Abstract
The primary structures of human and rabbit beta-globin mRNAs are compared. Using as a standard the extent of nucleotide substitutions inferred from the hypervariable amino acid residues of fibrinopeptides A and B, which are thought to change largely by neutral evolution, we show that not all silent mutations in globin mRNA are neutral. The divergence of the sequences is limited in part by the selective usage of synonymous codons. The divergent nucleotides tend to be distributed nonrandomly: in the coding region silent substitutions are most rare in segments that are also deficient in substitutions leading to replacements.
Full text
PDF
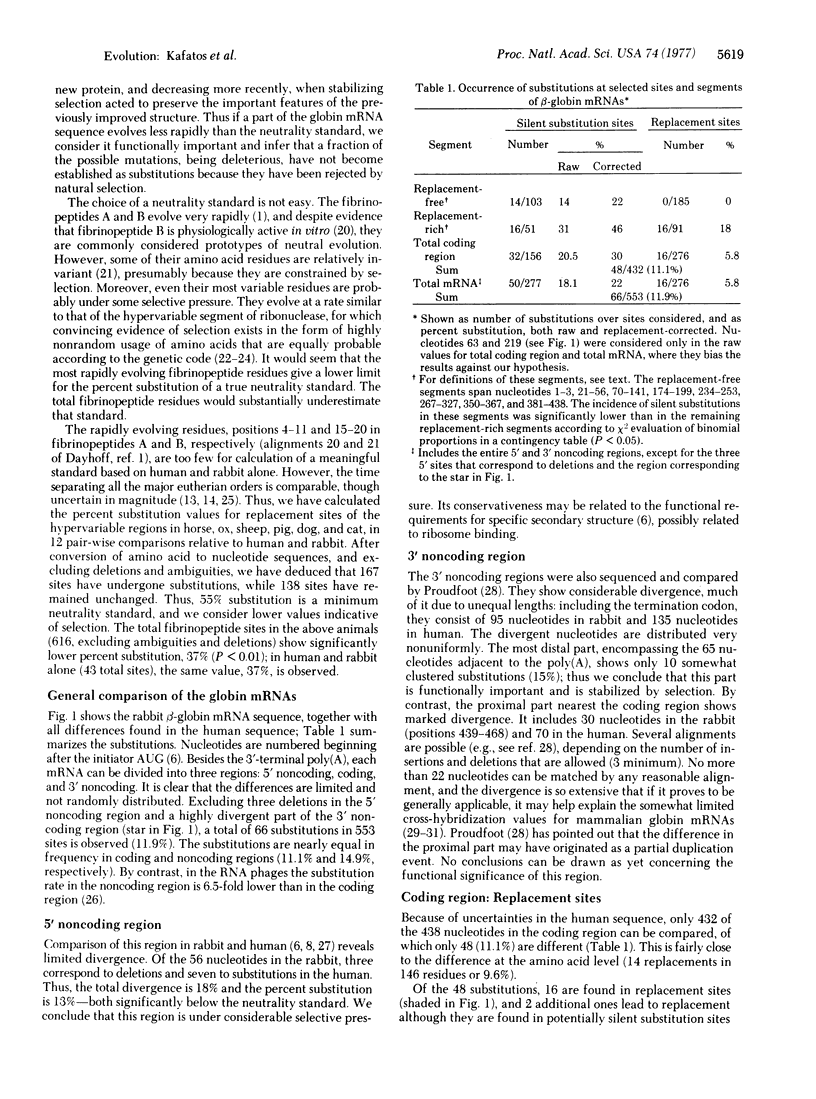


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baralle F. E. Complete nucleotide sequence of the 5' noncoding region of rabbit beta-globin mRNA. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):549–558. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard E. A., Cohen M. S., Gold M. H., Kim J. K. Evolution of ribonuclease in relation to polypeptide folding mechanisms. Nature. 1972 Dec 15;240(5381):395–398. doi: 10.1038/240395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne J. K., Paddock G. V., Liu A., Clarke P., Heindell H. C., Salser W. Nucleotide sequences from the rabbit beta globin gene inserted into Escherichia coli plasmids. Science. 1977 Jan 28;195(4276):389–391. doi: 10.1126/science.318762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. The structures of cytochrome c and the rates of molecular evolution. J Mol Evol. 1971;1(1):26–45. doi: 10.1007/BF01659392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C., Maniatis T. The primary structure of rabbit beta-globin mRNA as determined from cloned DNA. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):571–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elton R. A., Russell G. J., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Doublet frequencies and codon weighting in the DNA of Escherichia coli and its phages. J Mol Evol. 1976 Aug 3;8(2):117–135. doi: 10.1007/BF01739098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favre A., Morel C., Scherrer K. The secondary structure and poly(A) content of globin messenger RNA as a pure RNA and in polyribosome-derived ribonucleoprotein complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):147–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiers W., Contreras R., Duerinck F., Haegeman G., Iserentant D., Merregaert J., Min Jou W., Molemans F., Raeymaekers A., Van den Berghe A. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage MS2 RNA: primary and secondary structure of the replicase gene. Nature. 1976 Apr 8;260(5551):500–507. doi: 10.1038/260500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M. Is there selection against wobble in codon-anticodon pairing? Science. 1976 Dec 10;194(4270):1173–1174. doi: 10.1126/science.996548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galizzi A. Polymorphic alleles of the gene for the beta-chain of rabbit haemoglobin. Nat New Biol. 1971 Feb 3;229(5):142–143. doi: 10.1038/newbio229142a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garel J. P. Functional adaptation of tRNA population. J Theor Biol. 1974 Jan;43(1):211–225. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(74)80054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrick M. D., Hafner R., Bricker J., Garrick L. M. Genetic variation in the primary structure of the beta chain of rabbit hemoglobin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Nov 29;241(0):436–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb21899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M., Moore G. W., Matsuda G. Darwinian evolution in the genealogy of haemoglobin. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):603–608. doi: 10.1038/253603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gummerson K. S., Williamson R. Sequence divergence of mammalian globin messenger RNA. Nature. 1974 Feb 1;247(5439):265–267. doi: 10.1038/247265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder J. W., Lingrel J. B. Determination of secondary structure in rabbit globin messenger RNA by thermal denaturation. Biochemistry. 1975 Sep 23;14(19):4209–4215. doi: 10.1021/bi00690a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Housman D., Forget B. G., Skoultchi A., Benz E. J., Jr Quantitative deficiency of chain-specific globin messenger ribonucleic acids in the thalassemia syndromes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1809–1813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jou W. M., Fiers W. Studies on the bacteriophages MS2. XXXIII. Comparison of the nucleotide sequences in related bacteriophage RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1976 Oct 5;106(4):1047–1060. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90352-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jou W. M., Van Montagu M., Fiers W. On the possible modulating role of the isoleucine AUA-codon in bacteriophage MS2 RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 20;73(4):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90234-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kacian D. L., Gambino R., Dow L. W., Grossbard E., Natta C., Ramirez F., Spiegelman S., Marks P. A., Bank A. Decreased globin messenger RNA in thalassemia detected by molecular hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1886–1890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M. Evolutionary rate at the molecular level. Nature. 1968 Feb 17;217(5129):624–626. doi: 10.1038/217624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M., Ohta T. On some principles governing molecular evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2848–2852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M., Ohta T. Protein polymorphism as a phase of molecular evolution. Nature. 1971 Feb 12;229(5285):467–469. doi: 10.1038/229467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M. Preponderance of synonymous changes as evidence for the neutral theory of molecular evolution. Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):275–276. doi: 10.1038/267275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. L., Jukes T. H. Non-Darwinian evolution. Science. 1969 May 16;164(3881):788–798. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3881.788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotta C. A., Wilson J. T., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. Human beta-globin messenger RNA. III. Nucleotide sequences derived from complementary DNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5040–5053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min Jou W., Haegeman G., Ysebaert M., Fiers W. Nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for the bacteriophage MS2 coat protein. Nature. 1972 May 12;237(5350):82–88. doi: 10.1038/237082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. W., Goodman M., Callahan C., Holmquist R., Moise H. Stochastic versus augmented maximum parsimony method for estimating superimposed mutations in the divergent evolution of protein sequences. Methods tested on cytochrome c amino acid sequences. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 25;105(1):15–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90193-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBAHR A. J., GLADNER J. A., LAKI K. STUDIES ON THE PHYSIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF THE PEPTIDE RELEASED DURING THE FIBRINOGEN-FIBRIN CONVERSION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jun 8;86:535–542. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90093-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T., Kimura M. Functional organization of genetic material as a product of molecular evolution. Nature. 1971 Sep 10;233(5315):118–119. doi: 10.1038/233118a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. Complete 3' noncoding region sequences of rabbit and human beta-globin messenger RNAs. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):559–570. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Herrera A. E., Lehmann H., Joysey K. A., Friday A. E. Molecular evolution of myoglobin and the fossil record: a phylogenetic synthesis. Nature. 1973 Dec 14;246(5433):389–395. doi: 10.1038/246389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell G. J., Walker P. M., Elton R. A., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Doublet frequency analysis of fractionated vertebrate nuclear DNA. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov;108(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W., Bowen S., Browne D., el-Adli F., Fedoroff N., Fry K., Heindell H., Paddock G., Poon R., Wallace B. Investigation of the organization of mammalian chromosomes at the DNA sequence level. Fed Proc. 1976 Jan;35(1):23–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W., Isaacson J. S. Mutation rates in globin genes: the genetic load and Haldane's dilemma. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;19:205–220. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60919-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Air G. M., Barrell B. G., Brown N. L., Coulson A. R., Fiddes C. A., Hutchison C. A., Slocombe P. M., Smith M. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage phi X174 DNA. Nature. 1977 Feb 24;265(5596):687–695. doi: 10.1038/265687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamatoyannopoulos G. The molecular basis of hemoglobin disease. Annu Rev Genet. 1972;6:47–70. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.06.120172.000403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerkandl E., Pauling L. Molecules as documents of evolutionary history. J Theor Biol. 1965 Mar;8(2):357–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(65)90083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerkandl E. The appearance of new structures and functions in proteins during evolution. J Mol Evol. 1975 Dec 31;7(1):1–57. doi: 10.1007/BF01732178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


