Abstract
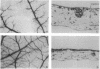
Neovascularization is associated with the regulation of tissue development, wound healing, and tumor metastasis. A number of studies have focused on the role of heparin-like molecules in neovascularization; however, little is known about the role of heparin-degrading enzymes in neovascularization. We report here that the heparin-degrading enzymes, heparinases I and III, but not heparinase II, inhibited both neovascularization in vivo and proliferation of capillary endothelial cells mediated by basic fibroblast growth factor in vitro. We suggest that the role of heparinases in inhibition of neovascularization is through depletion of heparan sulfate receptors that are critical for growth factor-mediated endothelial cell proliferation and hence neovascularization. The differences in the effects of the three heparinases on neovascularization could be due to different substrate specificities for the enzymes, influencing the availability of specific heparin fragments that modulate heparin-binding cytokines involved in angiogenesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baird A., Ling N. Fibroblast growth factors are present in the extracellular matrix produced by endothelial cells in vitro: implications for a role of heparinase-like enzymes in the neovascular response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 30;142(2):428–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90292-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Shing Y. Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):10931–10934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitay-Goren H., Soker S., Vlodavsky I., Neufeld G. The binding of vascular endothelial growth factor to its receptors is dependent on cell surface-associated heparin-like molecules. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6093–6098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Cheng J. Heparin protects basic and acidic FGF from inactivation. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Sep;128(3):475–484. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041280317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Baird A. A dual receptor system is required for basic fibroblast growth factor activity. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):229–231. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90173-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., D'Amore P. A. Regulators of angiogenesis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:217–239. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusaka M., Sudo K., Fujita T., Marui S., Itoh F., Ingber D., Folkman J. Potent anti-angiogenic action of AGM-1470: comparison to the fumagillin parent. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 14;174(3):1070–1076. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91529-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblom A., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Fransson L. A. Domain structure of endothelial heparan sulphate. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 1;279(Pt 3):821–829. doi: 10.1042/bj2790821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linhardt R. J., Turnbull J. E., Wang H. M., Loganathan D., Gallagher J. T. Examination of the substrate specificity of heparin and heparan sulfate lyases. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 13;29(10):2611–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00462a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse D. L., Linhardt R. J. Purification and characterization of heparin lyases from Flavobacterium heparinum. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24347–24355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D. High and low affinity binding sites for basic fibroblast growth factor on cultured cells: absence of a role for low affinity binding in the stimulation of plasminogen activator production by bovine capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Apr;131(1):123–130. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D. Metabolism of receptor-bound and matrix-bound basic fibroblast growth factor by bovine capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):753–759. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses M. A., Sudhalter J., Langer R. Identification of an inhibitor of neovascularization from cartilage. Science. 1990 Jun 15;248(4961):1408–1410. doi: 10.1126/science.1694043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses M. A., Sudhalter J., Langer R. Isolation and characterization of an inhibitor of neovascularization from scapular chondrocytes. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(2):475–482. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.2.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nader H. B., Dietrich C. P., Buonassisi V., Colburn P. Heparin sequences in the heparan sulfate chains of an endothelial cell proteoglycan. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3565–3569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent M. A., Edelman E. R. Kinetics of basic fibroblast growth factor binding to its receptor and heparan sulfate proteoglycan: a mechanism for cooperactivity. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 22;31(37):8876–8883. doi: 10.1021/bi00152a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A. C., Krufka A., Olwin B. B. Requirement of heparan sulfate for bFGF-mediated fibroblast growth and myoblast differentiation. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1705–1708. doi: 10.1126/science.1646484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Yamaguchi Y. Proteoglycans as modulators of growth factor activities. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):867–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90308-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasisekharan R., Bulmer M., Moremen K. W., Cooney C. L., Langer R. Cloning and expression of heparinase I gene from Flavobacterium heparinum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3660–3664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudhalter J., Folkman J., Svahn C. M., Bergendal K., D'Amore P. A. Importance of size, sulfation, and anticoagulant activity in the potentiation of acidic fibroblast growth factor by heparin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6892–6897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton S. C., Mueller S. N., Levine E. M. Human endothelial cells: use of heparin in cloning and long-term serial cultivation. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):623–625. doi: 10.1126/science.6635659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull J. E., Fernig D. G., Ke Y., Wilkinson M. C., Gallagher J. T. Identification of the basic fibroblast growth factor binding sequence in fibroblast heparan sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10337–10341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlrich S., Lagente O., Lenfant M., Courtois Y. Effect of heparin on the stimulation of non-vascular cells by human acidic and basic FGF. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 30;137(3):1205–1213. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90353-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Fridman R., Ishai-Michaeli R., Sasse J., Klagsbrun M. Endothelial cell-derived basic fibroblast growth factor: synthesis and deposition into subendothelial extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2292–2296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Fuks Z., Ishai-Michaeli R., Bashkin P., Levi E., Korner G., Bar-Shavit R., Klagsbrun M. Extracellular matrix-resident basic fibroblast growth factor: implication for the control of angiogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 1991 Feb;45(2):167–176. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240450208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Korner G., Ishai-Michaeli R., Bashkin P., Bar-Shavit R., Fuks Z. Extracellular matrix-resident growth factors and enzymes: possible involvement in tumor metastasis and angiogenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1990 Nov;9(3):203–226. doi: 10.1007/BF00046361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayon A., Klagsbrun M., Esko J. D., Leder P., Ornitz D. M. Cell surface, heparin-like molecules are required for binding of basic fibroblast growth factor to its high affinity receptor. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90512-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]