Abstract
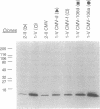
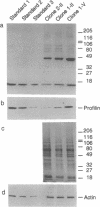
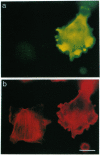
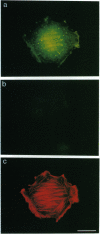
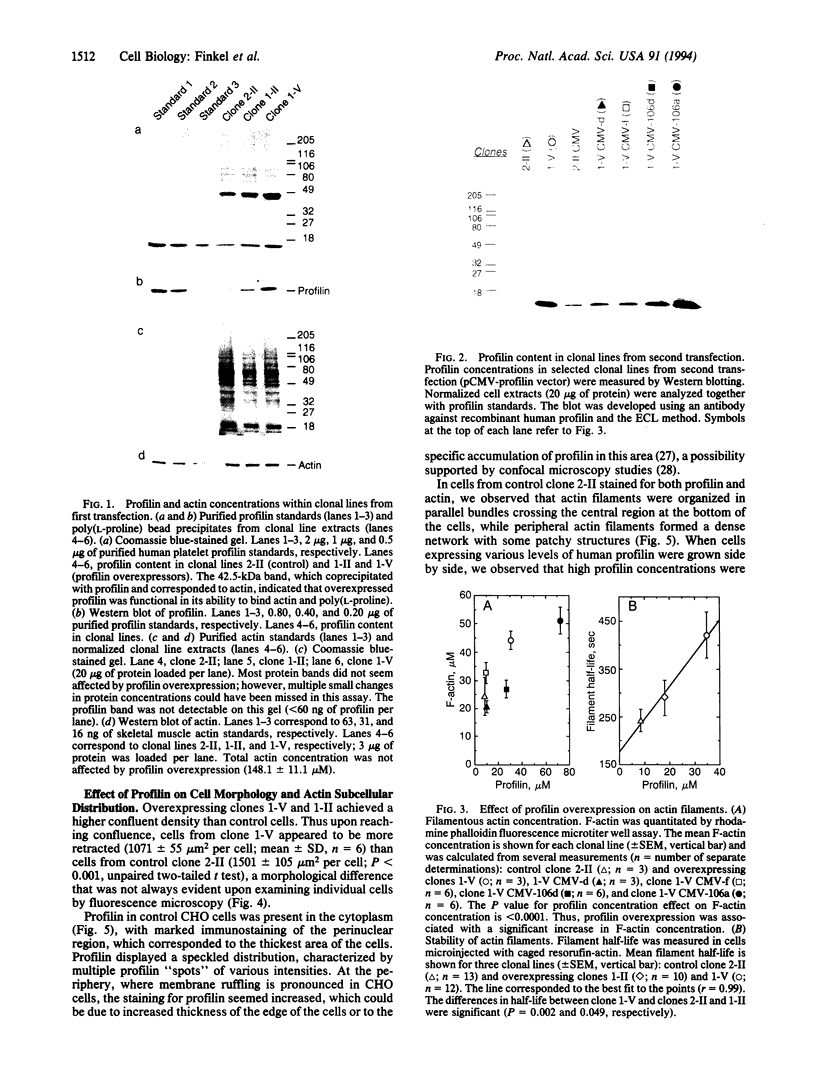
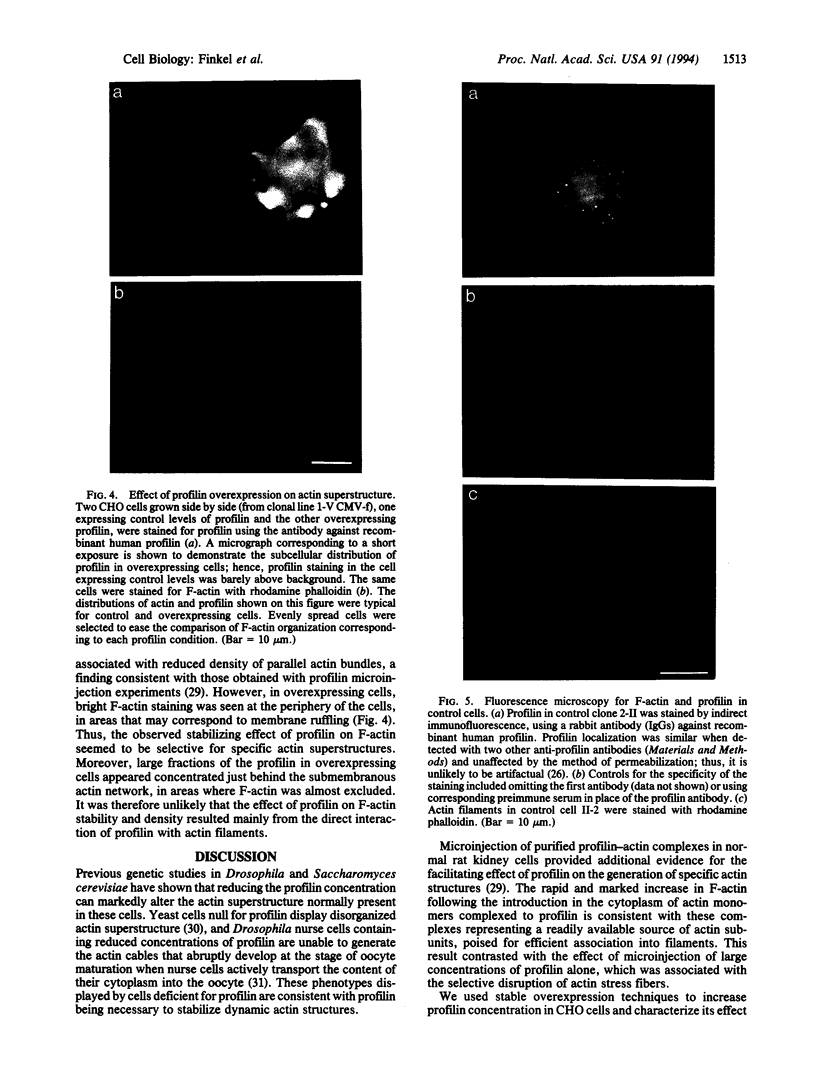
We describe the production and analysis of clonal cell lines in which we have overexpressed human profilin, a small ubiquitous actin monomer binding protein, to assess the role of profilin on actin function in vivo. The concentration of filamentous actin is increased in cells with higher profilin levels, and actin filament half-life measured in these cells is directly proportional to the steady-state profilin concentration. The distribution of actin filaments is altered by profilin overexpression. While parallel actin bundles crossing the cells are virtually absent in cells overexpressing profilin, the submembranous actin network of these cells is denser than in control cells. These results suggest that in vivo profilin regulates the stability, and thereby distribution, of specific dynamic actin structures.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babcock G., Rubenstein P. A. Control of profilin and actin expression in muscle and nonmuscle cells. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1993;24(3):179–188. doi: 10.1002/cm.970240305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Rotin D., Batzer A., Mandiyan V., Schlessinger J. SH3 domains direct cellular localization of signaling molecules. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90296-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss F., Temm-Grove C., Henning S., Jockusch B. M. Distribution of profilin in fibroblasts correlates with the presence of highly dynamic actin filaments. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1992;22(1):51–61. doi: 10.1002/cm.970220106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cano M. L., Lauffenburger D. A., Zigmond S. H. Kinetic analysis of F-actin depolymerization in polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysates indicates that chemoattractant stimulation increases actin filament number without altering the filament length distribution. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):677–687. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao L. G., Babcock G. G., Rubenstein P. A., Wang Y. L. Effects of profilin and profilactin on actin structure and function in living cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(5):1023–1029. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.5.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. F., Jean C., Rieger K. J., Lenfant M., Pantaloni D. Modulation of the interaction between G-actin and thymosin beta 4 by the ATP/ADP ratio: possible implication in the regulation of actin dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5034–5038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson L., Nyström L. E., Sundkvist I., Markey F., Lindberg U. Actin polymerizability is influenced by profilin, a low molecular weight protein in non-muscle cells. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooley L., Verheyen E., Ayers K. chickadee encodes a profilin required for intercellular cytoplasm transport during Drosophila oogenesis. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):173–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90128-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A. The role of actin polymerization in cell motility. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:585–605. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.003101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dadabay C. Y., Patton E., Cooper J. A., Pike L. J. Lack of correlation between changes in polyphosphoinositide levels and actin/gelsolin complexes in A431 cells treated with epidermal growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(6):1151–1156. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.6.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotto G. P., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Specific growth response of ras-transformed embryo fibroblasts to tumour promoters. Nature. 1985 Dec 5;318(6045):472–475. doi: 10.1038/318472a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Furman M. I., Wachsstock D., Safer D., Nachmias V. T., Pollard T. D. The control of actin nucleotide exchange by thymosin beta 4 and profilin. A potential regulatory mechanism for actin polymerization in cells. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Sep;3(9):1015–1024. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.9.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Janmey P. A. Profilin, a weak CAP for actin and RAS. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):419–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Kim J. W., Machesky L. M., Rhee S. G., Pollard T. D. Regulation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by profilin and tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1231–1233. doi: 10.1126/science.1848725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Machesky L. M., Baldassare J. J., Pollard T. D. The actin-binding protein profilin binds to PIP2 and inhibits its hydrolysis by phospholipase C. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1575–1578. doi: 10.1126/science.2157283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Machesky L. M., Doberstein S. K., Pollard T. D. Mechanism of the interaction of human platelet profilin with actin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1081–1089. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Mendelsohn M. E., Gibbs J. B. Rac and Rho in control. Curr Biol. 1992 Dec;2(12):669–671. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(92)90135-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Leavitt J., Muscat G., Ng S. Y., Kedes L. A human beta-actin expression vector system directs high-level accumulation of antisense transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4831–4835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haarer B. K., Lillie S. H., Adams A. E., Magdolen V., Bandlow W., Brown S. S. Purification of profilin from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and analysis of profilin-deficient cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):105–114. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H., Kwiatkowski D. J. Actin-binding proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;3(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D., Carlier M. F., Pantaloni D. Actin polymerization and ATP hydrolysis. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):638–644. doi: 10.1126/science.3672117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Bruns G. A. Human profilin. Molecular cloning, sequence comparison, and chromosomal analysis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5910–5915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laham L. E., Lamb J. A., Allen P. G., Janmey P. A. Selective binding of gelsolin to actin monomers containing ADP. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):14202–14207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessard J. L. Two monoclonal antibodies to actin: one muscle selective and one generally reactive. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1988;10(3):349–362. doi: 10.1002/cm.970100302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machesky L. M., Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Pollard T. D. The affinities of human platelet and Acanthamoeba profilin isoforms for polyphosphoinositides account for their relative abilities to inhibit phospholipase C. Cell Regul. 1990 Nov;1(12):937–950. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.12.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melan M. A., Sluder G. Redistribution and differential extraction of soluble proteins in permeabilized cultured cells. Implications for immunofluorescence microscopy. J Cell Sci. 1992 Apr;101(Pt 4):731–743. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.4.731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mockrin S. C., Korn E. D. Acanthamoeba profilin interacts with G-actin to increase the rate of exchange of actin-bound adenosine 5'-triphosphate. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5359–5362. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida E. Opposite effects of cofilin and profilin from porcine brain on rate of exchange of actin-bound adenosine 5'-triphosphate. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 26;24(5):1160–1164. doi: 10.1021/bi00326a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Cooper J. A. Quantitative analysis of the effect of Acanthamoeba profilin on actin filament nucleation and elongation. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6631–6641. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D. Rate constants for the reactions of ATP- and ADP-actin with the ends of actin filaments. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2747–2754. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pring M., Weber A., Bubb M. R. Profilin-actin complexes directly elongate actin filaments at the barbed end. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1827–1836. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Johnston C. L., Diekmann D., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santerre R. F., Allen N. E., Hobbs J. N., Jr, Rao R. N., Schmidt R. J. Expression of prokaryotic genes for hygromycin B and G418 resistance as dominant-selection markers in mouse L cells. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. On the crawling of animal cells. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1086–1094. doi: 10.1126/science.8493552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam J. P. Synthetic peptide vaccine design: synthesis and properties of a high-density multiple antigenic peptide system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5409–5413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J. Actin microfilament dynamics in locomoting cells. Nature. 1991 Jul 11;352(6331):126–131. doi: 10.1038/352126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J. The nucleation-release model of actin filament dynamics in cell motility. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;2(8):219–222. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90298-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Bonder E. M., Coluccio L. M., Mooseker M. S. Actin from Thyone sperm assembles on only one end of an actin filament: a behavior regulated by profilin. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):112–124. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtek A., Haarer B., Field J., Gerst J., Pollard T. D., Brown S., Wigler M. Evidence for a functional link between profilin and CAP in the yeast S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):497–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. L. Exchange of actin subunits at the leading edge of living fibroblasts: possible role of treadmilling. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):597–602. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]