Abstract
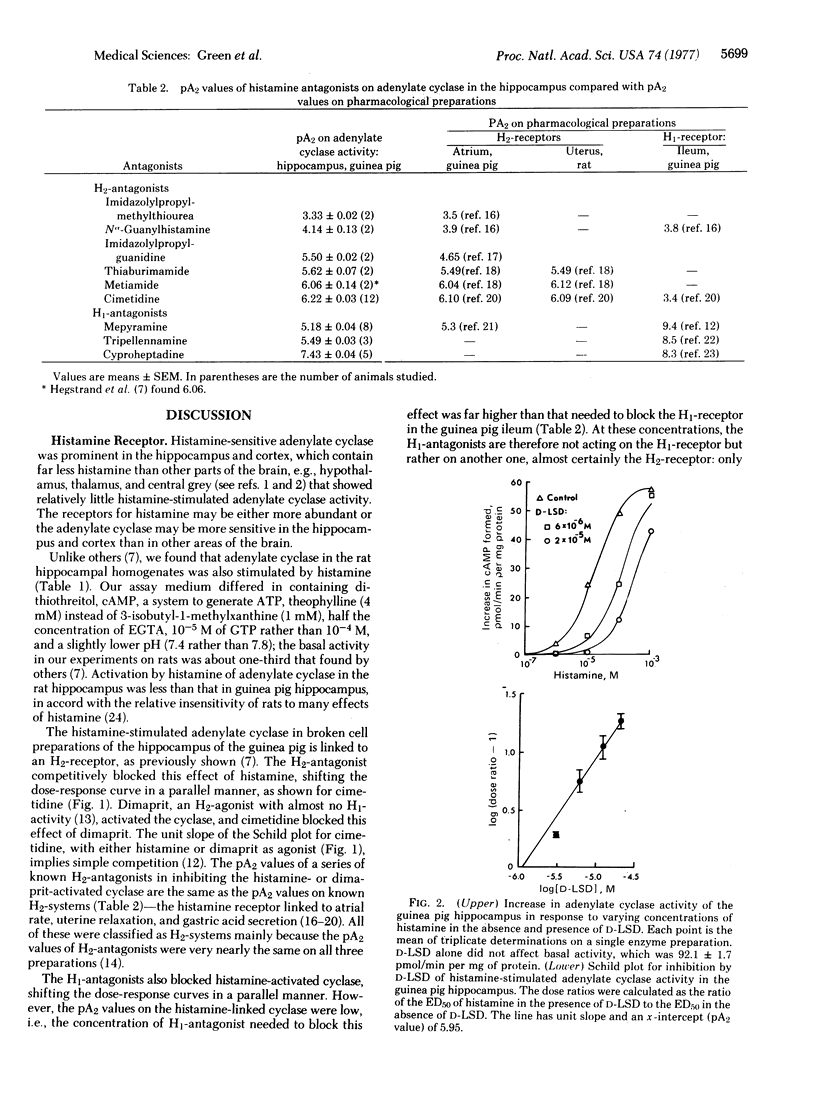
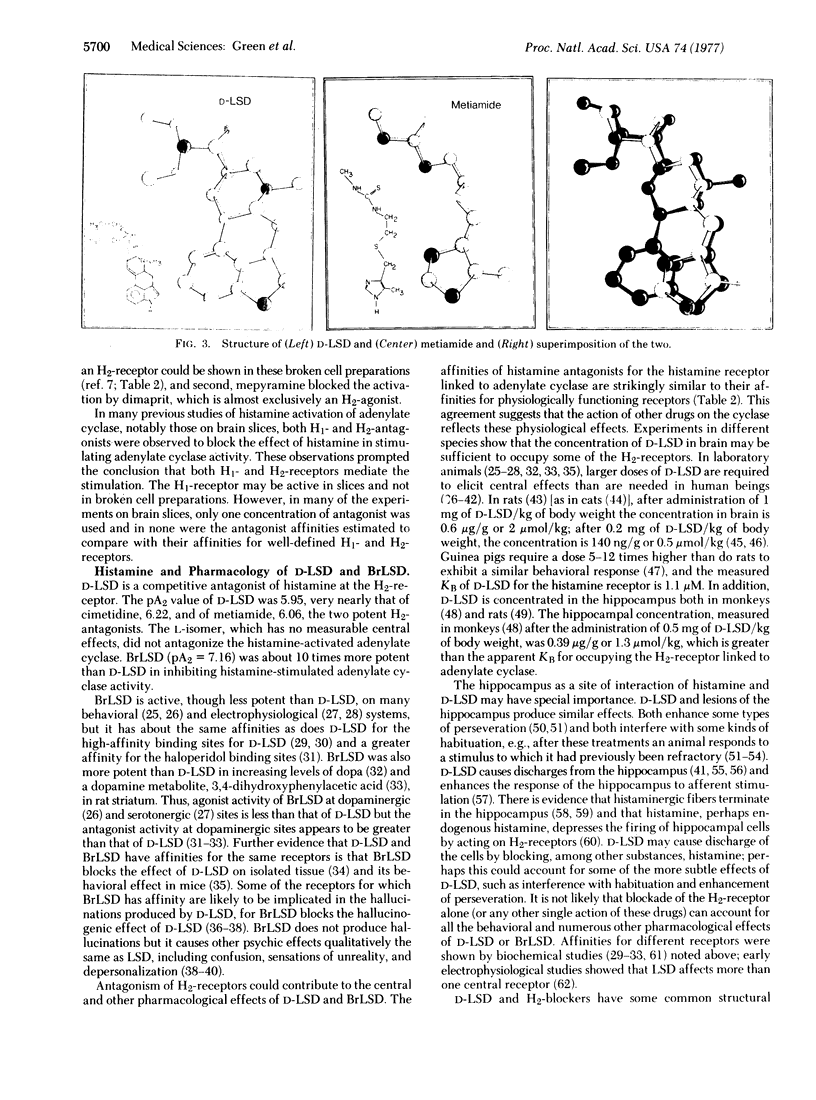
D-Lysergic acid diethylamide and D-2-bromolysergic acid diethylamide are competitive antagonists of the histamine activation of adenylate cyclase [ATP pyrophosphate-lyase (cyclizing); E.C. 4.6.1.1] in broken cell preparations of the hippocampus and cortex of guinea pig brain. The adenylate cyclase is linked to the histamine H2-receptor. Both D-lysergic acid diethylamide and D-2-bromolysergic acid diethylamide show topological congruency with potent H2-antagonists. D-2-Bromolysergic acid diethylamide is 10 times more potent as an H2-antagonist than cimetidine, which has been the most potent H2-antagonist reported, and D-lysergic acid diethylamide is about equipotent to cimetidine. Blockade of H2-receptors could contribute to the behavioral effects of D-2-bromolysergic acid diethylamide and D-lysergic acid diethylamide.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMSON H. A., SKLAROFSKY B., BARON M. O., FREMONT-SMITH N. Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD-25) antagonists. II. Development of tolerance in man to LSD-25 by prior administration of MLD-41 (1-methyl-d-lysergic acid diethylamide). AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1958 Feb;79(2):201–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ADEY W. R., BELL F. R., DENNIS B. J. Effects of LSD-25, psiolocybin, and psilocin on temporal lobe EEG patterns and learned behavior in the cat. Neurology. 1962 Sep;12:591–602. doi: 10.1212/wnl.12.9.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AXELROD J., BRADY R. O., WITKOP B., EVARTS E. V. The distribution and metabolism of lysergic acid diethylamide. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Mar 14;66(3):435–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb40739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aghajanian G. K., Foote W. E., Sheard M. H. Action of psychotogenic drugs on single midbrain raphe neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Feb;171(2):178–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aghajanian G. K. LSD and 2-bromo-LSD: comparison on effects on serotonergic neurones and on neurones in two serotonergic projection areas, the ventral lateral geniculate and amygdala. Neuropharmacology. 1976 Sep;15(9):521–528. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(76)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTINO J. R., KLEE G. D., WEINTRAUB W. Cholinesterase, dlysergic acid diethylamide, and 2-bromolysergic acid diethylamide. J Clin Exp Psychopathol Q Rev Psychiatry Neurol. 1959 Jul-Sep;20:218–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbin G., Garbarg M., Schwartz J. C., Storm-Mathisen J. Histamine synthesizing afferents to the hippocampal region. J Neurochem. 1976 Feb;26(2):259–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb04474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. P., Jr, Snyder S. H. Serotonin and lysergic acid diethylamide binding in rat brain membranes: relationship to postsynaptic serotonin receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 May;12(3):373–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. W., Duncan W. A., Durant C. J., Ganellin C. R., Parsons E. M. Definition and antagonism of histamine H 2 -receptors. Nature. 1972 Apr 21;236(5347):385–390. doi: 10.1038/236385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. W., Durant G. J., Emmett J. C., Ganellin C. R. Sulphur-methylene isosterism in the development of metiamide, a new histamine H2-receptor antagonist. Nature. 1974 Mar 1;248(5443):65–67. doi: 10.1038/248065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunce K. T., Parsons M. E. A quantitative study of metiamide, a histamine H2-antagonist, on the isolated whole rat stomach. J Physiol. 1976 Jun;258(2):453–465. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butters N. The effect of LSD-25 on spatial and stimulus perseverative tendencies in rats. Psychopharmacologia. 1966;8(6):454–460. doi: 10.1007/BF00406494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corne S. J., Pickering R. W. A possible correlation between drug-induced hallucinations in man and a behavioural response in mice. Psychopharmacologia. 1967;11(1):65–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00401509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese I., Burt D. R., Synder S. H. The dopamine receptor: differential binding of d-LSD and related agents to agonist and antagonist states. Life Sci. 1975 Dec 1;17(11):1715–1719. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOEPFNER W. Biochemical observations on LSD-25 and Deseril. Experientia. 1962 Jun 15;18:256–257. doi: 10.1007/BF02148217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. W. The nature of receptors regulating the formation of cyclic AMP in brain tissue. Life Sci. 1976 Jun 15;18(12):1349–1358. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diab I. M., Freedman D. X., Roth L. J. ( 3 H)lysergic acid diethylamide: cellular autoradiographic localization in rat brain. Science. 1971 Sep 10;173(4001):1022–1024. doi: 10.1126/science.173.4001.1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durant G. J., Ganellin C. R., Parsons M. E. Chemical differentiation of histamine H1- and H2-receptor agonists. J Med Chem. 1975 Sep;18(9):905–909. doi: 10.1021/jm00243a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durant G. J., Parsons M. E., Black J. W. Potential histamine H2-receptor antagonists. 2. N-alpha-Guanylhistamine. J Med Chem. 1975 Aug;18(8):830–833. doi: 10.1021/jm00242a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer D. C., Gant D. W. Vasoconstriction produced by hallucinogens on isolated human and sheep umbilical vasculature. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Feb;184(2):366–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faragalla F. F. The subcellular distribution of lysergic acid diethylamide in the rat brain. Experientia. 1972 Dec 15;28(12):1426–1427. doi: 10.1007/BF01957828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINZEL K. H., MAYER-GROSS W. Prevention of psychological effects of d-lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD 25) by its 2-brom derivative (BOL 148). Nature. 1956 Jul 28;178(4526):210–210. doi: 10.1038/178210a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREINER T., BURCH N. R., EDELBERG R. Psychopathology and psychophysiology of minimal LSD-25 dosage; a preliminary dosage-response spectrum. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1958 Feb;79(2):208–210. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1958.02340020088016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbarg M., Barbin G., Bischoff S., Pollard H., Schwartz J. C. Dual localization of histamine in an ascending neuronal pathway and in non-neuronal cells evidenced by lesions in the lateral hypothalamic area. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 23;106(2):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)91029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Wolf P. Central actions of histamine: microelectrophoretic studies. Brain Res. 1977 Feb 18;122(2):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90294-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegstrand L. R., Kanof P. D., Greengard P. Histamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase in mammalian brain. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):163–165. doi: 10.1038/260163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISBELL H., MINER E. J., LOGAN C. R. Relationships of psychotomimetic to anti-serotonin potencies of congeners of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD-25). Psychopharmacologia. 1959;1:20–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00408108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. L., Mizoguchi H. The interaction of histamine and guanylnucleotides with cardiac adenylate cyclase and its relationship to cardiac contractility. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Jan;200(1):174–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi S., Rall T. W. The influence of chemical agents on the accumulation of adenosine 3',5'-Phosphate in slices of rabbit cerebellum. Mol Pharmacol. 1968 Jul;4(4):367–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key B. J. The effect of LSD-25 on the interaction between conditioned and non-conditioned stimuli in a simple avoidance situation. Psychopharmacologia. 1964 Nov 11;6(5):319–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00404242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler C. Habituation after dorsal hippocampal lesions: a test dependent phenomenon. Behav Biol. 1976 Sep;18(1):89–110. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6773(76)91780-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIBERSON W. T., KARCZMAR A. G., SCHWARTZ E., ELLEN P. SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION IN THE HIPPOCAMPUS AND PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGICAL AGENTS. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1963 Dec;2:291–302. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(63)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovell R. A., Freedman D. X. Stereospecific receptor sites for d-lysergic acid diethylamide in rat brain: effects of neurotransmitters, amine antagonists, and other psychotropic drugs. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;12(4):620–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL P. B. Some chemical and physical properties associated with histamine antagonism. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1955 Sep;10(3):270–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1955.tb00870.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONROE R. R., HEATH R. G., MICKLE W. A., LLEWELLYN R. C. Correlation of rhinencephalic electrograms with behavior; a study on humans under the influence of LSD and mescaline. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1957 Nov;9(4):623–642. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(57)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PURPURA D. P. Electrophysiological analysis of psychotogenic drug action. II. General nature of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) action on central synapses. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1956 Feb;75(2):132–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. B., Waud D. R. Pharmacological estimation of drug-receptor dissociation constants. Statistical evaluation. I. Agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Apr;177(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons M. E., Blakemore R. C., Durant G. J., Ganellin C. R., Rasmussen A. C. Proceedings: 3-(4(5)-imidazolyl) propylguanidine (SK&F 91486) - a partial agonist at histamine H2-receptors. Agents Actions. 1975 Dec;5(5):464–464. doi: 10.1007/BF01972676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons M. E., Owen D. A., Ganellin C. R., Durant G. J. Dimaprit -(S-[3-(N,N-dimethylamino)prophyl]isothiourea) - a highly specific histamine H2 -receptor agonist. Part 1. Pharmacology. Agents Actions. 1977 Mar;7(1):31–37. doi: 10.1007/BF01964878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson S. A. Effects of LSD and 2-bromo LSD on striatal DOPAC levels. Life Sci. 1977 Apr 1;20(7):1199–1205. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90493-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson S. A. The effect of LSD and 2-bromo LSD on the striatal DOPA accumulation after decarboxylase inhibition in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 May 1;43(1):73–83. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90162-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosecrans J. A., Lovell R. A., Freedman D. X. Effects of lysergic acid diethylamide on the metabolism of brain 5-hydroxytryptamine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Oct;16(10):2011–2021. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90313-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNECKLOTH R., PAGE I. H., DEL GRECO F., CORCORAN A. C. Effects of serotonin antagonists in normal subjects and patients with carcinoid tumors. Circulation. 1957 Oct;16(4):523–532. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.16.4.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. C. Histaminergic mechanisms in brain. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1977;17:325–339. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.17.040177.001545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Reivich M. Regional localization of lysergic acid diethylamide in monkey brain. Nature. 1966 Mar 12;209(5028):1093–1095. doi: 10.1038/2091093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRENDELENBURG U. The action of histamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine on isolated mammalian atria. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1960 Dec;130:450–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trulson M. E., Stark A. D., Jacobs B. L. Comparative effects of hallucinogenic drugs on rotational behavior in rats with unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesions. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Jul 15;44(2):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90097-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]