 343.0392. MS (EI, m/z, %): 345 (M+, 0.75), 343 (M+, 0.74), 167 (100), 136 (19). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): δ 1.42 (m, 2 H, CH2), 1.60 (m, 2 H, CH2), 1.84 (m, 2 H, CH2), 2.42 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.55 (t, J = 6.7 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.79 (s, 3 H, OCH3), 6.94 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1 H, 5-H), 7.58 (dd, J = 2.0 Hz, J = 8.5 Hz, 1 H, 6-H), 8.52 (s, 1 H, 2-H), 9.28 (s, 1 H, NH), 10.83 (s, 1 H, OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): 22.50 (CH2), 26.5 (CH2), 27.8 (CH2), 32.6 (CH2), 35.7 (CH2), 51.7 (OCH3), 115.1 (aromat.CH), 120.14 (quat. C), 123.3 (aromat. CH), 126.2 (aromat. CH), 126.4 (quat. C), 152.2 (quat. C), 166.1 (CO), 171.8 (CO).
Methyl 3-[(cyclohexylacetyl)amino]-4-hydroxybenzoate (4c)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 2” from 211 mg (0.66 mmol) 3c to give 171 mg (89%) of 4c as a pale yellow solid of mp 165°C. IR (KBr), v, cm-1: 3288, 2922, 2851, 1712, 1623, 1591, 1549, 1450, 1297, 1234, 1131, 764. HR-MS: Calcd. for C16H21NO4: 291.1471. Found: 291.1500. MS (EI) m/z (%) = 291 (10), 167 (100). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, D3COD, TMS): 0.98-1.89 (m, 11 H, CH, 5 CH2), 2.31 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.84 (s, 3 H, OCH3), 6.89 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1 H, 5-H), 7.68 (dd, J = 2.2 Hz, J = 8.5 Hz, 1 H, 6-H), 8.41 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1 H, 2-H), 9.23 (s, 1 H, NH, only in d-DMSO), 10.93 (s, 1 H, OH, only in d-DMSO). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, D3COD, TMS): 27.3 (2 CH2), 27.30 (CH2), 34.1 (2 CH2), 37.0 (CH), 45.6 (CH2), 52.3 (OCH3), 116.6 (aromat. CH), 122.0 (quat. C), 125.5 (aromat. CH), 127.2 (quat. C), 128.6 (aromat. CH), 154.8 (quat. C), 168.5 (CO), 174.5 (CO).
Methyl 3-[(blcyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-ylacetyl)amlno]-4-hydroxybenzoate (4d)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 2” from 335 mg (1.0 mmol) 3d to give 257 mg (77%) of 4d as a pale yellow solid of mp 146°C. IR (KBr), v, cm-1: 3407, 2949, 2867, 1708, 1660, 1611, 1595, 1541, 1449, 1434, 1288, 1280, 1262, 1125, 767. HR-MS: Calcd. for C17H21NO4: 303.147059. Found: 303.1478. MS (EI) m/z (%) = 303 (M+, 8), 167 (100), 136 (16), 112 (20). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, d-acetone, TMS): 1.02-1.58 (m, 10 H, 2 CH, 4 CH2), 1.96-2.23 (m, 1 H, CH2), 2.35 (dd, J = 7.9 Hz, J = 14.3 Hz, 1 H, CH2), 2.48 (dd, J = 7.9 Hz, J = 14.4 Hz, 1 H, CH2), 3.81 (s, 3 H, OCH3), 6.95 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H, 5-H), 7.65 (dd, J = 2.0 Hz, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H, 6-H), 8.42 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1 H, 2-H), 9.17 (s, 1 H, OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, d-acetone, TMS): 29.1 (CH2), 30.3 (CH2), 35.5 (CH2), 37.3 (CH), 38.4 (CH2), 39.7 CH), 41.6 (CH), 43.9 (CH2), 51.7 (OCH3), 117.4 (aromat. CH), 121.2 (quat. C), 123.3 (aromat. CH), 127.5 (aromat. CH), 127.6 (quat. C), 154.0 (quat. C), 166.8 (CO), 172.8 (CO).
Methyl 4-hydroxy-3-(octadecanoylamlno)benzoate (4e)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 2” from 390 mg (0.84 mmol) 3e to give 190 mg (52%) of 4e as a pale brown solid. MS (CI, m/z, %): 434 (M++1, 54), 326 (74), 312 (100), 285 (46), 267 (46), 168 (98). MS (El, m/z, %): 433 (M+, 4), 167 (100). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): δ 0.86 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, CH3), 1.24 (m, 28 H, 14 CH2), 1.59 (m, 2 H, CH2), 2.40 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.80 (s, 3 H, OCH3), 4.08 (s, 1 H, NH), 6.94 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 7.59 (dd, J = 2.0 Hz, J = 8.5 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 8.49 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): 14.0 (CH3), 22.3 (CH2), 25.4 (CH2), 28.8 (CH2), 28.9 (CH2), 29.0 (CH2), 29.1 (CH2), 29.2 (CH2), 29.2 (CH2), 29.2 (CH2), 29.24 (5 CH2), 31.49 (CH2), 36.14 (CH2), 51.6 (OCH3), 115.3 (aromat. CH), 120.6 (quat. C), 123.3 (aromat. CH), 126.3 (aromat. CH), 152.0 (quat. C), 166.2 (CO), 172.2 (CO).
Methyl 4-hydroxy-3-(undecanoylamino)benzoate (41)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 2” from 250 mg (0.69 mmol) 3e to give 190 mg (82%) of 4e as a pale yellow solid. HR-MS: Calcd. for C19H29NO4: 335.209659 g/mol. Found: 335.2097 g/mol. MS (CI, m/z, %): 336 (M++1, 100), 167 (20). MS (EI, m/z, %): 335 (M+, 2), 167 (100). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 0.86 (t, J = 6.7 Hz, 3 H, CH3), 1.23 (m, 14 H, 7 CH2), 1.61 (m, 2 H, CH2), 2.32 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.84 (s, 3 H, OCH3), 6.98 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 7.74 (dd, J = 2.0 Hz, J = 8.5 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 7.85 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 8.32 (s, 1 H, NH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 14.1 (CH3), 22.6 (CH2), 24.8 (CH2), 25.8 (CH2), 29.2 (CH2), 29.3 (CH2), 29.4 (CH2), 31.8 (CH2), 33.99 (CH2), 36.8 (CH2), 52.0 (OCH3), 119.2 (aromat. CH), 124.0 (aromat. CH), 125.8 (quat. C), 128.4 (aromat. CH), 153.1 (quat. C), 166.8 (quat. C), 174.4 (CO), 179.5 (CO).
Methyl 3-(acetylamlno)-4-hydroxybenzoate (4g)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 2” from 900 mg (4.56 mmol) 3g to give 710 mg (74%) of 4d as pale brown crystals of mp 176°C. IR (NaCl, film), v, cm-1: 3278, 3092, 2965, 2721, 1907, 1714, 1592, 1554, 1504, 1425, 1382, 1282, 1231, 1129, 1095, 988, 902, 832, 763. HR-MS: Calcd. for C10H11NO4: 209.0688 g/mol Found: 209.0667 g/mol. MS (CI, m/z, %): 210 (M++1, 100). MS (EI) m/z (%) = 193 (14), 167 (32), 79 (32). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 2.10 (s, 3 H, COCH3), 3.78 (s, 3 H, OCH3), 6.94 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H, CH), 7.58 (dd, J = 2.0 Hz, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H, CH), 8.48 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1 H, CH), 9.32 (s, 1 H, NH), 10.81 (s, 1 H, OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): δ (ppm) = 23.6 (CH3), 51.6 (OCH3), 116.0 (aromat. CH), 120.0 (quat. C), 123.2 (aromat. CH), 126.1 (aromat. CH), 126.2 (quat. C), 152.1 (quat. C), 166.0 (CO), 168.9 (CO). The compound is also described in the literature [19].
4-Hydroxy-3-[(3-phenylpropanoyl)amino]benzoic acid (5a)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 3” from 140 mg (0.46 mmol) of 4a to give 48 mg (37%) of 5a as a pale yellow oil. IR (NaCl, film), v, cm-1: 3423, 2360, 2342, 1709, 1665, 1597, 1547, 1439, 1383, 1274, 784, 768, 668. MS (CI, m/z, %): 286 (M++1, 4), 272 (12), 165 (20), 151 (100), 139 (88), 133 (94), 120 (58), 102 (62). MS (El, m/z, %): 285 (M+, 2), 167 (14), 139 (22), 104 (26), 91 (100). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 2.72 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 2.90 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 6.90 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, 5-H), 7.19 (m, 3 H, 3 aromat. CH), 7.28 (m, 2 H, 2 aromat. CH), 7.53 (dd, J = 2.0 Hz J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, 6-H), 8.43 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1 H, 2-H), 9.34 (s, 1 H, OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 30.9 (CH2), 37.4 (CH2), 114.9 (aromat. CH), 123.3 (aromat. CH), 125.8 (aromat. CH), 126.2 (aromat. CH), 128.1 (2 aromat. CH), 128.2 (2 aromat. CH), 140.8 (quat. C), 141.1 (quat. C), 152.2 (quat. C), 167.4 (quat. C), 170.8 (CO), 173.8 (CO).
3-(Acetylamlno)-4-hydroxybenzolc acid (5g)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 3” from 113 mg (0.54 mmol) of 4d to give 63 mg (60%) of 5d as a brown solid. Mp 239°C. IR (KBr, film), v, cm-1: 3423, 2964, 1673, 1596, 1543, 1458, 1411, 1282, 1242, 1123, 1098, 969, 836, 629, 585, 549. MS (EI, m/z, %): 195 (M+, 20), 153 (100), 136 (28), 109 (50), 80 (16). HR-MS: Calcd. for C9H9NO4: 195.053159 g/mol. Found: 195.0535 g/mol. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): δ 2.09 (s, 3 H, CH3), 6.90 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H, 5-H), 7.54 (dd, J = 2.0 Hz, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H, 6-H), 8.40 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1 H, 2-H), 9.28 (s, 1 H, NH), 10.64 (s, 1 H, OH), 12.42 (s, 1 H, COOH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 23.7 (CH3), 115.0 (aromat. CH), 121.3 (quat. C), 123.7 (aromat. CH), 126.2 (quat. C), 126.4 (aromat. CH), 151.9 (quat. C), 167.2 (CO), 169.0 (CO). The compound is described in the literature [20].
3-Hydroxy-2-nitrophenyl (E)-cinnamate (7a)
The compound was prepared according “General Procedure 2” (MW conditions) from 296 mg (2 mmol) cinnamic acid and 465 mg (3 mmol) 2-nitroresorcinol to give 215 mg (38%) of 7a as a yellow solid of mp 95°C. IR (NaCl, film), v, cm-1: 3425, 1740, 1636, 1613, 1585, 1541, 1449, 1346, 1221, 1196, 119, 1033, 762. ESI-MS (CI, m/z, %): 283 (10), 2 (100), 131 (15). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 6.67 (d, J = 15.7 Hz, 1 H, -CH=), 6.81 (dd, J = 1.2 Hz, J = 8.1 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 7.09 (dd, J = 1.2 Hz, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H, aromat. CH), 7.44 (m, 3 H, 3 aromat. CH), 7.53 (dd, J = 8.1 Hz, J = 8.6 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 7.61 (m, 2 H, 2 aromat. CH), 7.91 (d, J = 15.7 Hz, 1 H, -CH=), 10.39 (s, 1 H, OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 115.9 (CH), 115.9 (CH), 117.4 (CH), 128.5 (2 aromat. CH), 128.6 (quat. C), 129.0 (2 aromat. CH), 131.1 (aromat. CH), 133.8 (quat. C), 135.5 (aromat. CH), 145.5 (quat. C), 148.2 (-CH=), 155.5 (quat. C), 164.5 (CO).
3-Hydroxy-2-nitrophenyl 6-bromohexanoate (7b)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 1” from 0.982 g (5.0 mmol) 6-bromohexanoic acid and 1.53 g (9.9 mmol) 2-nitroresorcinol to give 0.624 g (37%) of 7b. IR (KBr), v, cm-1: 3374, 2940, 2866, 1771, 1616, 1586, 1541, 1461, 1353, 1190, 1108, 1056, 858, 808, 688. MS (EI, m/z, %): 179 (18), 177 (20), 155 (10), 97 (24), 69 (100), 60 (63), 55 (52). MS (CI, m/z, %): 179 (78), 177 (78), 122 (25), 115 (100). HR-MS: Calcd. for C12H14BrNO5: 331.0055 g/mol. Found: 331.0052 g/mol. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 1.60 (m, 2 H, CH2), 1.80 (m, 2 H, CH2), 1.93 (m, 2 H, CH2), 2.68 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 3.44 (t, J = 6.7 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 6.71 (dd, J = 1.4 Hz, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, 4-H), 7.07 (dd, J? = 8.6 Hz, J = 1.4 Hz, 1 H, 6-H), 7.51 (dd, J = 8.0 Hz, J = 8.6 Hz, 1 H, 5-H), 10.40 (s, 1 H, OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 23.5 (CH2), 27.5 (CH2), 32.3 (CH2), 33.4 (CH2), 33.8 (CH2), 115.9 (aromat. CH), 117.6 (aromat. CH), 129.0 (quat. C), 135.9 (aromat. CH), 145.6 (quat. C), 156.0 (quat. C), 171.2 (CO).
3-Hydroxy-2-nitrophenyl cyclohexylacetate (7c)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 1” from 0.717 g (5.05 mmol) 2-cyclohexylacetic acid and 0.7810 (5.04 mmol) 2-nitroresorcinol to give 312 mg (20%) of 7c. IR (NaCl, film), v, cm-1: 2925, 2852, 1772, 1616, 1586, 1540, 1462, 1450, 1353, 1211, 1101, 1057, 1027, 872, 858, 808, 687. MS (CI, m/z, %): 157 (9), 143 (23), 125 (100). MS (EI, m/z, %): 279 (M+, 1), 155 (4), 139 (3), 125 (100). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 1.23 (m, 6 H, 3 CH2), 1.68 (m, 4 H, 2 CH2), 1.93 (m, 1 H, CH), 2.52 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 6.69 (dd, J = 1.4 Hz, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, 4-H), 7.06 (dd, J = 1.4 Hz, J = 8.6 Hz, 1 H, 6-H), 7.50 (dd, J = 8.0 Hz, J = 8.6 Hz, 1 H, 5-H), 10.35 (s, 1 H, OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 26.0 (2 CH2), 26.1 (CH2), 33.0 (2 CH2), 34.4 (CH), 41.6 (CH2), 116.0 (aromat CH), 117.4 (aromat CH), 135.8 (aromat CH), 145.7 (quat. C), 155.9 (quat. C), 170.8 (CO).
3-Hydroxy-2-nitrophenyl bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-ylacetate (7d)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 1” from 0.783 g (5.6 mmol) norbornylacetic acid and 1.472 g (9.5 mmol) 2-nitroresorcinol to give 0.392 g (27%) of 7d as a pale yellow solid. IR (KBr), v, cm-1: 3356, 2951, 2870, 1773, 1617, 1586, 1541, 1458, 1353, 1208, 1169, 1120, 1103, 1057, 1031, 912, 856, 807, 687. HR-MS: Calcd. for C15H17NO5: 291.1107 g/mol Found: 291.1107 g/mol. MS (EI, m/z, %): 291 (M+, 8), 137 (100), 109 (90), 95 (60), 67 (62). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 1.18-1.62 (m, 9 H, CH, 4 CH2), 2.11 (m, 1 H, CH2), 2.27 (m, 1 H, CH2), 2.47 (dd, J = 7.8 Hz, J = 16.0 Hz, 1 H, CH2), 2.62 (dd, J = 7.8 Hz, J = 16.0 Hz, 1 H, CH2), 6.69 (dd, J = 1.4 Hz, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, 4-H), 7.06 (dd, J = 1.4 Hz, J = 8.6 Hz, 1 H, 6-H), 7.5 (dd, J = 8.0 Hz, J = 8.6 Hz, 1 H, 5-H), 10.37 (s, 1 H, OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 28.5 (CH2), 29.7 (CH2), 35.3 (CH2), 36.8 (CH), 37.9 (CH2), 37.9 (CH), 40.9 (CH2), 41.2 (CH), 117.0 (CH), 117.4 (CH), 135.8 (CH), 145.7 (quat. C), 155.9 (quat. C), 170.8 (CO).
3-Hydroxy-2-nitrophenyl octadecanoate (7e)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 1” from 302 mg (1 mmol) octadecanoyl chloride and 310 mg (2 mmol) 2-nitroresorcinol to give 75 mg (18%) of 7e as an orange solid of mp 58°C. IR (KBr), v, cm-1: 2954, 2923, 2849, 1764, 1617, 1546, 1469, 1349, 1140, 1122, 1055, 814, 691. HR-MS: Calcd. for C24H38NO5: 420.274999 g/mol. Found: 420.2755 g/mol. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 0.88 (t, J = 6.5 Hz, 3 H, CH3), 1.26 (m, 28 H, 14 CH2), 1.77 (tt, J = 7.3 Hz, J = 7.3 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 2.65 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 6.70 (dd, J = 1.3 Hz, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 7.07 (dd, J = 1.3 Hz, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 7.51 (dd, J = 8.0 Hz, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 10.42 (s, 1 H, OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 14.1 (CH3), 22.7 (CH2), 24.4 (CH2), 29.1 (CH2), 29.2 (CH2), 29.4 (CH2), 29.4 (CH2), 29.6 (CH2), 29.6 (CH2), 29.7 (CH2), 29.7 (5 CH2), 31.9 (CH2), 34.0 (CH2), 115.9 (aromat. CH), 117.5 (aromat. CH), 124.1 (quat. C), 135.8 (aromat. CH), 145.7 (quat. C), 155.9 (quat. C), 171.5 (CO).
3-Hydroxy-2-nitrophenyl undec-10-enoate (7f)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 1” from 368 mg (2 mmol) 10-undecenoic acid and 310 mg (2 mmol) 2-nitroresorcinol to give 165 mg (26%) 7f as a pale yellow oil. IR (KBr), v, cm-1: 2927, 2855, 1774, 1640, 1617, 1587, 1541, 1463, 1357, 1196, 1106, 1057, 1030, 910, 857. HR-MS (M+-1): Calcd. for C17H22NO5: 320.1498 g/mol. Found: 320.1505 g/mol. MS (EI, m/z, %): 274 (1), 183 (7), 167 (15), 149 (100), 139 (30), 107 (50). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 1.24-1.44 (m, 10 H, 5 CH2), 1.73 (m, 2 H, CH2), 2.04 (m, 2 H, CH2), 2.57 (t, J = 7.9 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 4.93 (m, 1 H, =CH2), 4.99 (m, 1 H, =CH2), 5.81 (ddt, J = 6.7 Hz, J = 10.4 Hz, J = 16.9 Hz, 1 H, -CH=), 6.69 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 7.01 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 7.38 (dd, J = 8.3 Hz, J = 8.3 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 10.49 (s, 1 H, OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 24.5 (CH2), 28.8 (CH2), 28.9 (CH2), 29.0 (CH2), 29.1 (CH2), 29.2 (CH2), 33.7 (CH2), 33.9 (CH2), 114.2 (H2C=), 114.7 (aromat. CH), 116.2 (aromat. CH), 131.9 (quat. C), 133.1 (aromat. CH), 139.1 (-CH=), 144.3 (quat. C), 153.1 (quat. C), 171.2 (CO).
3-Hydroxy-2-nitrophenyl 3-methylbut-2-enoate (7g)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 1” from 0.515 g (5.2 mmol) 3,3-dimethylacrylic acid and 0.775 g (5 mmol) 2-nitroresorcinol to give 0.095 g (8%) of 7g. IR (KBr), v, cm-1: 3224, 2979, 2935, 1739, 1693, 1649, 1614, 1585, 1537, 1442, 1348, 1115, 1057, 937, 818, 679. MS (CI, m/z, %): 302 (14), 288 (26), 122 (60), 115 (10), 101 (100). MS (EI, m/z, %): 146 (84), 83 (100), 55 (40). 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 2.03 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 3 H, CH3), 2.22 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 3 H, CH3), 5.98 (t, J = 1.2 Hz, 1 H, =CH), 6.73 (dd, J = 1.4 Hz, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, 4-H), 7.05 (dd, J = 1.4 Hz, J = 8.6 Hz, 1 H, 6-H), 7.52 (dd, J = 8.0 Hz, J = 8.6 Hz, 1 H, 5-H), 10.35 (s, 1 H, OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 20.7 (CH3), 27.8 (CH3), 114.2 (-CH=), 116.1 (aromat. CH), 117.1 (aromat. CH), 121.4 (quat. C), 135.7 (aromat. CH), 145.8 (quat. C), 155.7 (quat. C), 162.4 (quat. C), 163.7 (CO).
3-Hydroxy-2-nitrophenyl benzoate (7h)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 1” from 0.260 g (1.86 mmol) benzoyl chloride and 0.320 g (2.1 mmol) 2-nitroresorcinol to give 0.273 g (57%) of 7h as a yellow solid. IR (KBr), v, cm-1: 3230, 2929, 2358, 1982, 1739, 1614, 1579, 1535, 1265, 1228, 1054, 702. HR-MS: Calcd. for C13H9NO5: 259.0481. Found: 259.0480. MS (CI): m/z (%) = 123 (88), 122 (90), 105 (100). MS (EI, m/z, %): 122 (30), 105 (100), 93 (10), 77 (60), 51 (27). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ 6.86 (dd, J = 1,4 Hz, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, 6-H), 7.13 (dd, J = 1.4 Hz, J = 8.6 Hz, 1 H, 4-H) 7.55 (m, 3 H, 3’-H, 4’-H, 5’-H), 7.68 (dd, J = 8.0 Hz, J = 8,6 Hz, 1 H, 5-H), 8.12 (dd, J = 1.4 Hz, J = 8.0 Hz, 2 H, 2’-H, 6’-H), 10.43 (s, 1 H, OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): 116.1 (aromat. CH), 117.6 (aromat. CH), 128.5 (quat. C), 128.6 (quat. C), 128.7 (2 aromat. CH), 130.5 (2 aromat. CH), 134.2 (aromat. CH), 135.8 (aromat. CH), 145.9 (quat. C), 156.0 (quat. C), 164.5 (CO).
N-(2, 6-dihydroxyphenyl)-3-phenylpropanamide (8a)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 2” from 120 mg (0.42 mmol) 7a to give 78 mg (72%) of 8a as a dark brown oil. IR (KBr), v, cm-1: 3288, 2925, 1707, 1637, 1601, 1533, 1341, 1266, 1036, 778. HR-MS (M+-1): Calcd. for C15H14NO3: 256.0974 g/mol. Found: 256.0977 g/mol. MS (EI, m/z, %): 257 (M+, 7), 125 (100). 1 H-NMR (400 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): δ 2.80 (t, J = 8.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 2.97 (t, J = 8.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 6.39 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2 H, 2 aromat. CH), 6.87 (t, J = 8.2 Hz, aromat. CH), 7.14–7.22 (m, 5 H, 5 aromat. CH), 9.37 (s, 2 H, 2 OH), 9.40 (s, 1 H, NH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): 31.1 (CH2), 36.8 (CH2), 107.7 (2 aromat. CH). 114.2 (quat. C), 125.7 (aromat. CH), 126.1 (aromat. CH), 128.0 (2 aromat. CH), 128.0 (2 aromat. CH), 140.7 (quat. C), 151.0 (2 quat. C), 172.5 (CO).
6-Bromo-N-(2, 6-dihydroxyphenyl)hexanamide (8b)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 2” from 0.203 g (0.61 mmol) 7b to give 0.159 g (86%) of 8b. IR (KBr), v, cm-1: 3289, 2936, 2864, 1709, 1640, 1600, 1537, 1532, 1475, 1343, 1267, 1036, 779, 719, 637. HR-MS: Calcd. for C12H16BrNO3: 301.0314 g/mol. Found: 301.0311 g/mol. MS (CI, m/z, %): 304 (84), 302 (M++1, 92), 224 (94), 222 (70),134 (95), 126 (100), 125 (75), 115 (43) MS (EI, m/z, %): 303 (2), 301 ([M]+, 2), 125 (100), 69 (17). 1 H-NMR (400 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): δ 1.55 (m, 2 H, CH2), 1.75 (m, 2 H, CH2), 1.92 (m, 2 H, CH2), 2.55 (m, 2 H, CH2), 3.46 (m, 2 H, CH2), 6.44 (m, 2 H, 3-H, 5-H), 6.88 (m, 1 H, 4-H), 8.95 (s, 2 H, OH), 9.54 (s, 1 H, OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): 23.7 (CH2), 26.2 (CH2), 31.1 (CH2), 32.7 (CH2), 34.6 (CH2), 107.3 (CH), 113.7 (quat. C), 125.2 (CH), 149.0 (quat. C), 172.4 (quat. C).
2-Cyclohexyl-N-(2, 6-dihydroxyphenyl)acetamide (8c)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 2” from 232 mg (0.83 mmol) 7c to give 184 mg (89%) of 8c as a pale yellow solid. IR (KBr), v, cm-1: 3251, 2927, 1609, 1542, 1473, 1339, 1279, 1261, 1038, 778. HR-MS: Calcd. for C14H19NO3: 249.136494 g/mol. Found: 249.1369 g/mol. MS (CI, m/z, %): 250 (M++1, 100), 125 (58). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): δ 0.94–1.81 (m, 11 H, CH, 5 CH2), 2.31 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 6.35 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2 H, 2 aromat. CH), 6.87 (t, J = 8.3 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 9.39 (s, 2 H, 2 OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): 25.7 (CH2), 25.9 (2 CH2), 35.1 (CH), 3.41 (2 CH2), 42.9 (CH2), 107.7 (2 aromat. CH), 114.3 (quat. C), 126.6 (aromat. CH), 151.7 (2 quat. C), 172.6 (CO).
2-(Bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-yl)-N-(2, 6-dihydroxyphenyl)acetamide (8d)
The compound was prepared from 0.209 g (0.7 mmol) of 7d according to “General Procedure 2” to give 159 mg (85%) of 8d. IR (NaCl, film), v, cm-1: 3181, 2949, 2869, 2361, 1721, 1633, 1597, 1531, 1475, 1455, 1345, 1267, 1194, 1038, 778, 718. HR-MS: Calcd. for C16H15NO4: 261.1365 g/mol. Found: 261.1368 g/mol. MS (CI, m/z, %): 262 (M++1, 100), 248, (30), 210 (28), 126 (45), 125 (42). MS (EI, m/z, %): 261 (M+, 8), 125 (100), 95 (15), 67 (24). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): δ 1.11 (m, 4 H, 2 CH2), 1.43 (m, 4 H, 2 CH2), 1.88 (m, 1 H, CH), 2.04 (m, 1 H, CH), 2.19 (m, 1 H, CH), 2.28 (dd, J = 7.7 Hz, J = 13.8 Hz, 1 H, CH2), 2.39 (dd, J = 8.0 Hz, J = 13.8 Hz, 1 H, CH2), 6.35 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2 H, 3-H, 5-H), 6.87 (t, J = 8.1 Hz, 1 H, 4-H), 9.36 (s, 2 H, OH), 9.40 (s, 1 H, NH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): 36.2 (CH), 42.0 (CH2), 107.7 (2 aromat. CH), 114.3 (quat. C), 126.6 (aromat. CH), 151.8 (2 quat. C), 172.7 (CO).
N-(2, 6-dihydroxyphenyl)octadecanamide (8e)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 2” from 100 mg (0.24 mmol) of 7e to give 65 mg (69%) of 8e as a brown solid of mp 98°C. IR (KBr), v, cm-1: 3377, 3318, 2919, 2848, 1641, 1606, 1537, 1471, 1354, 1259, 1168, 1037, 972, 815, 772, 719, 656. HR-MS: Calcd. for C24H42NO3: 392.3165 g/mol. Found: 392.3158 g/mol. MS (CI, m/z, %): 392 (M++1, 100), 331 (12), 279 (6), 126 (5). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): δ 0.86 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 3 H, CH3), 1.24 (m, 26 H, 13 CH2), 1.59 (m, 2 H, CH2), 2.43 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 6.36 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2 H, 2 aromat. CH), 6.85 (t, J = 8.3 Hz, aromat. CH). 9.33 (s, 1 H, NH), 9.38 (s, 2 H, 2 OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): 13.4 (CH3), 21.7 (CH2), 25.0 (CH2), 28.4 (CH2), 28.54 (CH2), 28.57 (CH2), 28.59 (CH2), 28.6 (6 CH2), 28.7 (CH2), 30.9 (CH2), 40.5 (CH2), 107.27 (2 aromat. CH), 115.5 (quat. C), 125.9 (aromat. CH), 151.1 (2 quat. C), 173.0 (CO).
N-(2, 6-Dihydroxyphenyl)undecanamide (8f)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 2” from 253 mg (0.79 mmol) of 7f to give 164 mg (71%) of 8f as a dark brown solid. IR (KBr), v, cm-1: 2925, 2854, 1709, 1602, 1532, 1468, 1347, 1268, 1038, 778. HR-MS [M+-1]: Calcd. for C17H26NO3: 292.1913 g/mol. Found: 292.1918 g/mol. MS (EI, m/z, %): 293 (M+, 3), 125 (100), 107 4). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): δ 0.86 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3 H, CH3), 1.14 – 1.61 (m, 16 H, 8 CH2), 2.41 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2 H, CH2), 6.35 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2 H, 2 aromat. CH), 6.87 (t, J = 8.3 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 9.35 (s, 1 H, NH), 9.40 (s, 2 H, 2 OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): 14.0 (CH3), 22.1 (CH2), 25.4 (CH2), 28.5 (CH2), 28.7 (CH2), 28.8 (CH2), 28.9(CH2), 29.0 (CH2), 33.6 (CH2), 39.6 (CH2), 107.6 (2 aromat. CH), 126.5 (aromat. CH), 114.2 (quat. C), 151.8 (2 quat. C), 173.4 (CO).
N-(2, 6-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3-methylbutanamide (8g)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 2” from 200 g (0.8 mmol) 7e to give 140 mg (84%) of 8e as a brown oil. IR (KBr), v, cm-1: 3265, 2959, 1640, 1597, 1533, 1474, 1343, 1270, 1038, 1023, 781. ESI-HR-MS: Calcd. for C11H14NO3: 208.0974 g/mol. Found: 208.0978 g/mol. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CD2CI2, TMS): δ 1.03 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 6 H, 2 CH3), 2.19 (m, 1 H, CH), 2.36 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, CH2), 6.47 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2 H, 2 aromat. CH), 6.91 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H, aromat. CH), 7.96 (s, 1 H, NH), 8.85 (s, 2 H, 2 OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CD2Cl2, TMS): 22.4 (2 CH3), 26.8 (CH), 46.3 (CH2), 109.2 (2 aromat. CH), 115.1 (quat. C), 126.7 (aromat. CH), 149.0 (2 quat. C), 173.5 (CO).
N-(2, 6-Dihydroxyphenyl)benzamide (8h)
The compound was prepared according to “General Procedure 2” from 0.307 g (1.19 mmol) of 7d to give 0.249 g (91%) of 8h as a pale brown oil. IR (KBr), v, cm-1: 3415, 3141, 1649, 1612, 1572, 1537, 1450, 1356, 1257, 1028, 777, 696, 677, 609. HR-MS: Calcd. for C13H11NO3: 229.0739 g/mol. Found: 229.0738 g/mol. MS (CI, m/z, %): 230 (M++1, 100), 126 (10), 105 (28). MS (EI, m/z, %): 229 (M+, 12), 105 (100), 77 (42). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): δ 6.47 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2 H, 3-H, 5-H), 6.93 (t, J = 8.1 Hz, 1 H, 4-H), 7.53 (m, 3 H, 3’-H, 4’-H, 5’-H), 8.01 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2 H, 2’-H, 6’-H), 9.25 (s, 1 H, NH), 9.67 (s, 2 H, OH). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, d-DMSO, TMS): 107.0 (2 CH, 3-C, 5-C), 113.2 (quat. C, 1-C), 125.5 (CH, 4-C), 126.4 (2 CH, 2’-C, 6’-C), 127.3 (2 CH, 3’-C, 5’-C), 130.8 (CH, 4’-C), 131.9 (quat. C, 1’-C), 149.6 (2 quat. C, 2-C, 6-C), 165.3 (CO).
Acknowledgement
We wish to thank Martina Stadler for technical support.
Authors’ Statement
Competing Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Jayasuriya H, Herath KB, Zhang C, Zink DL, Basilio A, Genilloud O, Diez MT, Vicente F, Gonzalez I, Salazar O, Pelaez F, Cummings R, Ha S, Wang J, Singh SB. Isolation and Structure of Platencin: A FabH and FabF Dual Inhibitor with Potent Broad-Spectrum Antibiotic Activity. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2007; 46; 4684–4688. http://dx.doi.Org/10.1002/anie.200701058 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wang J, Soisson SM, Young K, Shoop W, Kodali S, Galgoci A, Painter R, Parthasarath G, Tang YS, Cummings R, Ha S, Dorso K, Motyl M, Jayasuriya H, Ondeyka J, Herath K, Zhang C, Hernandez L, Allocco J, Basilio A, Tormo JR, Genilloud O, Vicente F, Pelaez F, Colwell L, Lee SH, Michael B, Felcetto T, Gill C, Silver LL, Hermes JD, Bartizal K, Barrett J, Schmatz D, Becker JW, Cully D, Singh SB. Platensimycin is a selective FabF inhibitor with potent antibiotic properties. Nature. 2006; 441: 358–361. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature04784 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wright CHT, Reynolds KA. Antibacterial targets in fatty acid biosynthesis. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007; 10: 447–453. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2007.07.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Manallack DT, Crosby IT, Khakham Y, Capuano B. Platensimycin: A Promising Antimicrobial Targeting Fatty Acid Synthesis. Curr Med Chem. 2008; 15: 705–710. http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/092986708783885255 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tiefenbacher K, Mulzer J. A Nine-Step Total Synthesis of (-)-Platencin. J Org Chem. 2009; 74: 2937–2941. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jo9001855 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nicolaou KC, Lister T, Denton RM, Montero A, Edmonds DJ. Adamantaplatensimycin: A Bioactive Analogue of Platensimycin. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2007; 46: 4712–4714. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.200701548 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nicolaou KC, Li A, Edmonds DJ. Total Synthesis of Platensimycin. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2006; 45: 7086–7090. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.200603892 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bandow JE, Chen DY-K, Leung GYC, Li H, Toh QY, Ng AM-Y, Sum RJ. Total Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of the Fab-Inhibitory Antibiotic Platencin and Analogues Thereof. Eur J Org Chem. 2011; 183–196. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201001281 [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hirai S, Nakada M. Enantioselective divergent approaches to both (-)-platensimycin and (-)-platencin. Tetrahedron. 2011; 67: 518–530. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2010.10.076 [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zhang C, Ondeyka J, Herath K, Jayasuriya H, Guan Z, Zink DL, Dietrich L, Burgess B, Ha SN, Wang J. Platensimycin and platencin congeners from Streptomyces platensis. J Nat Prod. 2011; 74: 329–340. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/np100635f [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jang KP, Kim CH, Na SW, Jang DS, Kim H, Kang H, Lee E. 7-Phenylplatensimycin and 11-methyl-7-phenylplatensimycin: More potent analogs of platensimycin. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010; 20: 2156–2158. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.02.037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lee E, Jang KP, Kim CH, Na SW, Jang DS. Platensimycin derivatives, their intermediates and process for preparing the same, and new process for preparing platensimycin. US 8471043 B2, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wang J, Sintim HO. Dialkylamino-2,4-dihydroxybenzoic Acids as Easily Synthesized Analogues of Platensimycin and Platencin with Comparable Antibacterial Properties. Chem Eur J. 2011; 17: 3352–3357. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/chem.201002410 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Krauss J, Knorr V, Manhardt V, Scheffel S, Bracher F. Synthesis of Platensimycin Analogues and Their Antibiotic Potency. Arch Pharm Chem Life Sci. 2008; 341: 386–392. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ardp.200700177 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Plesch E, Bracher F, Krauss J. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Evaluation of Novel Platensimycin Analogues. Arch Pharm Chem Life Sci. 2012; 345: 657–662. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ardp.201100455 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Böhmer V, Wörsdorfer K, Becher U. Nachbargruppeneffekte bei der Aminolyse von Estern. Tetrahedron. 1978; 34: 2737–2742. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0040-4020(78)88412-9 [Google Scholar]
- 17.Satterthwait AC, Jencks WP. The Mechanism of the Aminolysis of Acetate Esters. J Am Chem Soc. 1974; 96: 7018–7031. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja00829a034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Alfonso I, Gotor V. Biocatalytic and biomimetic aminolysis reactions: useful tools for selective transformation on polyfunctional substrates. Chem Soc Rev. 2004; 33: 201–209. http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/b307785n [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mao Y, Li J, Xie K, Li H, Zhang R, Duan H, Guo H, Shen J. Process for preparation of 6-nitroacetophenone compounds. WO 2009149622 A1, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nagano T, Matsumura K. Preparation of 3’, 4’-Dihydroxy-6-carboxyflavonol. J Am Chem Soc. 1953; 75: 6237–6238. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja01120a038 [Google Scholar]
- 21.DIN Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V. Methoden zur Empfindlichkeitsprüfung von mikrobiellen Krankheitserregern gegen Chemotherapeutika. DIN 58940, Teil 3 - Beiblatt 1 und Teil 4 - Beiblatt 1 Beuth Verlag, Berlin; 1998. [Google Scholar]


