Abstract
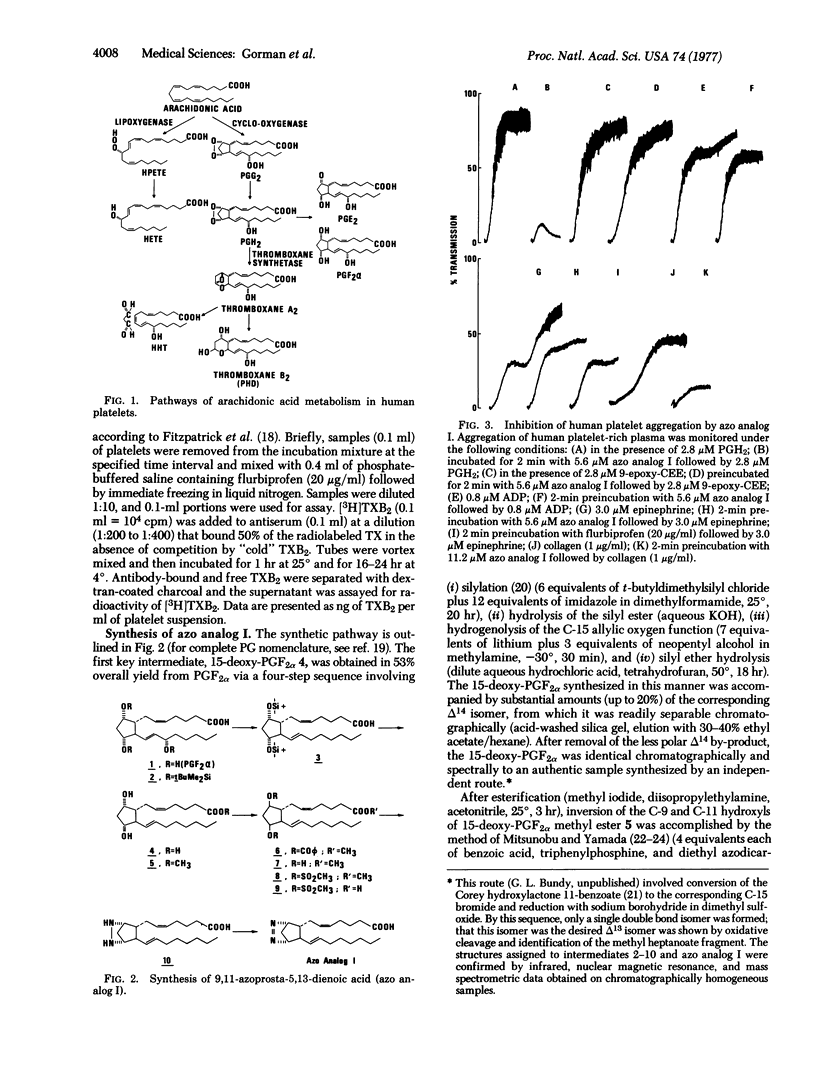
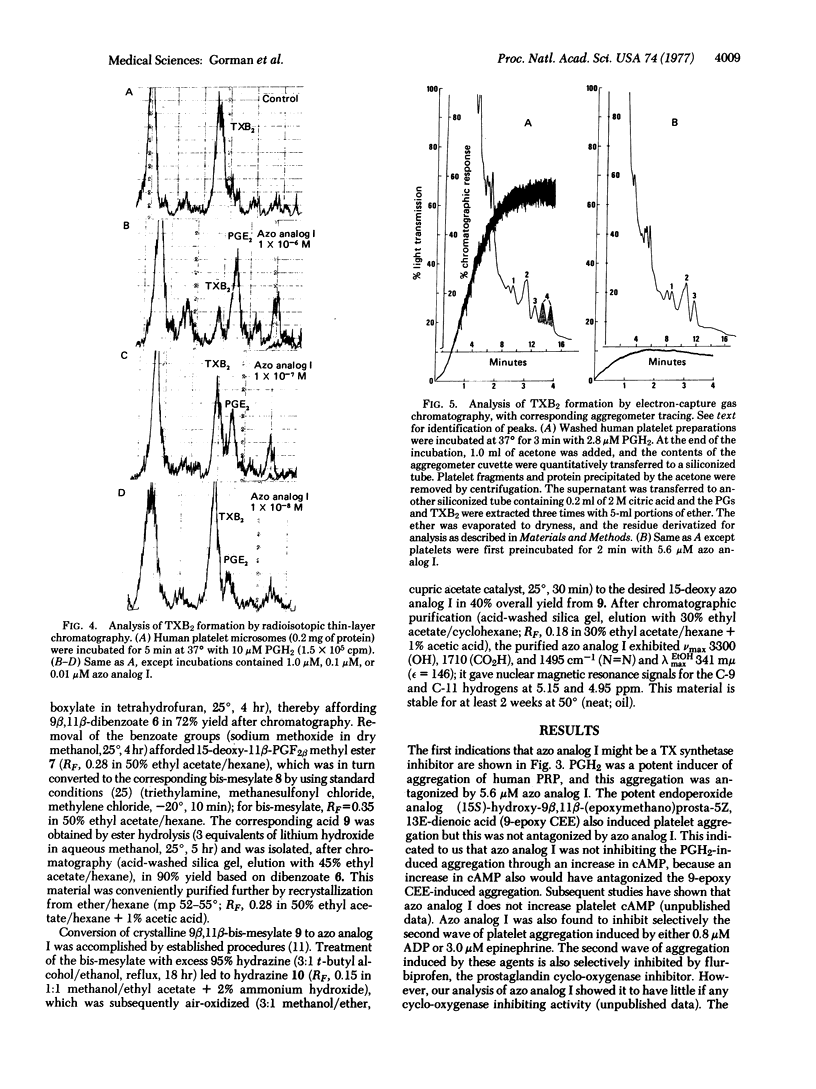
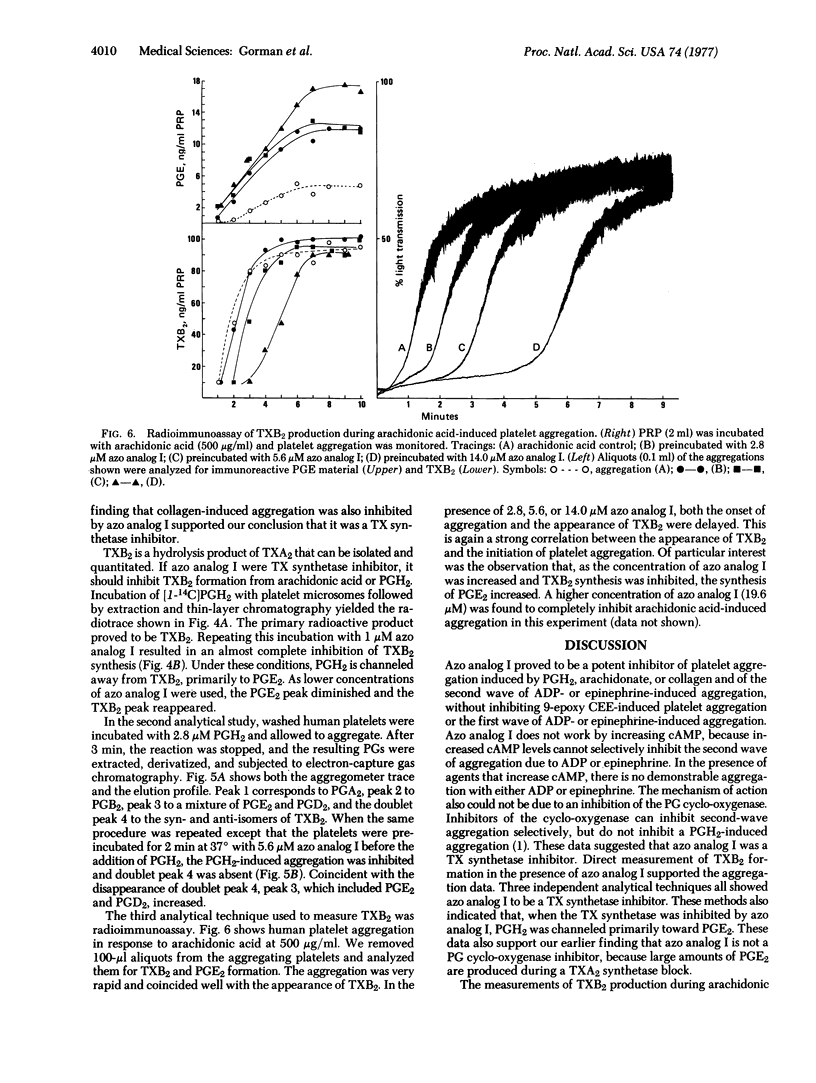
The synthetic prostaglandin analog 9,11-azoprosta-5,13-dienoic acid (azo analog I) has been found to be a potent inhibitor of human platelet thromboxane synthetase by three independent analytical methods: electron-capture gas chromatography, radioisotopic thin-layer chromatography, and radioimmunoassay. In the presence of azo analog I, human platelet aggregation induced by either the prostaglandin endoperoxide PGH2 or arachidonic acid was antagonized. The addition of azo analog I shifted the transformation of endoperoxides away from thromboxane synthesis and toward prostaglandin E2 synthesis. The specificity of azo analog I is demonstrated by its selective inhibition of the second wave of either ADP- or epinephrine-induced platelet aggregation. These data indicate that PGH2 must be converted to thromboxane A2 in order to induce human platelet aggregation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Corey E. J., Nicolaou K. C., Machida Y., Malmsten C. L., Samuelsson B. Synthesis and biological properties of a 9,11-azo-prostanoid: highly active biochemical mimic of prostaglandin endoperoxides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3355–3358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey E. J., Weinshenker N. M., Schaaf T. K., Huber W. Stereo-controlled synthesis of prostaglandins F-2a and E-2 (dl). J Am Chem Soc. 1969 Sep 24;91(20):5675–5677. doi: 10.1021/ja01048a062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick F. A., Gorman R. R., Wynalda M. A. Electron capture gas chromatographic detection of thromboxane B2. Prostaglandins. 1977 Feb;13(2):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman R. R., Bunting S., Miller O. V. Modulation of human platelet adenylate cyclase by prostacyclin (PGX). Prostaglandins. 1977 Mar;13(3):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman R. R., Sun F. F., Miller O. V., Johnson R. A. Prostaglandins H1 and H2. Convenient biochemical synthesis and isolation. Further biological and spectroscopic characterization. Prostaglandins. 1977 Jun;13(6):1043–1053. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. Prostaglandin endoperoxides. Novel transformations of arachidonic acid in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3400–3404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Svensson J., Samuelsson B. Thromboxanes: a new group of biologically active compounds derived from prostaglandin endoperoxides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2994–2998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Svensson J., Wakabayashi T., Samuelsson B. Isolation and structure of two prostaglandin endoperoxides that cause platelet aggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):345–349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. L., Katz A. J., Feinstein M. B. Plasmin inhibition of thrombin-induced platelet aggregation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Apr 30;33(2):286–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. V., Gorman R. R. Modulation of platelet cyclic nucleotide content by PGE1 and the prostaglandin endoperoxide PGG2. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1976;2(2):79–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. V., Johnson R. A., Gorman R. R. Inhibition of PGE1-stimulated cAMP accumulation in human platelets by thromboxane a2. Prostaglandins. 1977 Apr;13(4):599–609. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Gryglewski R., Bunting S., Vane J. R. An enzyme isolated from arteries transforms prostaglandin endoperoxides to an unstable substance that inhibits platelet aggregation. Nature. 1976 Oct 21;263(5579):663–665. doi: 10.1038/263663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Minkes M., Raz A. Thromboxanes: selective biosynthesis and distinct biological properties. Science. 1976 Jul 9;193(4248):163–165. doi: 10.1126/science.945611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Moncada S., Bunting S., Vane J. R., Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. Identification of an enzyme in platelet microsomes which generates thromboxane A2 from prostaglandin endoperoxides. Nature. 1976 Jun 17;261(5561):558–560. doi: 10.1038/261558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N. A. Prostaglandin nomenclature. J Med Chem. 1974 Sep;17(9):911–918. doi: 10.1021/jm00255a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper P. J., Vane J. R. Release of additional factors in anaphylaxis and its antagonism by anti-inflammatory drugs. Nature. 1969 Jul 5;223(5201):29–35. doi: 10.1038/223029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateson J. E., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Effects of prostacyclin (PGX) on cyclic AMP concentrations in human platelets. Prostaglandins. 1977 Mar;13(3):389–397. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker N., Bunting S., Salmon J., Moncada S., Vane J. R., Johnson R. A., Morton D. R., Kinner J. H., Gorman R. R., McGuire J. C. The chemical structure of prostaglandin X (prostacyclin). Prostaglandins. 1976 Dec;12(6):915–928. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(76)90126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



