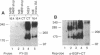Abstract
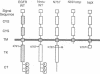
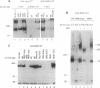
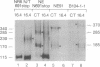
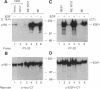
We have shown that members of the erbB family undergo homodimer and heterodimer formation. The rat p185c-neu and the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) can associate into an active heterodimeric tyrosine kinase. Overexpression of these two receptors also results in a transformed phenotype. We now show that mutant Neu proteins resulting from a point mutation at the ATP-binding site (N757) or cytoplasmic domain deletions (N691stop) are still able to undergo EGF-induced heterodimerization with EGFR. Analysis of heterodimer formation between EGFR and truncated Neu proteins revealed that heterodimerization is preferred over homodimerization of EGFR. N757 can be transphosphorylated by associated EGFR upon EGF stimulation. However, the heterodimer composed of EGFR and N691stop is kinase inactive. These results provided evidence that the Neu ectodomain is sufficient to associate with EGFR physically, and the cytoplasmic domain interaction is required for heterodimeric kinase activation, indicating that Neu/c-erbB2 is not just a simple substrate for EGFR but a transactivator as well.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. Multiple independent activations of the neu oncogene by a point mutation altering the transmembrane domain of p185. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90779-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. The neu oncogene encodes an epidermal growth factor receptor-related protein. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):226–230. doi: 10.1038/319226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Weinberg R. A. Oncogenic activation of the neu-encoded receptor protein by point mutation and deletion. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2043–2052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03044.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorge J. D., Chan T. O., Antczak M., Kung H. J., Fujita D. J. Activated type I phosphatidylinositol kinase is associated with the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor following EGF stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3816–3820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böni-Schnetzler M., Kaligian A., DelVecchio R., Pilch P. F. Ligand-dependent intersubunit association within the insulin receptor complex activates its intrinsic kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6822–6828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly P. A., Stern D. F. The epidermal growth factor receptor and the product of the neu protooncogene are members of a receptor tyrosine phosphorylation cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6054–6057. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., MacAuley A. Potential positive and negative autoregulation of p60c-src by intermolecular autophosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4232–4236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. J., Harris P. Effects of platelet-derived growth factor on phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in human skin fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9204–9209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobashi K., Davis J. G., Mikami Y., Freeman J. K., Hamuro J., Greene M. I. Characterization of a neu/c-erbB-2 protein-specific activating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8582–8586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougall W. C., Qian X., Greene M. I. Interaction of the neu/p185 and EGF receptor tyrosine kinases: implications for cellular transformation and tumor therapy. J Cell Biochem. 1993 Sep;53(1):61–73. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240530108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drebin J. A., Link V. C., Stern D. F., Weinberg R. A., Greene M. I. Down-modulation of an oncogene protein product and reversion of the transformed phenotype by monoclonal antibodies. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):697–706. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazioli F., Bottaro D. P., Minichiello L., Auricchio A., Wong W. T., Segatto O., Di Fiore P. P. Identification and biochemical characterization of novel putative substrates for the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5155–5161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R., Levy R. B., Peles E., Yarden Y. Heterodimerization of the erbB-1 and erbB-2 receptors in human breast carcinoma cells: a mechanism for receptor transregulation. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 18;29(50):11024–11028. doi: 10.1021/bi00502a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Evidence for epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced intermolecular autophosphorylation of the EGF receptors in living cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4035–4044. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashles O., Yarden Y., Fischer R., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. A dominant negative mutation suppresses the function of normal epidermal growth factor receptors by heterodimerization. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1454–1463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. D., Haldeman B. A., Grant F. J., Murray M. J., Seifert R. A., Bowen-Pope D. F., Cooper J. A., Kazlauskas A. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) stimulates PDGF receptor subunit dimerization and intersubunit trans-phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8987–8992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Borrello I., Bellot F., Comoglio P., Schlessinger J. Egf binding to its receptor triggers a rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of the erbB-2 protein in the mammary tumor cell line SK-BR-3. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1647–1651. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02991.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokai Y., Cohen J. A., Drebin J. A., Greene M. I. Stage- and tissue-specific expression of the neu oncogene in rat development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8498–8501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokai Y., Dobashi K., Weiner D. B., Myers J. N., Nowell P. C., Greene M. I. Phosphorylation process induced by epidermal growth factor alters the oncogenic and cellular neu (NGL) gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5389–5393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokai Y., Myers J. N., Wada T., Brown V. I., LeVea C. M., Davis J. G., Dobashi K., Greene M. I. Synergistic interaction of p185c-neu and the EGF receptor leads to transformation of rodent fibroblasts. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):287–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90843-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori S., Akiyama T., Yamada Y., Morishita Y., Sugawara I., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. C-erbB-2 gene product, a membrane protein commonly expressed on human fetal epithelial cells. Lab Invest. 1989 Jul;61(1):93–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peles E., Levy R. B., Or E., Ullrich A., Yarden Y. Oncogenic forms of the neu/HER2 tyrosine kinase are permanently coupled to phospholipase C gamma. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2077–2086. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07739.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press M. F., Cordon-Cardo C., Slamon D. J. Expression of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in normal human adult and fetal tissues. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):953–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M., Herschman H. R. Variants of 3T3 cells lacking mitogenic response to epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3918–3921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quian X. L., Decker S. J., Greene M. I. p185c-neu and epidermal growth factor receptor associate into a structure composed of activated kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1330–1334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter A. L., Stern D. F., Vaidyanathan L., Decker S. J., Drebin J. A., Greene M. I., Weinberg R. A. The neu oncogene: an erb-B-related gene encoding a 185,000-Mr tumour antigen. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):513–516. doi: 10.1038/312513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivak-Kroizman T., Rotin D., Pinchasi D., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Lax I. Heterodimerization of c-erbB2 with different epidermal growth factor receptor mutants elicits stimulatory or inhibitory responses. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8056–8063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Kamps M. P. EGF-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of p185neu: a potential model for receptor interactions. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):995–1001. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02906.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg M. J., Gullick W. J. A sequence motif in the transmembrane region of growth factor receptors with tyrosine kinase activity mediates dimerization. Protein Eng. 1990 Mar;3(4):245–248. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.4.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe Y., Seiki M., Fujisawa J., Hoy P., Yokota K., Arai K., Yoshida M., Arai N. SR alpha promoter: an efficient and versatile mammalian cDNA expression system composed of the simian virus 40 early promoter and the R-U5 segment of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):466–472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada T., Qian X. L., Greene M. I. Intermolecular association of the p185neu protein and EGF receptor modulates EGF receptor function. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1339–1347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90697-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner D. B., Kokai Y., Wada T., Cohen J. A., Williams W. V., Greene M. I. Linkage of tyrosine kinase activity with transforming ability of the p185neu oncoprotein. Oncogene. 1989 Oct;4(10):1175–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner D. B., Liu J., Cohen J. A., Williams W. V., Greene M. I. A point mutation in the neu oncogene mimics ligand induction of receptor aggregation. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):230–231. doi: 10.1038/339230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Ikawa S., Akiyama T., Semba K., Nomura N., Miyajima N., Saito T., Toyoshima K. Similarity of protein encoded by the human c-erb-B-2 gene to epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):230–234. doi: 10.1038/319230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid, reversible aggregation of the purified epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1443–1451. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]