Abstract
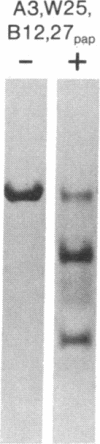
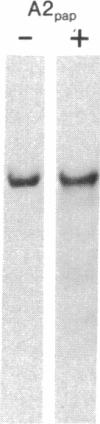
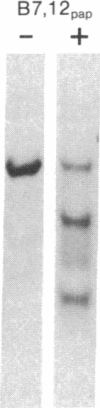
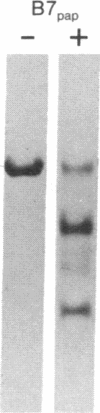
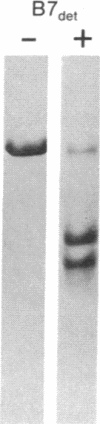
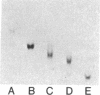
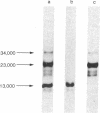
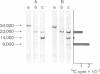
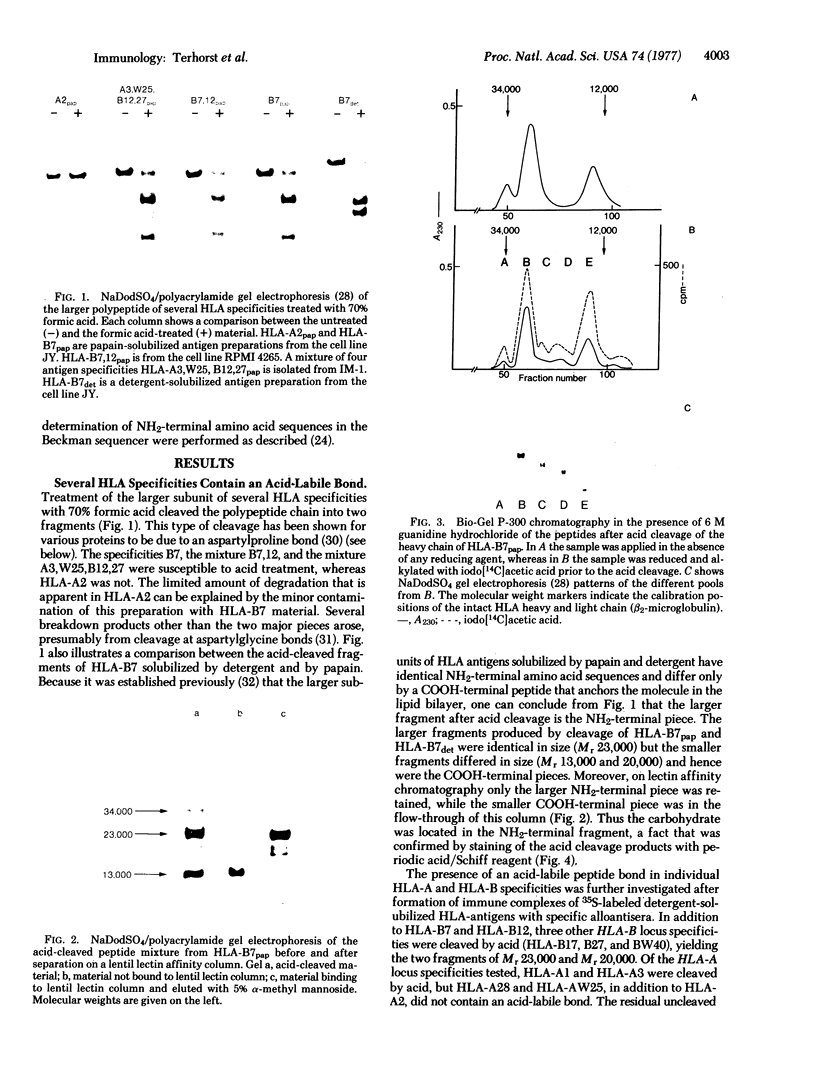
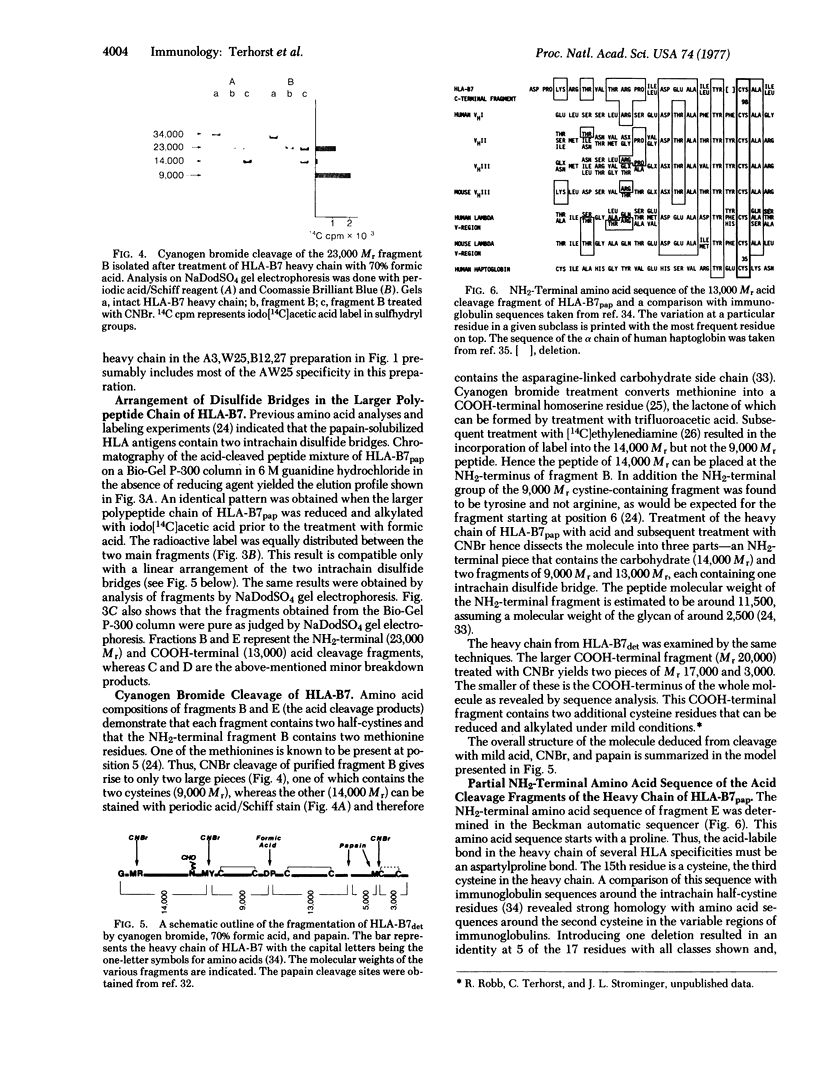
The papain-solubilized fragment of the heavy chain of HLA-B7, which is the NH2-terminal part of the whole polypeptide chain, can be divided into three regions by mild acid and cyanogen bromide cleavages. The first 100 amino acids terminating in a methionine residue contain the carbohydrate moiety; this segment is followed by two others of molecular weights 9,999 and 13,000, each containing an intrachain disulfide bridge. The two intrachain disulfide bridges are separated by a stretch of amino acids containing an acid-labile aspartyl-prolHLA-2, A28, and AW25 contain this acid-labile peptide bond in their larger subunit. Sequencing from the acid cleavage site of HLA-7 through the third half-cystine revealed consideralbe homology with amino acid sequences around a half-cystine in immunoglobulin variable regions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach F. H., van Rood J. J. The major histocompatibility complex--genetics and biology. (First of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 7;295(15):806–813. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610072951504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. A., Dixon G. H. Amino-acid sequence of alpha chains of human haptoglobins. Nature. 1968 May 25;218(5143):736–741. doi: 10.1038/218736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cresswell P., Robb R. J., Turner M. J., Strominger J. L. Papain-solubilized HL-A antigens. Chromatographic and electrophoretic studies of the two subunits from different specificities. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2828–2832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cresswell P., Springer T., Strominger J. L., Turner M. J., Grey H. M., Kubo R. T. Immunological identity of the small subunit of HL-A antigens and beta2-microglobulin and its turnover on the cell membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2123–2127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS E., WITKOP B. Nonenzymatic cleavage of peptide bonds: the methionine residues in bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1856–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gally J. A., Edelman G. M. The genetic control of immunoglobulin synthesis. Annu Rev Genet. 1972;6:1–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.06.120172.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. N., Jones E. A., Van Heyningen V., Solomon E., Bobrow M., Miggiano V., Bodmer W. F. The beta2-microglobulin gene is on chromosome 15 and not in the HL-A region. Nature. 1975 Mar 20;254(5497):267–269. doi: 10.1038/254267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey H. M., Kubo R. T., Colon S. M., Poulik M. D., Cresswell P., Springer T., Turner M., Strominger J. L. The small subunit of HL-A antigens is beta 2-microglobulin. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1608–1612. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J., Crumpton M. J. Isolation of glycoproteins from pig lymphocyte plasma membrane using Lens culinaris phytohemagglutinin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):923–930. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90581-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. L. Hydrolysis of proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1965;20:37–107. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60388-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn M. J. Amination of carboxyl-terminal homoserine peptides as an aid in peptide separation. Anal Biochem. 1975 Dec;69(2):583–589. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90163-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamuro K., Tanigaki N., Pressman D. Multiple common properties of human beta2-microglobulin and the common portion fragment derived from HL-A antigen molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2863–2865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmand A. P., Gerwurz H., Friedenson B. Partial amino-acid sequences of human and rabbit C-reactive proteins: homology with immunoglobulins and histocompatibility antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1214–1218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Terhorst C., Herrmann H., Humphreys R. E., Waterfield M. D., Strominger J. L. Immunological and chemical purity of papain-solubilized HL-A antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1594–1598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Benacerraf B. Functional specificity of thymus- dependent lymphocytes. Science. 1977 Mar 25;195(4284):1293–1300. doi: 10.1126/science.320663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A., Cunningham B. A., Berggård I., Edelman G. M. 2 -Microglobulin--a free immunoglobulin domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1697–1701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A., Rask L., Lindblom J. B. Highly purified papain-solubilized HL-A antigens contain beta2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):35–39. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A., Rask L., Sege K., Klareskog L., Anundi H., Ostberg L. Evolutionary relationship between immunoglobulins and transplantation antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1612–1616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piszkiewicz D., Landon M., Smith E. L. Anomalous cleavage of aspartyl-proline peptide bonds during amino acid sequence determinations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Sep 10;40(5):1173–1178. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90918-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S., Richardson D. C., Thomas K. A., Silverton E. W., Davies D. R. Similarity of three-dimensional structure between the immunoglobulin domain and the copper, zinc superoxide dismutase subunit. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 5;102(2):221–235. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Strominger J. L. Rapid purification of detergent-solubilized HLA antigen by affinity chromatography employing anti-beta2-microglobulin serum. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5427–5428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer G. M., Rehn T. G., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M. Role of the murine major histocompatibility complex in the specificity of in vitro T-cell-mediated lympholysis against chemically-modified autologous lymphocytes. Transplant Rev. 1976;29:222–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb00203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shreffler D. C., David C. S. The H-2 major histocompatibility complex and the I immune response region: genetic variation, function, and organization. Adv Immunol. 1975;20:125–195. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J., Hood L. Detergent-solubilised H-2 alloantigen is associated with a small molecular weight polypeptide. Nature. 1974 Jun 21;249(459):764–765. doi: 10.1038/249764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Poulik M. D. Initiation of protein synthesis at an unusual position in an immunoglobulin gene? Science. 1972 Jan 14;175(4018):187–189. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4018.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Strominger J. L. Detergent-soluble HLA antigens contain a hydrophilic region at the COOH-terminus and a penultimate hydrophobic region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2481–2485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Strominger J. L., Mann D. Partial purification of detergent-soluble HL-A antigen and its cleavage by papain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1539–1543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strominger J. L., Cresswell P., Grey H., Humphreys R. E., Mann D., McCuneJ, Parham P., Robb R., Sanderson A. R., Springer T. A. The immunoglobulin-like structure of human histocompatibility antigens. Transplant Rev. 1974;21(0):126–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1974.tb01549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M. J., Cresswell P., Parham P., Strominger J. L., Mann D. L., Sanderson A. R. Purification of papain-solubilized histocompatibility antigens from a cultured human lymphoblastoid line, RPMI 4265. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4512–4519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharius R. M., Zell T. E., Morrison J. H., Woodlock J. J. Glycoprotein staining following electrophoresis on acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jul;30(1):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler A., Harrison S. C., Leberman R. The minor proteins in tomato bushy stunt and turnip crinkle viruses. Virology. 1974 Jun;59(2):509–515. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90460-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. H-2 compatability requirement for T-cell-mediated lysis of target cells infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Different cytotoxic T-cell specificities are associated with structures coded for in H-2K or H-2D;. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1427–1436. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Someren H., Westerveld A., Hagemeijer A., Mees J. R., Meera Khan P., Zaalberg O. B. Human antigen and enzyme markers in man-Chinese hamster somatic cell hybrids: evidence for synteny between the HL-A, PGM3, ME1, and IPO-B loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):962–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]