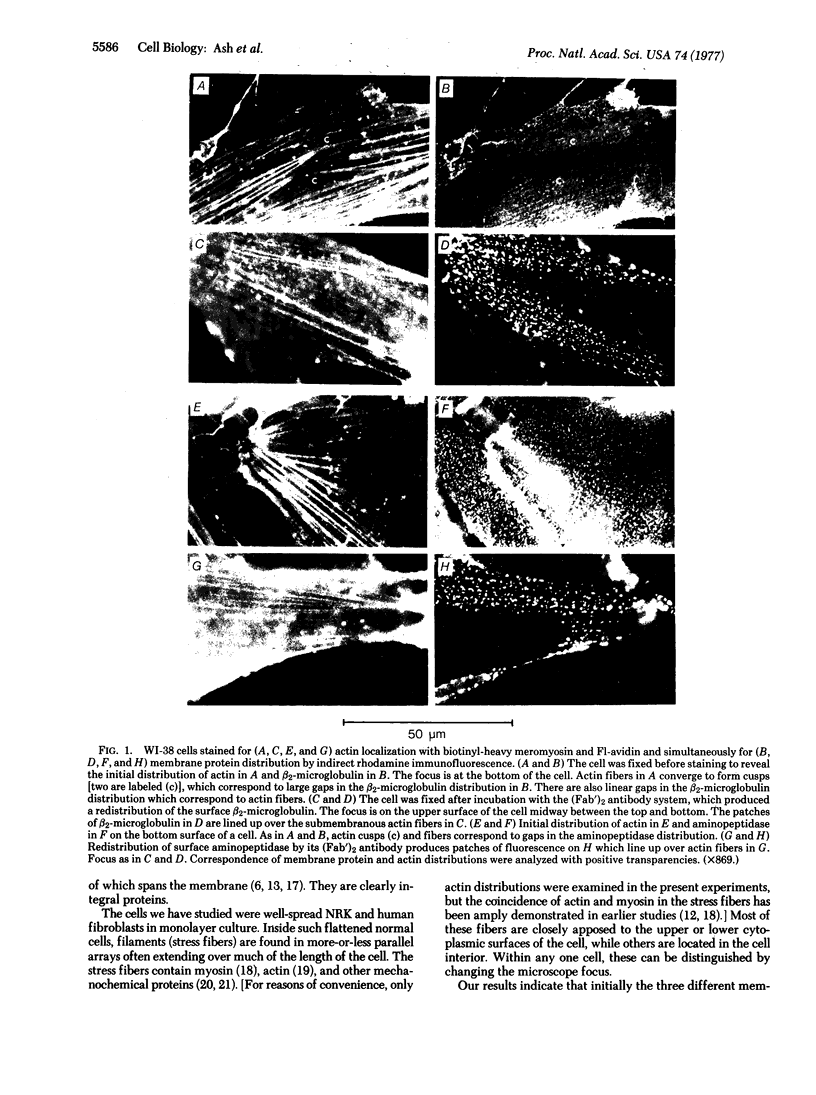
Abstract
The surface distributions of three different membrane integral proteins, beta2-microglobulin (part of the histocompatibility antigen complex), aminopeptidase (alpha-aminoacyl-peptide hydrolase; EC 3.4.11.2), and the Na+,K+-ATPase (ATP phosphohydrolase; EC 3.6.1.3) on human fibroblasts grown in monolayer culture have been studied with their specific antibodies by immunofluorescence. On the same cells, the distribution of intracellular actin was observed by a spectrally distinct fluorescent staining procedure. If each of the antibody reagents was permitted to cluster its specific protein in the plane of the membrane, these clusters apparently became linked, through the membrane, to actin- and myosin-containing filaments (stress fibers) underneath the membrane, and were thereby immobilized. From these and other experiments, it appears that most, if not all, integral proteins can, upon clustering, form such transmembrane linkages to actin and myosin. A molecular mechanism for the formation of these linkages is proposed which postulates that actin is associated with the cytoplasmic surface of plasma membranes by peripheral attachment to a ubiquitous integral protein X in the membrane; when other integral proteins are induced to form clusters, they become bound to X and hence to actin (and myosin). The possible physiological role of these transmembrane linkages is briefly discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyagi T., Suda H., Nagai M., Ogawa K., Suzuki J. Aminopeptidase activities on the surface of mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 8;452(1):131–143. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ash J. F., Singer S. J. Concanavalin-A-induced transmembrane linkage of concanavalin A surface receptors to intracellular myosin-containing filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4575–4579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon L. Y., Singer S. J. Transmembrane interactions and the mechanism of capping of surface receptors by their specific ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5031–5035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Conjugates of immunoglobulin G with different fluorochromes. I. Characterization by anionic-exchange chromatography. Scand J Immunol. 1973;2(3):273–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb02037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Receptor-mediated control of cholesterol metabolism. Science. 1976 Jan 16;191(4223):150–154. doi: 10.1126/science.174194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Surface modulation in cell recognition and cell growth. Science. 1976 Apr 16;192(4236):218–226. doi: 10.1126/science.769162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heggeness M. H., Ash J. F. Use of the avidin-biotin complex for the localization of actin and myosin with fluorescence microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jun;73(3):783–788. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.3.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heggeness M. H., Wang K., Singer S. J. Intracellular distributions of mechanochemical proteins in cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3883–3887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E. Muscular contraction and cell motility. Nature. 1973 Jun 22;243(5408):445–449. doi: 10.1038/243445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J. The reactions of sodium and potassium ion-activated adenosine triphosphatase with specific antibodies. Implications for the mechanism of active transport. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3652–3660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Two general classes of cytoplasmic actin filaments in tissue culture cells: the role of tropomyosin. J Supramol Struct. 1976;5(4):531(383)–563(415). doi: 10.1002/jss.400050410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Weber K. Actin antibody: the specific visualization of actin filaments in non-muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2268–2272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard D., Semeriva M., Maroux S. The brush-border intestinal aminopeptidase, a transmembrane protein as probed by macromolecular photolabelling. J Mol Biol. 1976 Oct 5;106(4):1023–1035. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90350-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. The molecular basis of the biological activities of complement. Harvey Lect. 1971;66:75–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NACHLAS M. M., MONIS B., ROSENBATT D., SELIGMAN A. M. Improvement in the histochemical localization of leucine aminopeptidase with a new substrate, L-leucyl-4-methoxy-2-naphthylamide. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Apr;7:261–264. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Transmembrane control of the receptors on normal and tumor cells. I. Cytoplasmic influence over surface components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 13;457(1):57–108. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Weihing R. R. Actin and myosin and cell movement. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):1–65. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisfeld R. A., Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S. The immunologic and molecular profiles of HLA antigens isolated from urine. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):264–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoho A., Kyte J. Photoaffinity labeling of the ouabain-binding site on (Na+ plus K+) adenosinetriphosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2352–2356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Koppel D. E., Axelrod D., Jacobson K., Webb W. W., Elson E. L. Lateral transport on cell membranes: mobility of concanavalin A receptors on myoblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2409–2413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F., Unanue E. R. Membrane and cytoplasmic changes in B lymphocytes induced by ligand-surface immunoglobulin interaction. Adv Immunol. 1976;24:37–165. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. The molecular organization of membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):805–833. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solheim B. G., Thorsby E. Beta-2-microglobulin is part of the HL-A molecule in the lymphocyte membrane. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):36–38. doi: 10.1038/249036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Strominger J. L. Detergent-soluble HLA antigens contain a hydrophilic region at the COOH-terminus and a penultimate hydrophobic region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2481–2485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Ash J. F., Singer S. J. Filamin, a new high-molecular-weight protein found in smooth muscle and non-muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4483–4486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Groeschel-Stewart U. Antibody to myosin: the specific visualization of myosin-containing filaments in nonmuscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4561–4564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- berggard I. beta2-Microglobulins: isolation, properties, and distribution. Fed Proc. 1976 Apr;35(5):1167–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]