Abstract
In a sequence of 214 nucleotides at the 5′ terminus of the I gene mRNA, which codes for the lactose repressor protein of Escherichia coli, (i) an untranslated leader sequence of 28 residues precedes the repressor coding region; (ii) a GUG initiates synthesis of the wild-type repressor; (iii) GUG and AUG are the functional initiators for the synthesis of restart polypeptides activated by early I gene amber mutations, confirming previous assignments for these residues based on protein sequencing data; and (iv) sequences complementary to 16S ribosomal RNA provide stronger potential mRNA·16S rRNA interaction at the wild-type initiation site than at the restart sites. When I mRNA is used to direct the formation of initiation complexes in vitro, ribosomes bind only to the wild-type initiator region.
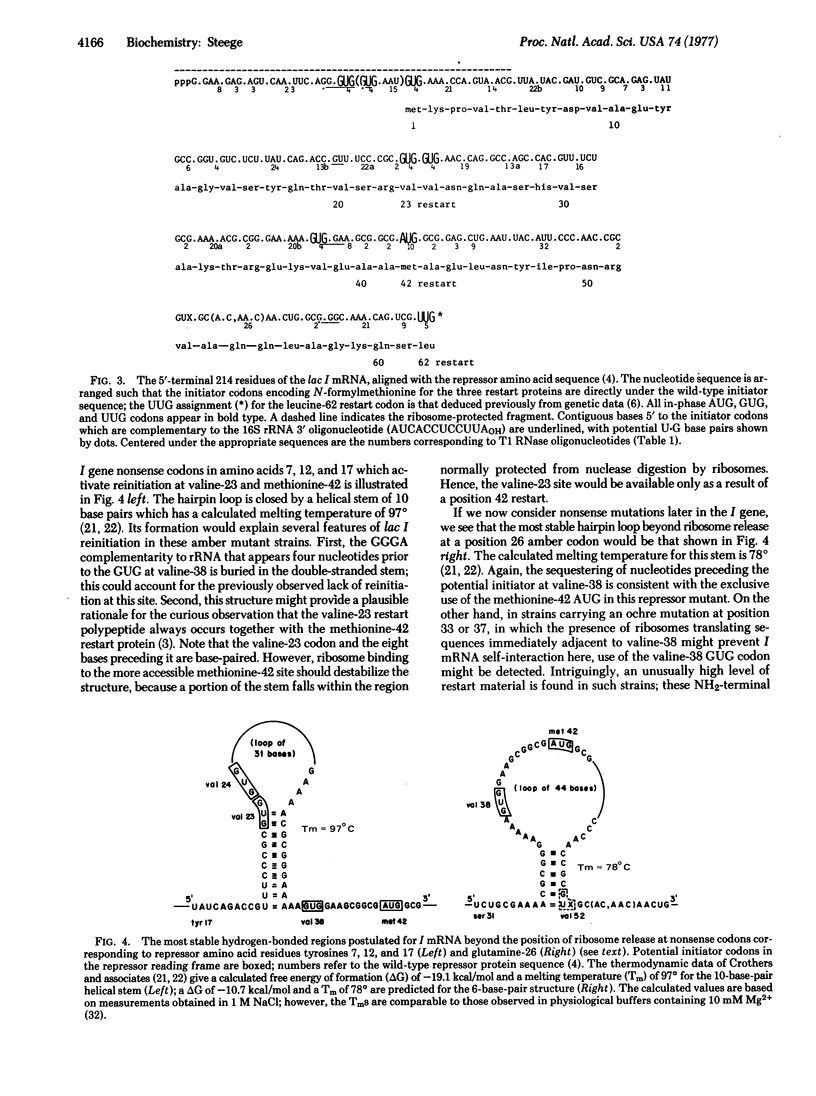
A striking feature of the I mRNA sequence is the presence of a number of in-phase GUGs that have not been observed to serve as initiation signals in vivo in the nonsense mutant strains examined. The selective use of potential initiator triplets in the I mRNA leads to the following conclusions. First, when presented with several neighboring initiator triplets at the wild-type initiator region, ribosomes select the one preceded by the strongest appropriately positioned complementarity to the 16S 3′ end. Second, ribosomes do not restart after termination simply by moving to the next available initiator codon. Third, the formation of stable secondary structures predicted for the untranslated I mRNA beyond chain-terminating nonsense mutations may prevent ribosome access to some potential reinitiation sites.
Keywords: lac operon regulatory gene, in vitro transcription, RNA sequencing, RNA secondary structure
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beyreuther K., Adler K., Geisler N., Klemm A. The amino-acid sequence of lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3576–3580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billeter M. A., Dahlberg J. E., Goodman H. M., Hindley J., Weissmann C. Nucleotide sequence analysis of an enzymatically synthesized RNA corresponding to the 5'-terminal region of Q beta RNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:635–646. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B. F., Marcker K. A. The role of N-formyl-methionyl-sRNA in protein biosynthesis. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;17(2):394–406. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80150-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiers W., Contreras R., Duerinck F., Haegmean G., Merregaert J., Jou W. M., Raeymakers A., Volckaert G., Ysebaert M., Van de Kerckhove J. A-protein gene of bacteriophage MS2. Nature. 1975 Jul 24;256(5515):273–278. doi: 10.1038/256273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Files J. G., Weber K., Coulondre C., Miller J. H. Identification of the UUG codon as a translational initiation codon in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jun 25;95(2):327–330. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90398-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Files J. G., Weber K., Miller J. H. Translational reinitiation: reinitiation of lac repressor fragments at three internal sites early in the lac i gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):667–670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Miller J. H., Files J. G., Platt T., Weber K. Reinitiation of a lac repressor fragment at a codon other than AUG. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3165–3169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh H. P., Söll D., Khorana H. G. Studies on polynucleotides. LXVII. Initiation of protein synthesis in vitro as studied by using ribopolynucleotides with repeating nucleotide sequences as messengers. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):275–298. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90142-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralla J., Crothers D. M. Free energy of imperfect nucleic acid helices. II. Small hairpin loops. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 5;73(4):497–511. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90096-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralla J., Steitz J. A., Crothers D. M. Direct physical evidence for secondary structure in an isolated fragment of R17 bacteriophage mRNA. Nature. 1974 Mar 15;248(445):204–208. doi: 10.1038/248204a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizels N. M. The nucleotide sequence of the lactose messenger ribonucleic acid transcribed from the UV5 promoter mutant of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3585–3589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michels C. A., Zipser D. Mapping of polypeptide reinitiation sites within the beta-galactosidase structural gene. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):341–347. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H., Ganem D., Lu P., Schmitz A. Genetic studies of the lac repressor. I. Correlation of mutational sites with specific amino acid residues: construction of a colinear gene-protein map. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 15;109(2):275–298. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musso R. E., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I., Sklar J., Yot P., Weissman S. The 5'-terminal nucleotide sequence of galactose messenger ribonucleic acid of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4940–4944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Hill B., Crapo L., Gilbert W. Mutants that make more lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1259–1264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T., Files J. G., Weber K. Lac repressor. Specific proteolytic destruction of the NH 2 -terminal region and loss of the deoxyribonucleic acid-binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):110–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T., Weber K., Ganem D., Miller J. H. Translational restarts: AUG reinitiation of a lac repressor fragment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):897–901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarabhai A., Brenner S. A mutant which reinitiates the polypeptide chain after chain termination. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):145–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90357-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Jakes K. How ribosomes select initiator regions in mRNA: base pair formation between the 3' terminus of 16S rRNA and the mRNA during initiation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Wahba A. J., Laughrea M., Moore P. B. Differential requirements for polypeptide chain initiation complex formation at the three bacteriophage R17 initiator regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jan;4(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. E., Zinder N. D. Fate of the message-ribosome complex upon translation of termination signals. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jun 28;42(3):425–439. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalkin H., Yanofsky C., Squires C. L. Regulated in vitro synthesis of Escherichia coli tryptophan operon messenger ribonucleic acid and enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):465–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



